-
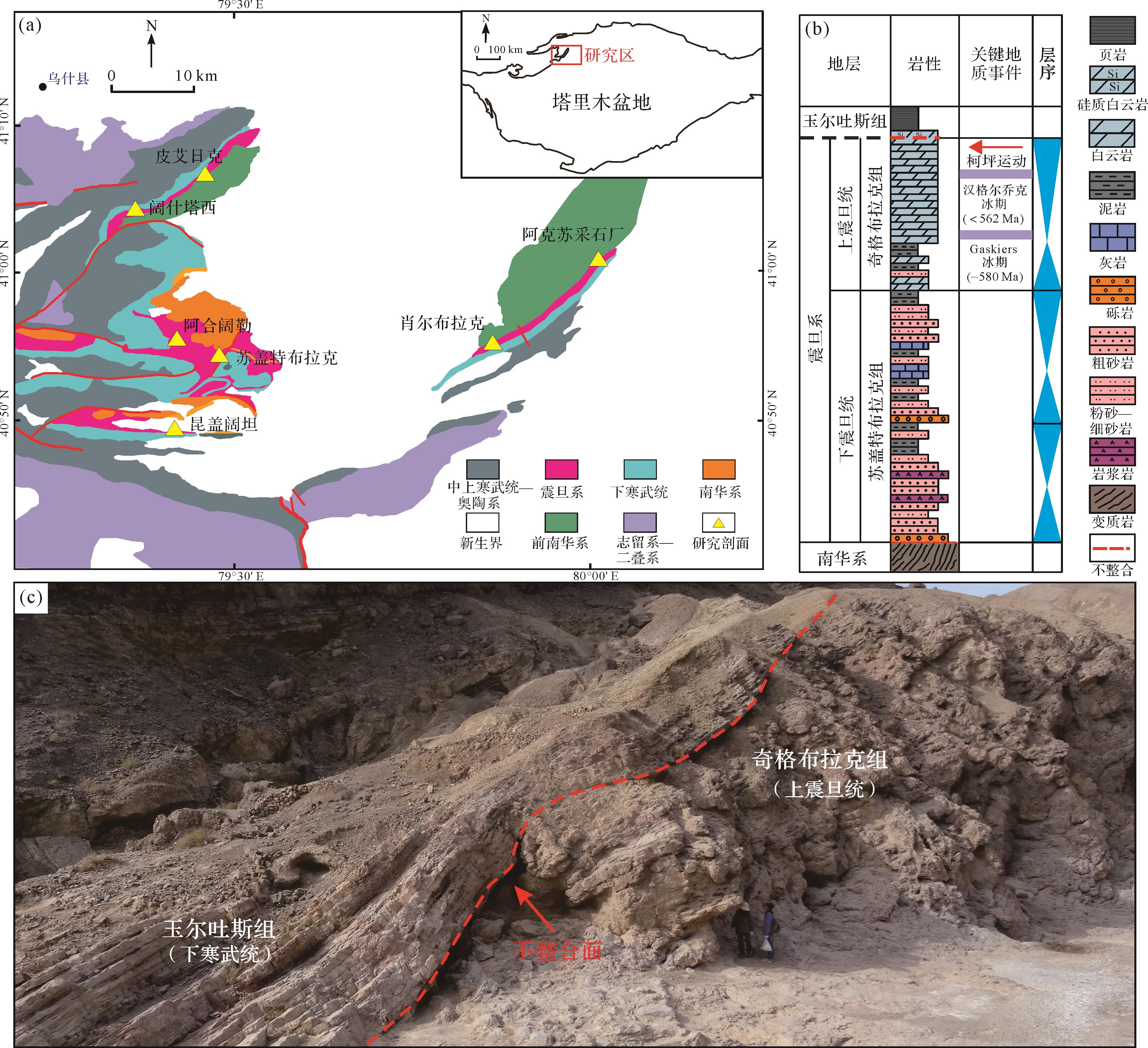
在油气勘探中,不整合面具有十分重要的意义,全球范围内许多大型油气田的发现都与不整合面密切相关[1⁃3]。作为地球演化史上的重大变革期,震旦纪—寒武纪之交在全球多个区域发育一套不整合面[4⁃6]。在塔里木盆地,该不整合面同样发育,主要见于盆地东北部库鲁克塔格和西北部阿克苏地区[7]。该不整合面之下的震旦系奇格布拉克组发育稳定分布的白云岩,为规模性储层的形成提供了良好的物质基础。近年来,塔里木盆地深层—超深层勘探工作稳步推进,尤其是2020年部署在塔北隆起的轮探1井在震旦系—寒武系不整合面之下的白云岩层段获得天然气流[8],从井下证实了该不整合面对优质白云岩储集体的发育具有重要的控制作用。
大量研究已表明,震旦纪末期的大气淡水淋滤事件可能是提升奇格布拉克组储层品质最为关键的因素[9⁃12]。尽管塔里木盆地奇格布拉克组埋深可超过8 700 m,但震旦系—寒武系不整合面之下的岩溶现象仍非常丰富,孔洞发育[8,13],充分说明该不整合面是值得关注的勘探新领域。针对该不整合面成因机制的研究,可以对下一步的油气勘探提供启示。鉴于此,基于塔里木盆地西北部阿克苏地区出露较好的剖面,从沉积学的视角,重点分析上震旦统奇格布拉克组顶部的沉积相类型及其与岩溶作用发育程度的匹配关系,并探讨该不整合面的成因,以期为该盆地震旦系的油气勘探提供借鉴和参考。
-
塔里木盆地被天山、昆仑山和阿尔金山所环绕,具有比较完整的前寒武纪基底,并且发育良好的新元古代沉积盖层[14]。塔西北地区新元古代地层格架记录了在相对稳定的构造背景下,从裂陷转化为坳陷的沉积演化过程[15]。南华纪之前,随着罗迪尼亚超大陆的裂解,塔里木板块逐渐从澳大利亚板块分离出来,导致塔里木盆地西北部裂谷盆地的形成,裂陷的中央区域快速沉积巨厚层的深水沉积物[16]。南华纪期间,尽管塔里木盆地北部仍处于拉张的构造环境,但拉张力度已开始减弱,火山活动也由强到弱,海水的侵入扩大了沉积范围,使得已经发育成型的裂谷连接起来[17]。早震旦世,裂谷盆地的大部分区域已被沉积物充填,塔里木盆地北部进入以坳陷作用为主的构造环境[18]。在持续海侵的影响下,原有的裂谷盆地被广泛地连接起来,早震旦世末期发育的碎屑岩—碳酸盐岩混合沉积代表了坳陷盆地的初始阶段[19]。晚震旦世,塔里木盆地西北部处于稳定构造背景下的坳陷环境,北部区域以发生热沉降为主[19]。随着陆源输入的持续减少,碳酸盐岩沉积体系非常发育,塔西北地区碳酸盐岩台地相几乎遍布全区[20⁃21]。
-
研究区震旦系主要出露于塔里木盆地西北缘柯坪隆起的阿克苏—乌什[22]一带(图1a),自下到上,分别发育以滨岸沉积为特征的苏盖特布拉克组和以浅水碳酸盐岩台地沉积为特征的奇格布拉克组[23⁃24](图1b),其中奇格布拉克组顶部普遍发育一套不整合面(图1c)。奇格布拉克组厚度介于160~180 m,根据岩性特征,自下而上可分为三段:奇1段、奇2段和奇3段[25]。奇1段位于奇格布拉克组底部,厚13~17 m,广泛发育碳酸盐岩与碎屑岩的混积,主要由细粉砂岩、微生物纹层白云岩、叠层石白云岩组成,局部夹鲕粒或砂屑白云岩,为混积滨岸环境(图2);奇2段位于奇格布拉克组下部,厚22~28 m,以发育暗灰色、薄板—薄层状的微生物纹层白云岩、泥晶白云岩为特征,可见水平层理以及小型的丘状交错层,含叠层石以及颗粒白云岩夹层(图2);本段整体上处于相对低能的内缓坡—中缓坡环境,沉积过程中受到风暴活动的影响。奇3段厚度最大(101~150 m),以大套的微生物白云岩沉积为特征,潮坪广泛发育,其中中下部以近水平状—波状的微生物纹层岩为主,中上部泡沫绵层白云岩较为常见,局部发育藻屑球粒,可见窗格孔、帐篷构造、葡萄—花边结构等(图2)。此外,本段顶部发育叠层石礁建造以及厚层颗粒滩,且与震旦系—寒武系不整合面相关的淡水淋滤和风化剥蚀现象明显。本次研究,针对奇3段顶部,重点对其沉积相及淋滤剥蚀现象进行探究。
-
研究区上震旦统与下寒武统之间表现为平行不整合接触[7],不整合界面处岩相变化较为明显,界面之下的奇格布拉克组为中厚层状白云岩,界面之上玉尔吐斯组为黑色页岩以及多层硅质岩(图2)。区内玉尔吐斯组的小壳化石可与梅树村阶对比,前者下部缺失梅树村阶标准剖面最底层位的化石Anabarites Primitivus[26],故奇格布拉克组与玉尔吐斯组之间存在沉积间断,可能缺失梅树村阶下部层位。在多个剖面,震旦系—寒武系不整合面之上可见0.1~0.3 m厚的红色土壤层(图3a)。与下伏的震旦系白云岩相比,这套红色土壤层表现为SiO2、Fe2O3、K2O、Na2O的大量富集和易溶元素Ca和Mg的大量流失,表明其形成可能与地表暴露的氧化环境相关[27]。研究区东部的肖尔布拉克剖面淡水淋滤现象明显,其奇格布拉克组顶部可见侵蚀面[28](图3b),是岩溶不整合面出现的典型标志。古洞穴通常被沉积物充填,洞穴直径可达2 m。由于岩溶水强烈的溶蚀作用,部分洞穴上覆地层受力失稳发生垮塌,形成岩溶塌陷体(图3c)。垮塌后的古洞穴内充填大量角砾岩,呈镶嵌状或棱角状,大小不一,混杂堆积(图3d)。

图 3 肖尔布拉克剖面震旦系—寒武系不整合面及其岩溶特征
Figure 3. Features of the Sinian⁃Cambrian unconformity and karst in the Xiaoerbrak section
地球化学响应方面,该不整合界面处呈现出明显的碳同位素负漂,在距界面之下0.1 m处δ13C值可低至-9.2‰ VPDB[29]。该负漂作为震旦系—寒武系界线处的标志之一,可在全球范围内进行地层对比[30⁃31]。主微量元素显示,Ca、Mg、La、Ce、Nd、Pr等易迁移元素在不整合界面之下的质量分数均值大于界面之上的均值,而Zr、Sr、Ba、Mn、Ni、Fe、Mn、S等难迁移元素在界面之下的均值小于界面之上的均值,同样显示出典型的暴露淋滤特征[32]。
-
野外露头观察以及镜下薄片鉴定表明,区内奇3段顶部岩溶段主要发育台地边缘相与斜坡相。
-
研究区台地边缘可划分为颗粒滩和台缘礁,主要由三种岩相构成,分别是厚层—块状鲕粒白云岩(MF1)、中—厚层状砂屑白云岩(MF2)、块状叠层石礁白云岩(MF3)。
-
描述:以浅灰色为主,呈厚层状—块状产出(图4a,b),可见大型板状或楔状交错层理。主要为颗粒支撑,颗粒成分以鲕粒为主,分选较好,含有少量砂屑。颗粒直径在粗砂级以上(图4a);靠近奇格布拉克组顶部,鲕粒内部多被溶蚀,且具一定的重结晶现象。垂向上,该岩相通常位于柱状叠层石礁(MF3)之下(图4b)。

图 4 奇3段顶部台地边缘沉积特征
Figure 4. Sedimentary features of platform margin facies in the uppermost 3rd member of the Qigebrak Formation
解释:厚层—块状层,大型交错层理的出现,颗粒支撑均表明MF1为高能环境下的产物[33⁃34]。特别是部分剖面的鲕粒直径可大于2 mm,肉眼可见(图4a),表明其具有更高的生长速率,拥有更强的水动力条件[35⁃36]。此外,结合MF1的垂向发育特征(位于MF3之下),可将MF1解释为台缘颗粒滩的产物。
-
描述:该岩相剖面上呈灰色,以中—厚层状产出(图4c),连续产出厚度可达10 m以上。主要由颗粒支撑,颗粒类型以砂屑为主(图4d),见少量的鲕粒以及球粒,颗粒直径多为粗砂级。垂向上,通常位于MF1 之上(图4c),MF3之下。
解释:该岩相为中—厚层状产出,且为颗粒支撑,说明MF2是高能环境产物,其颗粒结构的形成经历了水流的不断搬运和筛选作用[37⁃38]。结合其连续的、十米级的地层厚度,将其沉积环境解释为台缘颗粒滩。相较于MF1,MF2单层厚度变小,且向上过渡为块状叠层石礁(MF3),指示向上变浅的海退序列,这是台地向盆地进积的结果。总体上,该岩相应发育于颗粒滩靠近局限台地一侧。
-
描述:呈块状产出(图4b),叠层石形态多为柱状,向上分叉生长,形成良好的格架(图4e,f),格架间多被粒泥白云岩充填。叠层石紧密堆积,单个柱体高度可达1米以上,其生长方向垂直于岩层面(图4f)。柱体直径多在10 cm以内,柱体越细,叠层石纹层的隆起度越大。该岩相通常出现在MF2之上,且向上可过渡到滑塌角砾岩(MF4)。阿克苏西部昆盖阔坦剖面MF3溶蚀现象较弱(图4e),相比之下,研究区东部的肖尔布拉克剖面MF3可见大量溶洞(图4f),溶蚀作用较强。
解释:该岩相为柱状叠层石形成宏观的块状体,柱体彼此相连,说明其为抗浪建造(礁),生长于台地边缘的高能环境[39]。前人研究表明,前寒武纪微生物礁广泛地分布在台地边缘[40⁃42]。此外,考虑到其与中—厚层状砂屑白云岩(MF2)、滑塌角砾岩(MF4)的空间配位关系,将该岩相解释为台缘叠层石礁。
-
斜坡环境主要发育三种岩相类型:(1)滑塌角砾白云岩(MF4);(2)浊积岩(MF5);(3)薄层状粒泥白云岩(MF6)。
-
描述:该岩相呈不连续的块状产出,厚度可达数米以上。可见阶梯状分布的大型滑塌岩块(图5a),岩块的产状与地层产状明显不同。该岩相含大量不规则的角砾,角砾成分复杂,包括砂屑、微生物团块等,呈棱角状至次棱角状,分选差(图5b),粒径从几厘米到数十厘米不等,呈漂浮状分布在基质之中,且含礁前打碎的柱状叠层石(图5c);垂向上,该岩相通常位于MF3之上。

图 5 奇3段顶部斜坡相沉积特征
Figure 5. Sedimentary features of slope facies in the uppermost 3rd member of the Qigebrak Formation
解释:该岩相为不连续块状,具大型滑塌岩块,且包括杂乱堆积的基质和无分选、无磨圆的角砾,表明其为斜坡环境产生的重力沉积产物[39,43⁃44]。此外,角砾中含微生物结构,以及该角砾与柱状叠层石礁(MF3)的伴生关系,也说明该重力沉积为准原地来源,指示距离台缘较近的斜坡沉积环境[45⁃46]。
-
描述:该岩相主要见于昆盖阔坦剖面,以薄层—中层状产出,层面下弯(发育揉皱)(图5d);常见冲刷面、正粒序层理、波状层理等沉积构造,冲刷面附近可见底砾沉积(图5e)。手标本自下而上能清晰地识别出递变层段、波状纹层段以及水平纹层段(图5e)。垂向上,该岩相位于MF4的上方。
解释:由于该岩相发育的地层具有下弯的特征,具软沉积变形,表明处于有坡度的沉积环境。手标本中识别出的递变层段、波状纹层段和水平纹层段组合与浊流沉积特征非常符合[47]。由于单个浊积层底部发育冲刷面,且伴随砾石沉积,与下伏的浊积层为突变接触,因此其应属于近端浊流[47]。另外,该岩相发育在MF4之上,可进一步解释为中上斜坡环境。
-
描述:该岩相为浅灰—灰色,剖面上以薄层状或似扁豆状产出(图5f),局部可见揉皱;以白云质泥晶基质为主,可见少量球粒、砂屑(图5g)。此外,该岩相可见大型丘状交错层理(图5h),通常位于MF3之上。
解释:MF6具薄层状—似扁豆状产状,泥晶基质含量高,仅含少量颗粒,以及丘状交错层理发育,指示受风暴影响的低能潮下沉积环境[48⁃49]。由于该岩相局部发育滑塌揉皱且位于MF3 之上,因此将其解释为斜坡沉积环境的产物。
-
根据岩溶纵向分带结构,从上到下可依次分为渗流带、潜流带以及缓流带[50]。渗流带以岩溶水的垂直渗流为主,一般发育在岩溶顶部。研究区渗流带未成规模发育,竖直溶沟(缝)等特征仅在阿克苏东部剖面局部出现。潜流带的典型特征是岩溶水呈水平方向流动,具有较强的溶蚀作用。岩溶洞穴内充填紫红色或黄褐色泥岩等地下暗河沉积物(图3a,c)。据统计,潜流带范围在不整合之下0~30 m范围内,在研究区东部肖尔布拉克剖面、阿克苏采石厂剖面更为发育,厚度可达数十米(图6a),区内蜂窝状溶洞(图6b)、大型洞穴及相关垮塌体(图6c,d)均是潜流带岩溶水不断溶蚀后的产物。相比之下,深部缓流带溶蚀作用较弱,只产生少量溶孔(图6e)。深部缓流带之下则不再受岩溶作用的影响。岩溶带的垂向分布特征表明,位于阿克苏东部的肖尔布拉克剖面、阿克苏采石厂剖面遭受了更为强烈的近地表岩溶作用。
-
以往研究表明,塔里木盆地不整合面的成因通常受控于两大因素:区域上的构造抬升或大规模的海平面下降[51]。有研究认为,震旦纪末期整个塔里木盆地由于柯坪运动发生的构造抬升,造成原塔北基底古隆西侧的柯坪地区隆升幅度较大,且中央基底古隆周缘遭受大面积剥蚀[52]。然而,也有学者认为尽管震旦纪末期在塔里木盆地广泛发育了柯坪运动,但对阿克苏地区的影响较小,该震旦系—寒武系不整合的形成并不是由区域上的构造运动形成[53]。其理由是塔里木盆地西北部在震旦纪晚期并未有岩浆或者造山运动的记录,新元古界未出现强烈的构造变形[20⁃21,54],故震旦系顶部与寒武系底部为平行不整合接触。鉴于此,该项研究认为区内不整合面的形成是由大规模的海平面下降所致。尽管对海平面下降的机制认识还比较模糊[55],但晚震旦世的冰川事件可能是海平面大规模下降的重要因素[56⁃57]。在塔里木盆地东北部库鲁克塔格地区,碎屑锆石数据表明奇格布拉克组的年龄能够约束在615±4.8 Ma到541±6.0 Ma[58⁃59],且晚震旦世全球范围至少存在两期冰川事件,即发生在580.90~579.88 Ma的Gaskiers冰期和小于562 Ma的汉格尔乔克冰期[24],故晚震旦世的冰期事件可能造成研究区发生了大规模的海退。但是,塔里木盆地西北部目前并未发现有冰川记录的直接证据,故此种成因解释仍需考究。
本研究试图从研究剖面的沉积学资料重新阐释阿克苏地区震旦系—寒武系不整合面的成因。从岩溶发育程度上,位于阿克苏东部的肖尔布拉克剖面、阿克苏采石厂剖面岩溶作用更为发育,以水平潜流带为主(图6)。如前文所述,从沉积特征上看,肖尔布拉克剖面奇3段顶部30 m范围内从下到上依次可见柱状叠层石礁(图4f)、大型丘状交错层理(图5h),故由下到上从台缘相过渡到斜坡相,表现为沉积水体由浅到深的地层序列(图7);在阿克苏采石场剖面,可见大量叠层石礁及滑塌体(图6b),局部可见斜坡角砾岩,代表斜坡相沉积。相较而言,位于阿克苏西部的苏盖特布拉克剖面、阿合阔勒剖面顶部为颗粒滩相(图4a),岩溶作用不发育,未见大规模的溶孔及溶洞。

图 7 肖尔布拉克剖面奇格布拉克组岩溶段层序特征
Figure 7. Stratigraphic sequence of karst zones from the Qigebrak Formation, Xiaoerbrak section
一般而言,在海相碳酸盐岩台地背景下,颗粒滩等浅水环境的产物更易接受暴露溶蚀,而深水环境的产物不易被暴露溶蚀。从沉积环境与岩溶发育的匹配关系上看,奇3段顶部表现出了相反的特征,即发育深水沉积的剖面(肖尔布拉克剖面、阿克苏采石厂剖面)岩溶段厚度明显更大,且以发育潜流带为主,而顶部发育颗粒滩的剖面(苏盖特布拉克剖面)反而岩溶不发育(图8)。此外,斜坡相见大量叠层石礁的滑塌体,说明研究区台缘带可能发生了较强的断裂活动(图8)。从塔里木盆地的区域构造背景来看,其新元古代以正断层为主,断裂主要活动于南华纪、震旦纪,并从晚震旦世到早寒武世逐渐减弱[60]。震旦纪末期的构造变动进一步控制了早寒武世的沉积格局,可在盆内多个区域的玉尔吐斯组识别出同沉积断裂[61]。此次研究,除了从沉积相的变化趋势可以推测奇格布拉克组顶部存在断裂之外,位于阿克苏地区西部的皮艾日克剖面同样具有断层发育的直接证据(图9a)。该剖面奇格布拉克组顶部发育正断层(图9a,b),造成上覆的玉尔吐斯组相对下降,其小壳化石层的发育是玉尔吐斯组底部地层的典型标志(图9c,d),可见滑塌体(图9a)。由此可见,尽管与南华纪相比,塔里木盆地震旦纪的断裂活动虽有所减弱,但在研究区奇格布拉克组顶部仍有较好的响应。

图 8 奇格布拉克组顶部—玉尔吐斯组下部沉积特征
Figure 8. Sedimentary features of the uppermost Qigebrak Fomation and the lower Yuertusi Formation

图 9 皮艾日克剖面奇格布拉克组顶部—玉尔吐斯组下部断层发育特征
Figure 9. Fault development characteristics of the top of the uppermost Qigebrak Formation and the lower Yurtus Formation in the Piairike section
据此,提出阿克苏地区震旦系—寒武系不整合面成因的另一种假说,即构造掀斜运动[62⁃63]造成了奇格布拉克组顶部不整合面的形成(图10)。晚震旦世研究区总体处于浅水碳酸盐岩台地环境,台缘叠层石礁不断生长(图10a),随着沉积环境由台缘过渡到斜坡,台地水体逐渐加深(图10b)。震旦纪末期由台缘构造活动诱导的掀斜运动,使得加深过程被中断,并形成重力驱动的水文系统,从而导致了台地的暴露和溶蚀(图10c)。在此过程中,阿克苏西部地区相对抬升,因此苏盖特布拉克剖面、阿合阔勒剖面顶部为浅水颗粒滩相,而阿克苏东部地区相对下降,故肖尔布拉克剖面、阿克苏采石厂剖面顶部呈现丘状交错层理、斜坡滑塌体等深水沉积物(图8)。台地掀斜过程形成了向东流动的大气淡水水文系统,岩溶水在掀斜运动的支配下出现了差异性溶蚀,并顺层从阿克苏西部向东部汇聚溶蚀(图10c),造成东侧台缘带强烈的岩溶作用,可见大量顺层状溶洞。

图 10 阿克苏地区奇格布拉克组顶部岩溶作用及其不整合面成因模式
Figure 10. Process of karstification in the uppermost Qigebrak Formation and genetic mechanism of the Sinian⁃Cambrian unconformity, Aksu area
综上,研究区内震旦系—寒武系不整合面的形成,可能并非由大规模海平面下降造成,而受控于阿克苏地区西部的一次局部构造抬升事件。
以上解释,根据研究区下寒武统玉尔吐斯组的沉积特征,可以得到进一步证实。玉尔吐斯组下部整体为一套黑色页岩夹层状硅质岩,指示深水陆棚的沉积环境[64]。奇格布拉克组顶部的沉积相变化,表明研究区内沉积水体自西向东逐渐加深(图8)。玉尔吐斯组在研究区的厚度具有明显的差异性,具体表现为东部剖面(肖尔布拉克、阿克苏采石场)黑色页岩及硅质岩的厚度明显大于西部剖面(昆盖阔坦、苏盖特布拉克),说明在早寒武世玉尔吐斯组沉积期其可容纳空间更大,故也显示出自西向东沉积水体加深的趋势(图8)。基于此,玉尔吐斯组表现出了很好的继承性,同样是自西向东逐渐加深,趋势与奇格布拉克组顶部沉积特征保持了一致。此外,前人研究表明,研究区自东向西,玉尔吐斯组下部的富有机质泥页岩叠覆于奇格布拉克组顶部的不整合面之上,具有典型超覆特征[65]。因此,震旦纪末期在阿克苏西部地区发生的构造掀斜运动,进一步控制了早寒武世玉尔吐斯组的沉积样式。以上沉积特征从侧面说明本研究提出的不整合面成因假说的合理性。
-
(1) 塔里木盆地西北部阿克苏地区上震旦统奇格布拉克组顶部与下寒武统玉尔吐斯组之间发育一套平行不整合,且该不整合面之下可见大量洞穴及溶孔,岩溶现象发育。
(2) 奇格布拉克组顶部岩溶段沉积相以台地边缘相和斜坡相为主。相较于阿克苏西部的剖面,东部的肖尔布拉克、阿克苏采石厂剖面可见大量深水沉积,且岩溶现象更为明显,潜流带更为发育。
(3) 奇格布拉克组顶部的台缘带在震旦纪末期发生断裂活动,斜坡相可见台缘礁滑塌体。由台缘构造活动诱导的掀斜运动,导致阿克苏西部地区局部抬升,造成了加深台地的暴露和溶蚀,是区内震旦系—寒武系不整合面发育的主要机制。
(4) 研究区下寒武统玉尔吐斯组的沉积特征自西向东具有水体加深的趋势,与奇格布拉克组顶部岩溶段的沉积特征保持一致,其沉积样式具有明显的继承性,进一步支持本研究提出的成因模式。
Genesis of the Sinian-Cambrian Unconformity in the Northwestern Tarim Basin: Evidence from sedimentology
-
摘要: 目的 塔里木盆地西北部阿克苏地区广泛发育震旦系—寒武系平行不整合面,目前对其形成机制还存在争议。 方法 以沉积学方法为手段,基于上震旦统奇格布拉克组顶部的沉积相及其岩溶现象,通过详细的野外观察和镜下鉴定,对上述不整合面的成因开展研究。 结果 阿克苏地区奇格布拉克组顶部主要发育于台地边缘和斜坡环境。台地边缘包括颗粒滩和台缘礁,岩相为厚层—块状鲕粒白云岩、中—厚层状砂屑白云岩以及块状叠层石礁白云岩。斜坡环境包括的岩相有滑塌角砾白云岩、浊积岩以及薄层状粒泥白云岩。震旦纪晚期,阿克苏地区东部的沉积水体更深,岩溶发育程度也明显强于西部,垂向上以潜流带为主。此外,寒武纪早期沉积的玉尔吐斯组保持了与奇格布拉克组顶部相一致的沉积趋势,两者自西向东均表现为水体加深的地层序列。 结论 该不整合面由震旦纪末期台缘构造活动诱导的掀斜运动形成,导致阿克苏西部发生抬升,并形成了向东流动的大气淡水水文系统,使得东部台缘带岩溶作用强烈。该研究可为该区域震旦系白云岩储层的油气勘探提供参考。Abstract: Objective A Sinian-Cambrian parallel unconformity has been widely developed in the Aksu area of the northwestern Tarim Basin, and controversy remains over its formation mechanism. Methods Based on sedimentological research, the genesis of the above unconformity was studied through detailed field observation and microscopic identification, focusing on the sedimentary facies and karst phenomenon at the top of the Upper Sinian Qigebrak Formation. Results The results show that platform margin and slope facies are developed at the top of the Qigebrak Formation in the Aksu area. The platform margin includes grain beach and microbial reef, consisting of thick- to massive bedded dolo-oolite, medium- to thick-bedded intraclast dolopackstone and massive dolostromatolite reef. Lithofacies of the slope include: dolobreccia, turbidite, and thin- bedded dolowackestone. In the Late Sinian, the sedimentary water bodies in the eastern Aksu area were deeper, and the degree of karst development was significantly stronger than that in the western areas, which was dominated by horizontal phreatic zone vertically. In addition, in the Early Cambrian, the Yuertusi Formation maintained the same sedimentary trend as the top of the Qigebrak Formation, and both showed stratigraphic sequences of deepening water bodies from west to east. Conclusions This unconformity was formed by tilting movement induced by tectonic activity at the platform margin in the Late Sinian, which resulted in the uplift of the western Aksu area. In addition, this movement led to the atmospheric freshwater hydrological system flowing eastward, resulting in strong karstification in the eastern platform margin zone. This study could provide guidance for oil and gas explorations of the Sinian dolomite reservoirs in the region.
-
Key words:
- Sinian-Cambrian /
- Qigebrak Formation /
- unconformity /
- genetic mechanism /
- Aksu area
-
-
[1] Saller A H, Budd D A, Harris P M. Unconformities and porosity development in carbonate strata: Ideas from a Hedberg Conference[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1994, 78(6): 857-872. [2] 刘波,王英华,钱祥麟. 华北奥陶系两个不整合面的成因与相关区域性储层预测[J]. 沉积学报,1997,15(1):25-30. Liu Bo, Wang Yinghua, Qian Xianglin. The two Ordovician unconformities in N. China: Their origins and related regional reservoirs prediction[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(1): 25-30. [3] Gao Z Q, Fan T L. Unconformities and their influence on Lower Paleozoic petroleum reservoir development in the Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 133: 335-351. [4] Corsetti F A, Hagadorn J W. Precambrian-Cambrian transition: Death valley, United States[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(4): 299-302. [5] Banerjee D M, Schidlowski M, Siebert F, et al. Geochemical changes across the Proterozoic–Cambrian transition in the Durmala phosphorite mine section, Mussoorie Hills, Garhwal Himalaya, India[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1997, 132(1/2/3/4): 183-194. [6] Brasier M D, Magaritz M, Corfield R, et al. The carbon- and oxygen-isotope record of the Precambrian-Cambrian boundary interval in China and Iran and their correlation[J]. Geological Magazine, 1990, 127(4): 319-332. [7] 何金有,邬光辉,徐备,等. 塔里木盆地震旦系—寒武系不整合面特征及油气勘探意义[J]. 地质科学,2010,45(3):698-706. He Jinyou, Wu Guanghui, Xu Bei, et al. Characteristics and petroleum exploration significance of unconformity between Sinian and Cambrian in Tarim Basin [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2010, 45(3): 698-706. [8] 杨海军,陈永权,田军,等. 塔里木盆地轮探1井超深层油气勘探重大发现与意义[J]. 中国石油勘探,2020,25(2):62-72. Yang Haijun, Chen Yongquan, Tian Jun, et al. Great discovery and its significance of ultra-deep oil and gas exploration in well Luntan-1 of the Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(2): 62-72. [9] 李朋威,罗平,陈敏,等. 塔里木盆地西北缘上震旦统微生物碳酸盐岩储层特征与成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2015,36(3):416-428. Li Pengwei, Luo Ping, Chen Min, et al. Characteristics and origin of the Upper Sinian microbial carbonate reservoirs at the northwestern margin of Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(3): 416-428. [10] 严威,杨果,易艳,等. 塔里木盆地柯坪地区上震旦统白云岩储层特征与成因[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(3):295-307,321. Yan Wei, Yang Guo, Yi Yan, et al. Characteristics and genesis of Upper Sinian dolomite reservoirs in Keping area, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(3): 295-307, 321. [11] 朱永进,沈安江,刘玲利,等. 塔里木盆地晚震旦世—中寒武世构造沉积充填过程及油气勘探地位[J]. 沉积学报,2020,38(2):398-410. Zhu Yongjin, Shen Anjiang, Liu Lingli, et al. Tectonic-sedimentary filling history through the Later Sinian to the Mid-Cambrian in Tarim Basin and its explorational potential[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38()2: 398-410. [12] 郑剑锋,沈安江,杨翰轩,等. 塔里木盆地西北缘震旦系微生物白云岩地球化学、年代学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报,2021,37(7):2189-2202. Zheng Jianfeng, Shen Anjiang, Yang Hanxuan, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology characteristics and their geological significance of microbial dolomite in Upper Sinian, NW Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(7): 2189-2202. [13] Tang P, Chen D Z, Qian Y X, et al. Types, petrophysical properties and pore evolution of Late Ediacaran microbial carbonates, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(4): 1362-1375. [14] 贾承造. 塔里木盆地构造特征与油气聚集规律[J]. 新疆石油地质,1999,20(3):177-183. Jia Chengzao. Structural characteristics and oil/gas accumulative regularity in Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1999, 20(3): 177-183. [15] Shen W B, Zhu X K, Xie H Z, et al. Tectonic–sedimentary evolution during initiation of the Tarim Basin: Insights from Late Neoproterozoic sedimentary records in the NW basin[J]. Precambrian Research, 2022, 371: 106598. [16] 管树巍,吴林,任荣,等. 中国主要克拉通前寒武纪裂谷分布与油气勘探前景[J]. 石油学报,2017,38(1):9-22. Guan Shuwei, Wu Lin, Ren Rong, et al. Distribution and petroleum prospect of Precambrian rifts in the main cratons, China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(1): 9-22. [17] 石开波,刘波,姜伟民,等. 塔里木盆地南华纪—震旦纪构造—沉积格局[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2018,39(5):862-877. Shi Kaibo, Liu Bo, Jiang Weimin, et al. Nanhua-Sinian tectono-sedimentary framework of Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 862-877. [18] 吴林,管树巍,杨海军,等. 塔里木北部新元古代裂谷盆地古地理格局与油气勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报,2017,38(4):375-385. Wu Lin, Guan Shuwei, Yang Haijun, et al. The paleogeographic framework and hydrocarbon exploration potential of Neoproterozoic rift basin in northern Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(4): 375-385. [19] 杨云坤,石开波,刘波,等. 塔里木盆地西北缘震旦纪构造—沉积演化特征[J]. 地质科学,2014,49(1):19-29. Yang Yunkun, Shi Kaibo, Liu Bo, et al. Tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Sinian in the northwest Tarim Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2014, 49(1): 19-29. [20] Turner S A. Sedimentary record of Late Neoproterozoic rifting in the NW Tarim Basin, China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 181(1/2/3/4): 85-96. [21] 刘若涵,何碧竹,焦存礼,等. 新疆阿克苏地区新元古代沉积特征对裂谷发育过程的指示[J]. 岩石学报,2020,36(10):3225-3242. Liu Ruohan, He Bizhu, Jiao Cunli, et al. The indication of Neoproterozoic sedimentary characteristics to rift development process in Aksu area, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(10): 3225-3242. [22] Zhou X Q, Chen D Z, Qing H R, et al. Submarine silica-rich hydrothermal activity during the earliest Cambrian in the Tarim Basin, northwest China[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 56(15): 1906-1918. [23] 石开波,刘波,田景春,等. 塔里木盆地震旦纪沉积特征及岩相古地理[J]. 石油学报,2016,37(11):1343-1360. Shi Kaibo, Liu Bo, Tian Jingchun, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and lithofacies paleogeography of Sinian in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(11): 1343-1360. [24] Wang R M, Shen B, Lang X G, et al. A great Late Ediacaran ice age[J]. National Science Review, 2023, 10(8): nwad117. [25] 汪远征. 塔里木盆地西北部埃迪卡拉系上部碳酸盐序列的地层―沉积格架与台地演化的动力机制[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学,2022:35-40. Wang Yuanzheng. The strati-depositional framework of the Upper Ediacaran carbonate successions, and dynamics of platform evolution in the northwestern Tarim Basin[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022: 35-40. [26] 高振家,吴绍祖,李永安,等. 新疆阿克苏—柯坪地区震旦纪—寒武纪地层研究[J]. 科学通报,1981,26(12):741-743. Gao Zhenjia, Wu Shaozu, Li Yong'an, et al. Study of Sinian-Cambrian strata in Aksu-Keping area, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1981, 26(12): 741-743. [27] 何金有,贾承造,邬光辉,等. 新疆阿克苏地区震旦系风化壳古岩溶特征及其发育模式[J]. 岩石学报,2010,26(8):2513-2518. He Jinyou, Jia Chengzao, Wu Guanghui, et al. Characteristics and model of Sinian weathering paleo-karst in Aksu area, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(8): 2513-2518. [28] Zhu D Y, Liu Q Y, Wang J B, et al. Stable carbon and oxygen isotope data of Late Ediacaran stromatolites from a hypersaline environment in the Tarim Basin (NW China) and their reservoir potential[J]. Facies, 2021, 67(3): 25. [29] 何秀彬,徐备,袁志云. 新疆柯坪地区新元古代晚期地层碳同位素组成及其对比[J]. 科学通报,2007,52(1):107-113. He Xiubin, Xu Bei, Yuan Zhiyun. C-isotope composition and correlation of the Upper Neoproterozoic in Keping area, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(1): 107-113. [30] Kaufman A J, Knoll A H. Neoproterozoic variations in the C-isotopic composition of seawater: Stratigraphic and biogeochemical implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 1995, 73(1/2/3/4): 27-49. [31] Walter M R, Veevers J J, Calver C R, et al. Dating the 840-544 Ma Neoproterozoic interval by isotopes of strontium, carbon, and sulfur in seawater, and some interpretative models[J]. Precambrian Research, 2000, 100(1/2/3): 371-433. [32] Shang Y X, Gao Z Q, Fan T L, et al. The Ediacaran–Cambrian boundary in the Tarim Basin, NW China: Geological data anomalies and reservoir implication[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 111: 557-575. [33] Vernhet E, Reijmer J J G. Sedimentary evolution of the Ediacaran Yangtze Platform shelf (Hubei and Hunan provinces, central China)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2010, 225(3/4): 99-115. [34] Ruiz-Ortiz P A, Bosence D W J, Rey J, et al. Tectonic control of facies architecture, sequence stratigraphy and drowning of a Liassic carbonate platform (Betic Cordillera, southern Spain)[J]. Basin Research, 2004, 16(2): 235-257. [35] Trower E J, Grotzinger J P. Sedimentology, diagenesis, and stratigraphic occurrence of giant ooids in the Ediacaran Rainstorm member, Johnnie Formation, Death Valley region, California[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 180(1/2): 113-124. [36] Grotzinger J P, James N P. Precambrian carbonates: Evolution of understanding[M]//Grotzinger J P, James N P. Carbonate sedimentation and diagenesis in the evolving Precambrian world. Tulsa: SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology, 2000: 3-20. [37] Abadi M S, Kulagina E I, Voeten D F A E, et al. Sedimentologic and paleoclimatic reconstructions of carbonate factory evolution in the Alborz Basin (northern Iran) indicate a global response to Early Carboniferous (Tournaisian) glaciations[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2017, 348: 19-36. [38] Jiang G, Christie-Blick N, Kaufman A J, et al. Sequence stratigraphy of the Neoproterozoic Infra Krol Formation and Krol Group, Lesser Himalaya, India[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2002, 72(4): 524-542. [39] Tucker M E, Wright V P. Carbonate sedimentology[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Science, 1990: 1-482. [40] Kah L C, Bartley J K, Frank T D, et al. Reconstructing sea-level change from the internal architecture of stromatolite reefs: An example from the Mesoproterozoic Sulky Formation, Dismal Lakes Group, arctic Canada[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2006, 43(6): 653-669. [41] Kerans C, Donaldson J A. Deepwater conical stromatolite reef, Sulky Formation (Dismal Lakes Group), Middle Proterozoic, N.W.T.[M]//Geldsetzer H H J, James N P, Tebbutt G E. Reef, Canada and adjacent areas. Calgary: Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, 1988: 81-88. [42] 曹瑞骥,袁训来. 叠层石[M]. 合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社,2006:1-383. Cao Ruiji, Yuan Xunlai. Stromatolites[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2006: 1-383. [43] Basilone L, Sulli A, Morticelli M G. Integrating facies and structural analyses with subsidence history in a Jurassic–Cretaceous intraplatform basin: Outcome for paleogeography of the Panormide southern Tethyan margin (NW Sicily, Italy)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016, 339: 258-272. [44] Chen D, Tucker M E, Zhu J, et al. Carbonate sedimentation in a starved pull-apart basin, Middle to Late Devonian, southern Guilin, South China[J]. Basin Research, 2001, 13(2): 141-167. [45] Ding Y, Chen D Z, Zhou X Q, et al. Tectono-depositional pattern and evolution of the Middle Yangtze Platform (South China) during the Late Ediacaran[J]. Precambrian Research, 2019, 333: 105426. [46] Vernhet E, Heubeck C, Zhu M Y, et al. Large-scale slope instability at the southern margin of the Ediacaran Yangtze Platform (Hunan province, central China)[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 148(1/2): 32-44. [47] Flügel E. Microfacies of carbonate rocks: Analysis, interpretation and application[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 2010: 1-924. [48] Guo C, Chen D Z, Zhou X Q, et al. Depositional facies and cyclic patterns in a subtidal-dominated ramp during the Early-Middle Ordovician in the western Tarim Basin (NW China)[J]. Facies, 2018, 64(3): 16. [49] 宋亚芳,陈代钊,郭川,等. 塔里木盆地肖尔布拉克剖面肖尔布拉克组下段微生物碳酸盐岩沉积特征[J]. 沉积学报,2020,38(1):55-63. Song Yafang, Chen Daizhao, Guo Chuan, et al. Depositional characteristics of microbial carbonates from the lower Xiaoerbulak Formation in the Xiaoerbulake section, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(1): 55-63. [50] Loucks R G. Paleocave carbonate reservoirs: Origins, burial-depth modifications, spatial complexity, and reservoir implications[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(11): 1795-1834. [51] Lin C S, Li H, Liu J Y. Major unconformities, tectonostratigraphic frameword, and evolution of the superimposed Tarim Basin, northwest China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2012, 23(4): 395-407. [52] 魏国齐,朱永进,郑剑锋,等. 塔里木盆地寒武系盐下构造—岩相古地理、规模源储分布与勘探区带评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(6):1114-1126. Wei Guoqi, Zhu Yongjin, Zheng Jianfeng, et al. Tectonic-lithofacies paleogeography, large-scale source-reservoir distribution and exploration zones of Cambrian subsalt formation, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(6): 1114-1126. [53] He J Y, Qing H R, Xu B. The unconformity-related palaeokarst in the uppermost Ediacaran carbonate rocks in the northwestern Tarim Block, NW China: Implication for sedimentary evolution during the Ediacaran-Cambrian transition[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(7): 839-852. [54] Zhang C L, Zou H B, Li H K, et al. Tectonic framework and evolution of the Tarim Block in NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4): 1306-1315. [55] Peters S E, Gaines R R. Formation of the ‘Great Unconformity’ as a trigger for the Cambrian explosion[J]. Nature, 2012, 484(7394): 363-366. [56] Saylor B Z, Kaufman A J, Grotzinger J P, et al. A composite reference section for terminal Proterozoic strata of southern Namibia[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1998, 68(6): 1223-1235. [57] Germs G J B, Gaucher C. Nature and extent of A Late Ediacaran (ca. 547 Ma) glacigenic erosion surface in southern Africa[J]. South African Journal of Geology, 2012, 115(1): 91-102. [58] Xu B, Zou H B, Chen Y, et al. The Sugetbrak basalts from northwestern Tarim Block of northwest China: Geochronology, geochemistry and implications for Rodinia breakup and ice age in the Late Neoproterozoic[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 236: 214-226. [59] Ren R, Guan S W, Zhang S C, et al. How did the peripheral subduction drive the Rodinia breakup: Constraints from the Neoproterozoic tectonic process in the northern Tarim Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2020, 339: 105612. [60] 何碧竹,焦存礼,黄太柱,等. 塔里木盆地新元古代裂陷群结构构造及其形成动力学[J]. 中国科学(D辑):地球科学,2019,49(4):635-655. He Bizhu, Jiao Cunli, Huang Taizhu, et al. Structural architecture of Neoproterozoic rifting depression groups in the Tarim Basin and their formation dynamics[J]. Science China (Seri. D): Earth Sciences, 2019, 49(4): 635-655. [61] 管树巍,张春宇,任荣,等. 塔里木北部早寒武世同沉积构造:兼论寒武系盐下和深层勘探[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2019,46(6):1075-1086. Guan Shuwei, Zhang Chunyu, Ren Rong, et al. Early Cambrian syndepositional structure of the northern Tarim Basin and a discussion of Cambrian subsalt and deep exploration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6): 1075-1086. [62] Clarke P, Parnell J. Facies analysis of a back-tilted lacustrine basin in a strike-slip zone, Lower Devonian, Scotland[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1999, 151(1/2/3): 167-190. [63] 谈明轩,朱筱敏,张自力,等. 构造掀斜主导的断陷湖盆缓坡层序“源—汇”正演模拟定量研究[J]. 沉积学报,2022,40(6):1481-1493. Tan Mingxuan, Zhu Xiaomin, Zhang Zili, et al. Source-to-sink quantitative stratigraphic forward modeling on the tilted hanging-wall sequence architecture of a tectonically-driven lacustrine rift basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(6): 1481-1493. [64] Zhou X Q, Chen D Z, Zhang L Y, et al. Silica-rich seawater in the Early Cambrian: Sedimentological evidence from bedded cherts[J]. Terra Nova, 2021, 33(5): 494-501. [65] 金值民,谭秀成,唐浩,等. 浅水超覆沉积富有机质细粒沉积物沉积环境与岩石学特征:以塔里木盆地西北部寒武系玉尔吐斯组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(3):476-489. Jin Zhimin, Tan Xiucheng, Tang Hao, et al. Sedimentary environment and petrological features of organic-rich fine sediments in shallow water overlapping deposits: A case study of Cambrian Yuertus Formation in northwestern Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(3): 476-489. -





 下载:
下载: