[Objective] The origin of concretions in sedimentary rocks can not only reveal the depositional environment but also serve as key evidence for studying diagenetic evolution, holding significant importance for research on pore evolution in sedimentary rocks. [Methods] This study focuses on the Devonian Jinbaoshi Formation in the Gediba section of northwestern Sichuan Basin. Through detailed analysis of rock thin sections, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), the characteristics of concretions in the Jinbaoshi Formation were examined, and their genetic mechanisms were explored. [Results] The quartz sandstone in the Jinbaoshi Formation of the Gediba section exhibits high maturity and well-developed pores, with numerous ellipsoidal to sub-spherical concretions distributed along the bedding planes, displaying brown to dark brown surfaces. Microscopic analysis reveals that the quartz grains within the concretions are consistent with the surrounding sandstone in terms of morphology, size, sorting, roundness, and texture. Compared to the quartz sandstone, the quartz grains within the concretions are sparsely arranged, primarily in point contact, and are predominantly cemented by silica, followed by iron and clay minerals. Residual pores locally filled with crude oil were observed. The concretion-bearing intervals exhibit small-scale dome structures and bioturbation, with filamentous microbial remnants and silicified bacterial colonies identified under SEM. [Conclusion] Comprehensive analysis suggests that the formation of concretions in the Jinbaoshi Formation of the Gediba section is closely related to microbial mats. Gases produced by the decomposition of organic matter migrated upward, forming dome structures on the sediment surface. When the microbial mats were too thin to produce sufficient gas for upward migration, localized sparse distribution of detrital grains occurred, accompanied by early siliceous and ferruginous cementation. These concretions resisted compaction during subsequent burial processes, maintaining their spherical morphology, and turned brown due to oxidation after being uplifted to the surface. This study establishes a genetic evolution model of the concretions, which can provide insights into the diagenetic evolution and pore structure adjustment of the quartz sandstone in the Jinbaoshi Formation, offering important geological significance for hydrocarbon exploration.
Abstract: [Objective] The geochemical significance of phenanthrene series compounds within tricyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (TAHs) remains debated, particularly regarding the relative control of thermal maturity and depositional environment. This study focuses on variations in phenanthrene series parameters during thermal evolution and their controlling mechanisms.[Methods] Lacustrine shale samples from the Shahejie Formation (Es?) of Well X in the Bohai Bay Basin were subjected to closed-system pyrolysis using a DK-III thermal simulation apparatus at seven temperature points (275–450 °C) for 48 h. Aromatic fractions of expelled oil were analyzed via GC–MS to determine the distribution and evolution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).[Results] The original shale extract was dominated by aromatic steroids, followed by tricyclic aromatics. With increasing simulation temperature, bicyclic aromatics first increased then decreased, tricyclic and heteroaromatic hydrocarbons remained relatively stable, and tetracyclic and pentacyclic aromatics increased, while aromatic steroids decreased sharply. In the phenanthrene series, methylphenanthrenes (MPs) were dominant at low temperatures, gradually replaced by dimethylphenanthrenes (DMPs) at 300–400 °C, and phenanthrene (P) became dominant above 400 °C. Anthracene series abundance increased with temperature up to 400 °C, then declined. Bicyclic aromatics showed higher thermal stability below 375 °C, while aromatic steroids transformed into tri- and tetracyclic aromatics between 300–400 °C. Two new maturity parameters, DPR-3 (2,7-DMP/1,2-DMP) and DPR-4 [2,7-DMP/(2,10+1,3+3,10+3,9-DMP)], exhibited strong positive correlation with maturity, supplementing existing F1, F2, DPR-1, and DPR-2 indices.[Conclusions] Methylphenanthrene distributions are suitable for depositional environment assessment in low-maturity samples but are more reliable maturity indicators at mature to overmature stages. Aromatic steroids and bicyclic aromatics are sensitive to early-stage thermal evolution, whereas phenanthrene and anthracene series compounds are better indicators for high maturity. The newly proposed DPR-3 and DPR-4 parameters improve the accuracy and applicability of maturity evaluation, especially in high- to overmature stages. This work refines the understanding of phenanthrene series geochemical significance and provides a robust aromatic hydrocarbon framework for deep hydrocarbon resource assessment and thermal maturity classification.
[Objective] Shallow-water deltas are common sedimentary systems widely recorded in petroliferous basins and host abundant hydrocarbon resources. Based on differences in sediment types and contents supplied by rivers, they can be classified into three categories: sand-rich, sandy-muddy, and mud-rich deltas, which exhibit significant variations in geomorphology, sedimentary characteristics, sedimentary architecture, and sediment heterogeneity. [Methods] To clarify the sedimentary dynamics, sedimentary architecture patterns, and heterogeneity characteristics of these three delta types, this study employed sedimentary numerical simulations to reproduce their depositional evolution processes. Geomorphic and grain-size data were extracted to reconstruct 3D digital models of delta architecture and sediment grain-size distribution. Through detailed analysis of depositional evolution, sedimentary architecture patterns of shallow-water deltas were established, and heterogeneity characteristics within architectural frameworks were elucidated. [Conclusions and Discussion] The results indicate: (1) Variations in sediment types and contents supplied by rivers determine deltaic sediment composition, influence levee construction capacity and anti-scouring strength of distributary channels, and thereby control channel formation, evolution, filling characteristics, sedimentary architecture, and heterogeneity. (2) As the sand-to-mud ratio decreases, distributary channels exhibit reduced quantity, hierarchical complexity, and areal proportion, alongside increased sinuosity, enhanced stability, diminished lateral migration capacity, and a transition from lateral migration-dominated filling to abandonment-dominated filling. (3) Sand-rich deltas typically display lobate or triangular morphologies with extensively developed multi-stage radial distributary channels. Lateral migration dominates, forming broadly connected high-quality reservoirs in delta plains-to-fronts through complex stacking and incision, containing frequent fine-grained interbeds. Sandy-muddy deltas exhibit multi-finger branching patterns with fewer channels dominated by trunk distributaries that bifurcate terminally, forming laterally amalgamated finger-shaped bar complexes. These complexes create irregular broad-banded connected sand bodies with frequent muddy interbeds. Mud-rich deltas feature sparse, sinuous ribbon-like trunk channels lacking lateral accretion. Channels are predominantly filled with muddy sediments after abandonment, while bar complexes form bead-like discontinuous high-quality reservoirs along channel margins, laterally isolated by mud-filled channels. (4) Sand-rich deltas show near-continuous sand distribution with downstream fining. Coarsest grains occur in trunk channels, followed by mouth bars, yielding weak planar heterogeneity but strong vertical heterogeneity due to multi-stage lateral/progradational fine-grained interbeds. Sandy-muddy deltas exhibit broad-banded sand bodies with coarse-grained reservoirs in trunk channels and mouth bars, weak planar heterogeneity, and strong vertical heterogeneity from muddy interbeds. Mud-rich deltas display strong planar heterogeneity as reservoirs are restricted to mouth bar cores, laterally isolated by muddy channels, with weak vertical heterogeneity from multi-stage muddy interbeds.
Geochemical proxies such as the Chemical Index of Alteration (CIA) are essential for reconstructing paleoweathering intensity and climate regimes. However, their reliability is fundamentally constrained by conventional analytical methods due to their inability to distinguish mineral phases with identical chemical compositions yet possessing distinct genetic origins—such as detrital mica and diagenetic illite—often leading to significant misinterpretations of continental weathering and paleoclimatic conditions. To address this persistent challenge, this study applied the advanced SEM-EDS-Nanomin system, which integrates high-resolution field-emission scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) and an innovative mixed pixel deconvolution (Mixel) algorithm. This cutting-edge technology achieves nanoscale (<0.5 μm) mineral mapping and automatically correlates resolved compositional data with critical morphological characteristics (e.g., particle orientation, boundary sharpness, spatial relationships) to objectively classify clay minerals into detrital, authigenic, or diagenetic categories with high accuracy. The elevated bulk CIA values of the organic-rich shales from the Late Neoproterozoic intervals in South China (Cryogenian interglacial Datangpo Formation and Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation) and the Mesoproterozoic Velkerri Formation in northern Australia reflected intense chemical weathering under warm and humid climatic condition. However, the new generation of the SEM-EDS coupled with the Nanomin system in contrast revealed that these seemingly apparent chemical weathering signatures were substantially overprinted by the dominant contribution of diagenetic clay minerals to key element budgets. Specifically, aluminum-rich phases previously assumed to reflect pedogenic processes were identified as diagenetic products, especially illite and kaolinite formed via pseudomorphic replacement of precursor feldspar or mica grains during burial and diagenesis. After systematically excluding these secondary phases identified through Nanomin genetic discrimination and recalculating CIA based on primary mineral assemblages, the data in fact indicated physically dominated weathering operating under colder, more arid climatic conditions. This critical revision resolved long-standing paradoxes where high bulk CIA values conflicted with independent sedimentological, mineralogical, and isotopic evidence. Furthermore, beyond CIA correction, the technique demonstrated exceptional capability in identifying authigenic minerals such as saponite formed in restricted marine evaporitic settings during the Ediacaran biotic emergence. By providing essential mineralogical context, the SEM-EDS-Nanomin methodology fundamentally enhances the reliability of diverse geochemical proxies and analytical techniques including accurate neodymium isotope(εNd) analysis and high-precision Rb-Sr geochronology based on unaltered minerals (e.g., glauconite). By establishing the unambiguous determination of clay mineral origin as an indispensable prerequisite for robust paleoenvironmental interpretation, this SEM-EDS-Nanomin approach—through its unique synergy of high-resolution imaging, spectral deconvolution, and automated morphological correlation—provides a revolutionary framework for deciphering Earth's environmental dynamics during critical transitional periods marked by extreme climate shifts, tectonic reorganizations, and biological innovations. Its capacity to bridge nano-scale mineralogical observations with macro-scale geochemical signals represents a paradigm shift in reconstructing deep-time Earth system processes.
[Objective]The characteristics and types of stromatolites are of great significance for revealing the co-evolution of early life and the geological environment on Earth. The Neoproterozoic Wangshan Formation in the Xuhuai area on the southeastern margin of the North China Craton is widely developed with stromatolites, but the macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of the stromatolites and their response mechanisms to the sedimentary environment and paleoclimate significance remain unclear. [Methods]This study takes the stromatolites of the Wangshan Formation as the research object. Through the analysis of the macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of the stromatolites, combined with the analysis of major elements and carbon-oxygen isotopes, the sedimentary facies zones of the stromatolites in the Wangshan Formation are systematically divided, the main controlling factors of stromatolite growth are discussed, and the co-evolution relationship between stromatolites and the paleoenvironment is reconstructed.[Conclusions]The research results show that the Wangshan Formation mainly contains three types of stromatolites: columnar, wavy, and laminated. Columnar and wavy stromatolites are concentrated in high-energy intertidal zones, while laminated stromatolites are stably distributed in low-energy supratidal zones. During the sedimentary period of the Wangshan Formation, the climate changed frequently, and the sea level experienced three complete transgression-regression cycles, showing a general trend of gradual shallowing. The prosperous period of stromatolites is coupled with the shallow water environment under the background of an arid climate. By comparing the stromatolites in this study area with modern stromatolites, it is found that there may be multiple microorganisms on the microbial mats of the stromatolites in the Wangshan Formation, and their metabolic activities and interactions to some extent restrict the microscopic morphology of stromatolites. The intensity of terrigenous clastic input and storm events to some extent regulate the microbial ecological succession; accommodation space, light intensity and hydrodynamic environmental factors affect the macroscopic morphology of stromatolites. This study can provide new evidence for the co-evolution of life and environment in the Neoproterozoic.
[Objective] The Songliao Basin is a major hydrocarbon-producing region in China. After more than 60 years of exploration, conventional oil and gas development has entered a phase characterized by high cost and high technical difficulty, and the basin has now fully transitioned into the stage of unconventional hydrocarbon exploration. During the deposition of the Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou and Nenjiang formations, two large-scale lacustrine transgressions occurred, creating vast potential resources for shale oil. The first and second members of the Nenjiang Formation host thick intervals of dark, organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rocks deposited in deep to semi-deep lacustrine environments. However, current understanding of these deposits remains limited, necessitating a systematic characterization of their lithofacies and organic matter enrichment mechanisms. [Methods] Based on core data from Well A34, centimeter-scale high-resolution core descriptions were conducted for the first and second members of the Upper Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation in the Songliao Basin. Microscopic petrographic analysis, total organic carbon (TOC) content measurements, and elemental line and area scanning techniques were applied to further refine the classification of the structures and fabrics of fine-grained sedimentary rocks. [Results and Discussions] A total of 16 lithofacies and 6 facies assemblages of fine-grained sedimentary rocks were identified in the first and second members of the Nenjiang Formation. Based on sedimentological characteristics and elemental geochemistry, a clear distinction was observed between organic-rich intervals (TOC>6%) and those with lower organic content. Organic-rich intervals are predominantly composed of medium- to fine-grained dark mudstones with continuous lamination. The most favorable conditions for organic matter accumulation and lamina development occur at the base of the second member of the Nenjiang Formation. [Conclusions] Synthesizing previously published stable isotope data, it is proposed that a humid climate and nutrient influx from sediment sources were key factors in creating the high biological productivity and strongly reducing conditions in the Songliao Basin during the deposition of the first and second members of the Nenjiang Formation. These environmental conditions promoted the development of high TOC values and well lamination, leading to the widespread formation of organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rocks.
Abstract: [Objective] Carbonate outcrops are often affected by tectonic fragmentation, weathering, and vegetation cover, making it difficult to obtain complete and precise sedimentary and reservoir characteristics by traditional field survey methods. This study introduces terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) to address the challenges in high-resolution characterization of carbonate outcrops, improve lithofacies recognition accuracy, and explore its applicability in sedimentology and reservoir studies. [Methods] Taking the Gaojiashan section of the Dengying Formation in Ningqiang, Shaanxi as an example, high-precision point cloud data were acquired using TLS, and laser intensity information was analyzed quantitatively and qualitatively. Three-dimensional digital outcrop models were constructed through point cloud modeling and texture mapping. Combined with thin-section petrography, rock physical property tests, and field sedimentological investigations, lithofacies recognition, sedimentary facies classification, and depositional model reconstruction were carried out. [Results and Discussions] (1) A high-resolution digital outcrop model was established, which enables full-coverage 3D visualization and interactive analysis of the outcrop, allowing geological features such as lithology and stratigraphic geometry to be accurately preserved and studied. (2) A lithology recognition atlas based on laser intensity was established, clarifying the intensity features and thickness proportions of different lithologies within the profile. Dolostone facies such as algal dolostone and crystalline dolostone correspond to high laser intensity and relatively high porosity–permeability values, while micritic dolostone and argillaceous dolostone correspond to low intensity and poor reservoir quality, indicating a good correlation between laser intensity and reservoir properties. (3) Using the upper sub-member of the second member of the Dengying Formation as an example, sub-layer division was refined based on laser intensity, and the geometric characteristics of the 14th sub-layer were deeply characterized. Analysis of depositional patterns indicated that variations in laser intensity are closely related to sea-level fluctuations, revealing cyclic depositional evolution. [Conclusions] The integration of TLS with traditional geological methods provides a more intuitive representation of carbonate outcrop features and effectively preserves primary field data. The digital outcrop model established in this study offers valuable data support for hydrocarbon exploration and reservoir evaluation, demonstrating the broad prospects and significant potential of TLS applications in geological research.
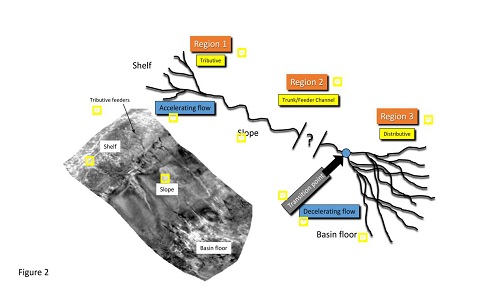
[Objective] This study aims to establish a quantitative model of downstream grain size diminution in large-scale Distributive Fluvial Systems(fluvial fans) to provide a knowledge base for predicting the distribution of sedimentary systems in intelligent oil and gas exploration and development. [Methods] The study conducted detailed descriptions of channel morphology and sediment grain size in the Dagle fluvial fan of the Qaidam Basin, Qinghai. with using geographic information software such as Google Earth , 91 Wei Tu and ImageJ combined with field investigations. Appropriate methods were selected to fit the grain size variation curves, and the longitudinal changes in gravel size were summarized. [Results] The findings are as follows: The sediments grain size of the Dagle Fluvial Fan are generally coarse, dominated by gravels, with the maximum clast size reaching 90 cm at the apex,showing a clear diminishing trend from the apex to the distal end. Exponential functions better fit the trend of gravel size diminution in the fluvial fan. The fitting function for maximum clast size vs. distance is Dmax= 90e-0.264x, and for average clast size vs. distance is D ?= 7.04 e-0.11x. By comparing the exponential models of maximum and average clast sizes, the critical role of hydraulic sorting in grain size diminution is highlighted. The longitudinal decay model of maximum clast size is deemed effective in reflecting the grain size variation trends of the entire distributive fluvial system (within the studied area), leading to the establishment of a sediment diminution model for the Dagle Distributive Fluvial System.[Conclusions] Sediment grain size variations are close related to the source , the sediment supply, the hydrodynamic conditions, and the depositional environments etc. This study provides a knowledge base for quantitatively sedimentary facies prediction and depositional system scale estimation of large-scale Distributive Fluvial Systems.
[Objective] The Early Cambrian Longmenshan tectonic belt hosts a series of sedimentary manganese deposits; however, their material sources, sedimentary environment, and precipitation mechanisms remain controversial. This study takes the Magong manganese deposit as an example, aiming to provide an in-depth discussion on the metallogenic model and precipitation mechanisms of this ore district, thereby offering a theoretical basis for research on sedimentary manganese deposits within this tectonic belt. [Methods] Electron microscopy and electron probe microanalysis were employed to analyze the characteristics of mineral assemblages and the particle size distribution of framboidal pyrite. Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) were used to determine the whole-rock major and trace element contents. Based on these analyses, the material sources, sedimentary environment, manganese precipitation mechanisms, and metallogenic processes of the Early Cambrian Magong manganese deposit on the northern margin of the Longmenshan tectonic belt were systematically investigated. [Result] Petrographic and mineralogical studies reveal that the manganese carbonate ore layers, pyrite layers, and siliceous rocks in the Magong manganese deposit are rhythmically interbedded. The primary manganese-bearing minerals include kutnohorite with microbial textures and alabandite, followed by psilomelane and pyrolusite. The gangue minerals consist of framboidal pyrite, organic matter, quartz, and dolomite. Major and trace element analyses show no significant positive correlation between MnO and Al2O3. Samples fall into the hydrothermal end-member in discrimination diagrams such as SiO2-Al2O3, (Co+Cu+Ni)×10-Fe-Mn, and (Zr+Y+Ce)×100-(Cu+Ni)×15-(Fe+Mn)/4. Most samples exhibit Fe/Ti>20 and Al/(Al+Fe+Mn)<0.35, further indicating that the ore-forming materials were primarily derived from submarine hydrothermal activity. Enriched EFU and EFMo values, along with EFMo/EFU>1, suggest a weakly restricted to restricted paleo-hydrodynamic environment. The stringent conditions required for the formation of alabandite, the presence of synsedimentary framboidal pyrite (<6 μm), and multiple geochemical indicators (such as V/Mo-Mo, V/Cr, Ni/Co, and V/(V+Ni)) collectively reflect that the Magong Manganese Deposit was formed in a relatively dynamic dysoxic-suboxic-euxinic environment. Euhedral to subhedral organic matter and extremely high EFMo, EFP, and EFCd values indicate high paleoproductivity conditions. [Conclusion] The geochemical characteristics suggest that the ore-forming materials of the Magong manganese deposit were mainly derived from submarine hydrothermal activity. The manganese carbonate ores were enriched in a relatively dynamic shelf-slope environment under dysoxic-suboxic-euxinic conditions. High paleoproductivity provided the material basis for the mineralization through water column stratification under the "sulfide wedge" model. The presence of microbial-textured kutnohorite, abundant organic matter, and framboidal pyrite indicates that the manganese precipitation process was significantly influenced by bacterial sulfate reduction (BSR) and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS): the BSR process provided HCO3- for the formation of manganese carbonates and H?S for the generation of pyrite and alabandite; the EPS secreted by bacteria provided adsorption sites for Mn2+, Mg2+, and Ca2+, promoting the precipitation of kutnohorite. During the mineralization process, iron and manganese were separated due to differences in their geochemical behaviors. This study provides new evidence for understanding the genesis of sedimentary manganese deposits in the Longmenshan tectonic belt and further refines the precipitation mechanism of sedimentary manganese ores within this metallogenic belt.
[Purpose]As a new type of unconventional natural gas, coal and rock gas has made a major breakthrough in the exploration of the central and western basins in recent years. At present, the research on coal and rock gas mainly focuses on the gas generation capacity and gas accumulation capacity of coal and rock, but the formation mechanism and distribution law of thick coal seams, the carrier of coal and rock gas, are obviously insufficient, which leads to the optimization of favorable coal and rock gas zones, especially the optimization of drilling intervals in thick coal seams of medium and low coal rank in the western basin.[Methods]Based on the description of the coring and macroscopic characteristics of underground coal and rock in the Tuha Basin, the microscopic component identification, major and trace element analysis and rock pyrolysis analysis of coal and rock samples of Xishanyao Formation were systematically carried out, and on this basis, the sedimentary environment, coal facies characteristics and characteristics of coal and rock gas sweet spot sections in thick coal seams were compared.[Results]The analysis of coal and rock microscopic components shows that there are not only various types of coal facies in the Xishanyao Formation in the Tuha Basin, but also various types of coal facies superimposed in the thick coal seam at the same location. The comparative analysis of the main and trace elements in coal and rock shows that there are multi-stage water inflow and water retreat cyclic characteristics in thick coal seams.[Conclusions]The results show that the coal-forming environment is different at different stages in the process of water inflow and retreat, resulting in the difference in the quality of coal and rock between different coal phases, and the cause of the thick coal seam is the longitudinal superposition of coal and rock of different types of coal facies caused by the rise and fall of water bodies in multiple stages. During the Jurassic period, the Tuha Basin was an intermountain continental basin, and different sedimentary facies zones were affected by the depth of the water body, and the ratio of peat production rate to the growth rate of the accommodating space was obviously different, resulting in the difference in the development and distribution of coal seams. In the thick coal seams in this area, the flooded interface and the tolerable spatial transition surface in the process of water retreat can be identified, among which the water degradation transition surface is the layer with the highest organic matter content in coal and rock, and it is also the sweet spot section of coal and rock gas exploration.
Abstract: [Objective] Accurate identification of carbonate sedimentary facies forms the basis for lithofacies paleogeographic reconstruction. However, challenges arise from the ambiguity of facies characteristics and the subjectivity of manual interpretation, while traditional well-log facies interpretation methods suffer from inefficiency and experience-dependent limitations. This study aims to construct a reusable intelligent interpretation model using machine learning algorithms to overcome the limitations in well-log facies interpretation and enhance the accuracy and efficiency of carbonate facies identification. [Methods] Five boreholes from the reef-shoal facies belt of the Changxing Formation in the Yuanba area of northeastern Sichuan Basin were selected as the study objects. Feature parameters, including acoustic log, gamma-ray well log , and other well-log curves, were used to establish a random forest algorithm-based model for carbonate well-log facies identification. To address class imbalance, the SMOTE-Nearmiss-1 resampling algorithm was implemented, while optimal hyperparameters were determined through grid search coupled with K-fold cross-validation. [Results] The improved model demonstrated significantly enhanced recognition capability for minority classes, achieving an accuracy of 0.87 in single well testing. This case highlights the significant potential of machine learning models in accurately identifying carbonate sedimentary facies.
[Objective]Contourites well developed along southern and western margin of Ordos Basin, where sedimentary characteristics very abundant. It is ideal area of research contourites. The mounded contourite, a special type of contourite formed in Kelimoli formation of Ordovician in western margin of Ordos Basin. [Methods] Using outcrop, thin section, and paleacurrent, mechanism of mounded contourites had been researched. [Results] (1) Micrite-, calcisiltite-, and muddy contourites are well favour in the study area. The lithology is mainly dark grey motted thin micrtici and calsisiltitic limestone with wavy boundary. They are lenticular-shape with unstabe along layer. Horizontal-, wavy- bedding, erosive surfaces are usually founded. Bioclastic fragments are relative rich. Bioturbation and burrow are well developed. And the paleocurrent direction is northeast, paralleling to slope. (2) Mounded contourites are mounded shape, and NW-SE orientation, about parallel to slope. (3) Contourites dunes developed in mounded contourites showing mounded shape are micrite and calcisiltite, some muddy limestone interbedded very thin mudstone in lower and upper parts. The thickness of mounded contourites being fine-coarse-fine cycle, is 152 cm, can be divided into 11 units. 4 small mounded contourites developed with a series progradation. Bioturbation and burrows are usually formed. (4) The mounded contourite can be divided into early initial, middle formative and late decline stages. They were resulting from secondary flow showing helical feature when high energy contour current moved northeastward. Helical flow can lead to erosion and deposition and form moat. Anticlockwise secondary flow also can transport sediment, and develop mounded contourite on the side of moat facing to deep sea basin. [Conclusion] This study demonstrate characteristics, processes, and depositional model of mounded contourite, not only add one example of mounded contourites, but also help to reconstruct contour current circulation and recover the palaeoenvironment.
The rapid advancement of information, intelligence, and automation technologies has significantly expanded the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-based oblique photogrammetry in geology. In recent years, its applications in field geology have advanced swiftly. This paper reviews the principles and developments of UAV-based photogrammetry, the associated primary products and modeling technologies, and its applications in sedimentology, stratigraphy, and reservoir geology. Key advancements include digital outcrop dataset collection paradigms, visual representation and digital twin technologies, sequence stratigraphy and modern sedimentary source-sink analyses, quantitative reservoir sedimentology, and 3D geological modeling. Based on a comprehensive literature review and current technological trends, future developments are expected to focus on intelligent identification and modeling of sedimentary geological features, enhancements to digital twin systems and visualization, deeper exploration of reservoir genesis and prototype modeling, multi-scale data calibration and integration, and the expansion of geological research directions.
Abstract: [Objective] To study a large number of Rhizocorallium in Guanling Formation in Xingyi area, and analyze the morphological and structural characteristics of its burrows, so as to reveal the behavioral habits of trace-making organisms and their indicative significance to the ancient sedimentary environment. [Methods] The cross-sectional diameter of the relict tube and the distance between the two wing tubes of Rhizocorallium U-shaped burrows were measured. The correlation of parameters was analyzed by linear regression, and the morphological structure and trace-making process were analyzed. The disturbance intensity was evaluated by bioturbation index (BI), and the sedimentary environment was revealed by combining lithology and other characteristics. [Results](1) The basic structure of Rhizocorallium is composed of U-shaped and linear burrows, and its formation mechanism is the mutual transformation of foraging-crawling behavior of trace-making organisms. (2) The cross-sectional diameter (0.1~2.6 cm) of the U-shaped trace tube was highly positively correlated with the distance between the two wing tubes (0.5~11.9 cm) (R2=0.92688), indicating that the behavior patterns of trace-building organisms from larvae to adults were highly consistent, which was consistent with the survival strategy characteristics of opportunistic species (r-selected).The bioclastic limestone and micritic limestone in the lower Guanling Formation are characterized by high-density Rhizocorallium ( BI = 3 ~ 5 ), mainly distributed in low-energy open platforms. The bioclastic limestone in the upper section of the is characterized by sparse Rhizocorallium ( BI = 1 ~ 3 ), which is mainly distributed in the high-energy intertidal zone. [ Conclusion ] In this study, the morphological identification and identification of Rhizocorallium revealed the characteristics and formation mechanism of its burrow structure, and further confirmed the consistency of behavior and its r-selection strategy in the process of individual development. More importantly, the study clarified the behavioral response and adaptive characteristics of Rhizocorallium to different sedimentary environments. These findings together indicate that Rhizocorallium can be used as a reliable ichnological marker for the reconstruction of paleoecology and paleosedimentary environment.
The Late Ordovician - Early Silurian witness changes in climate, however, the triggering mechanism are still under debate. In this study, the Longmaxi Formation in the Wanhe section, located in southwestern Sichuan Province, are selected to analyze the depositional and diagenetic processes using sedimentology, mineralogy and geochemistry. Furthermore, this study evaluates the formation mechanism of pyrite in the Longmaxi Formation/carbonate lenticle, and reveals the influences of early diagenesis on the changes in climate. The results show that the black shales in Longmaxi Formation are mainly deposited under euxinic anoxic water conditions, considering the high Corg/P ratios, high UEF and VEF values. The organic matter in the sediments is anaerobically oxidized by the microbial sulfate reduction (MSR) process due to anoxia of waters above the water?rock interface. In addition, the sulfate-driven anaerobic oxidation of methane (SD-AOM) resulted in the precipitation of euhedral pyrite with high Co contents and δ34Spyr values (>10‰) and low V contents. Of course, the influences of TSR in late diagenesis on the formation of pyrite in studied areas need more work in the future. Given that methane is a greenhouse gas, this study suggested that the release of methane formed in early diagenesis has the potential to influence the hydrochemical conditions in seawater or warming climate in early Silurian.
Abstract: [Objective] The Wangka section in the Changdu area, North Qiangtang terrane, records a critical lithological transition from limestone to clastic rocks in the Lower-Middle Permian Jiaoga Formation. The timing of this transition may hold significant implications for understanding the driving mechanisms of the Permian P3 glaciation. [Methods] We conducted an integrated study of the Jiaoga Formation tuffs, including petrography, zircon U-Pb geochronology, zircon trace element analysis, and whole-rock major/trace element geochemistry, to constrain their emplacement age and provenance. [Results] Zircon U-Pb dating yielded a weighted mean age of 268.2 ± 1.9 Ma for the tuffs. Zircon trace elements exhibit light rare earth element (LREE) depletion and heavy REE (HREE) enrichment. Whole-rock geochemistry shows High Al?O?/TiO?, Zr/TiO?, and Th/Sc ratios. Primitive mantle-normalized patterns with Nb-Ta-Ti depletion and Th-U enrichment. [Conclusions] The age of the Jiaoga Formation tuffs overlaps with the onset of the Permian P3 glaciation within analytical uncertainty. Their geochemical signatures suggest derivation from a volcanic island arc spanning the North Qiangtang-Simao terranes. Intensive weathering of this arc system may have triggered or amplified the P3 glaciation.
In order to break through the bottleneck of high cost of oil and gas exploration due to the difficulty of accurate prediction of sedimentary system, the study is based on the theory of distributive fluvial system, and takes the Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in Northwest Sichuan Basin as the sample, synthesizes the data of field outcrops, cores, and logging-recording wells, etc., and utilizes the research methods combining the analysis of the ground surface and the subsurface, and the analysis of the quantitative and qualitative analyses, so as to achieve the quantitative characterization of the sedimentary system of the Shaximiao Formation in the Northwest Sichuan Basin. The results of the study showed that: (1) The Shaximiao Formation in the central and northwest Sichuan basin has developed three types of sedimentary systems: distributive fluvial system, delta system, and lacustrine system. The distributive fluvial system of Shaximiao Formation in the study area can be divided into 3 subfacies and 6 microfacies types, the delta system can be divided into 2 subfacies and 4 microfacies types, and the lacustrine system can be further divided into shore-shallow lake beach-bar deposits. (2) The ratio of subfacies net-to-gross ratio is 50%-70% in the proximal, and the sand bodies are superimposed with thick layers. The medial subfacies net-to-gross ratio is between 30%-50%, and the sand body is distributed in thick layers. The distal subfacies net-to-gross ratio is 20%-30%, and the sand body is isolated. The delta and lacustrine facies systems are distributed in the middle Sichuan basin, and the net-to-gross ratio change is generally less than 15%. The sand bodies are also distributed in continuous sheets, but the maximum thickness of single sand bodies is thinner than that of the medial facies belt. (3) The Shaximiao Formation in the study area is mainly influenced by fluvial action, with the Sha 1 Member showing the distributive fluvial system terminating in a larger range of lacustrine deposits, and the Sha 2 Member showing the distributive fluvial system terminating in some small temporary lakes. (4) According to the modern sedimentary reference, in addition to the development of large high-quality reservoirs in the delta system, the medial and distal facies of the distributive fluvial system can also form continuous channel sand reservoirs. The results of the research are of great significance in characterizing the development scale and overlay style of different sand bodies, and also provide a reference basis for the study of the distribution of sedimentary systems in the context of similar fluvial deposits.
[Objective] The carbonate content is high in the source rocks of the Permian Pusige Formation in the southwestern depression of Tarim Basin, and the relationship between carbonate and organic matter remains unclear. This has hindered the evaluation of their potential for hydrocarbon generation.[Methods] Through analysis using techniques such as core examination, thin section analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), whole-rock X-ray diffraction (XRD), and geochemical studies, this research investigates the storage state and origin of carbonate, the distribution patterns of organic matter, and the relationship between carbonate and organic matter in the source rocks of the Permian Pusige Formation located at the peripheral areas of Kekeya in the southwestern depression of Tarim Basin. [Results] The source rocks of Permian Pusige Formation primarily exhibit three lithofacies associations: sand-mud, gray-mud, and sand-gray-mud. Calcite in the source rock mainly exists as cement and particles, displaying a multi-scale cycloidal feature of increasing and then decreasing from bottom to top within each “sand-gray-mud” cycle. The sources of carbonate include: 1) detrital particles derived from ancient continental sediments; 2) intra-depositional detritus or carbonate laminae; and 3) cementation or replacement products formed during the diagenetic phase. By conducting detailed analysis of the multi-scale cyclothem sequences, it was observed that organic matter tends to accumulate at the tops of these sequences. The main hydrocarbon-bearing intervals could be the laminites at the top of each cyclothem. Geochemical analysis revealed a strong negative correlation between carbonate minerals like calcite and Rock-Eval parameters such as TOC (Total Organic Carbon), PG (Pyrolytic Hydrocarbon Generation Potential), and HI (Hydrogen Index), reflecting a pattern of high calcium and low Rock-Eval parameters. The underlying cause is that calcium primarily resides in sandstone and calcitic layers at the cycle's base and middle sections, where stronger hydrodynamic conditions during deposition were unfavorable for organic accumulation and preservation. [Conclusion] The high-calcium source rocks within multi-scale "sand-gray-mud" cycles may possess unique characteristics pertaining to hydrocarbon generation conditions, expulsion efficiency, and oil/gas migration processes, indicating a substantial potential for hydrocarbon generation in the source rocks of Permian Pusige Formation in the Kekeya.
Abstract: In order to study the characteristics of hydrocarbon enrichment at oil source faults above mudstone caprocks in petroliferous basins with developed lower source rocks, based on the research on the mechanism and degree of weakening of hydrocarbon transport capacity of oil source faults by mudstone caprocks, we use the paleo-fault throw, dip angle, paleo-normal pressure generated by the weight of overlying sedimentary load, paleo-formation pore fluid pressure difference of source rocks, and hydrocarbon supply capacity index within the mudstone caprock to calculate the hydrocarbon transport capacity index of oil source faults that do not penetrate the mudstone caprock. Then, we divide this value by the paleo-connection thickness of the mudstone caprock to obtain the hydrocarbon transport capacity index of oil source faults that penetrate the mudstone caprock. According to the relative magnitudes of the two indices, we establish a method for assessing the degree of weakening of hydrocarbon transport capacity of oil source faults by mudstone caprocks. We apply this method to study the degree of weakening of hydrocarbon transport capacity from the Gangdong fault to the third member of the Dongying Formation (Ed3) by the mudstone caprock of the middle part of the first member of Shahejie Formation (Es1m) in the Qikou Sag of the Bohai Bay Basin. The results indicate that the degree of weakening of hydrocarbon transport capacity from the mudstone caprock of Es1m affecting the Gangdong fault to Ed3 is zero at measurement points 4-10, 100% at measurement points 1-3 and 11-12, and between 0% and 100% at measurement points 3-4 and 10-11. The measurement points 4-10, where the degree of weakening of the hydrocarbon transport capacity from the Es1m mudstone caprock to the Gangdong Fault for transporting hydrocarbons to Ed3 is relatively small, are favorable locations for the accumulation and reservoir formation of hydrocarbons supplied by the underlying third member of the Shahejie Formation (Es3) source rock in Ed3. This is consistent with the current distribution of hydrocarbons discovered in Ed3 at the Gangdong Fault, which are mainly concentrated at measurement points 6-10, indicating that the method is feasible for studying the degree of weakening of the hydrocarbon transport capacity of oil - source faults by mudstone caprocks.
The Late Triassic period in the Western Sichuan Foreland Basin represents a critical phase of the Indosinian orogeny. The sedimentary strata formed during this period not only preserve the geological records of the basin's tectonic evolution but also contain key information about volcanic activities during that time. Analyzing the material sources of tuff in the strata can provide important evidence for revealing the tectonic-magmatic activity patterns of the surrounding orogenic belts during the Indosinian Orogeny. This study selected the tuff of the Xujia Formation in the Jiguan Mountain section of the Western Sichuan Foreland Basin as the research object. Through a combination of petrological analysis, geochemical characteristic analysis, and zircon U-Pb isotopic dating techniques, the sedimentary age of this tuff layer and the source of its magma were revealed. Zircon U-Pb dating yielded ages of 213.5 Ma and 208.5 Ma, corresponding to the Late Triassic Norian-Rhaetian stage. The rare earth element (REE) patterns of the tuffaceous rocks exhibit a right-leaning distribution characterized by enriched light rare earth elements (LREEs) and relatively flat heavy rare earth elements (HREEs), with pronounced negative Eu anomalies. Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams show enrichment in large-ion lithophile elements (LILEs, e.g., Rb, Ba) and depletion in high-field-strength elements (HFSEs, e.g., Ta), consistent with geochemical signatures of continental lower crust. Zircon Hf isotopic data indicate that the magmas originated from a mixture of crustal contamination and depleted mantle sources. Building upon this foundation, and in consideration of the regional distribution and formation age of Late Triassic igneous rocks in the periphery of the western Sichuan foreland basin, integrated with geochemical characteristics of magmatic rocks, it is concluded that the volcanic material of tuff shares a common magmatic origin with the Late Triassic andesite of the Songpan-Ganzi terrane. This magmatic activity is closely associated with the melting of continental crust under the context of bidirectional plate subduction.
[Objective] The successful breakthrough in the Jurassic of Well Fusha 8 in the piedmont area of the southwest Tarim Basin marks the emergence of a new oil-bearing series, demonstrating promising prospects for oil and gas exploration. Currently, the insufficient understanding of the provenance characteristics and sedimentary evolution of the Jurassic system has become a critical issue constraining oil and gas exploration. [Methods] Taking the Jurassic in the piedmont area of the southwest Tarim Basin as the research object, this study investigates the provenance systems, sedimentary facies types, and sedimentary evolution processes based on field outcrops, drilling data, and other relevant materials. [Results] The Jurassic were primarily sourced from the West Kunlun Mountains and the West Tianshan Mountains, with weaker contributions from the slope area. Both the Fusha and Aketao Fault Depressions developed two major provenance systems: the southern (West Kunlun Mountains) and the northern (slope area). In contrast, the Kuzigongsu Fault Depression was mainly sourced from the West Tianshan Mountains. Fourteen lithofacies and fourteen lithofacies associations were found in the Jurassic, and seven sedimentary facies types were determined. The Fusha and Aketao Fault depressions in the piedmont area of the West Kunlun Mountains underwent a evolution during the Early to Middle Jurassic, progressing from the initial rifting stage to the intense rifting stage and finally to the rift-sag transition stage. The steep slope zone in the south primarily developed alluvial fan-fan delta sedimentary systems, while the gentle slope zone in the north developed small-scale braided river deltas and fan deltas. In the Kuzigongsu Fault Depression in front of the West Tianshan Mountains, the boundary faults remained active during the Early to Middle Jurassic. The main sub-depression developed an alluvial fan-fan delta sedimentary system, while the secondary sub-depression was initially filled and leveled by alluvial fan conglomerates. In the later stage, the rifting activity expanded westward, predominantly forming braided river-meandering river deposits. During the Late Jurassic, compression and regional aridification triggered basin basement uplift and enhanced sediment supply, resulting in widespread development of alluvial fan deposits across the study area, marking the terminal stage of rifted lake basin evolution. [Conclusions] Overall, the Jurassic strata in the piedmont area of the southwestern Tarim Basin experienced a transgression during the Early to Middle Jurassic and a regression during the Middle to Late Jurassic, reflecting a multi-stage sedimentary evolution. This study not only reconstructs the filling and evolution process of the Jurassic in the southwestern Tarim Basin but also provides valuable insights for the paleogeographic reconstruction of sedimentary areas in residual basins.
[Objective] Pore-laminar fracture system is an important reservoir space and seepage channel of shale oil, which controls the distribution of shale oil. Due to the internal relationship between pores and lamellar fractures in genesis, this paper will take the pore-laminar fracture system as a whole to be researched. [Methods] The shale of the Es3x-Es4s of the Paleogene in Jiyang Depression is selected as an example. Taking the lamina as a unit, a series of experiments were carried out on the two typical lithofacies of organic-rich laminated limestone and organic-rich laminated mudstone by means of microscope observation, scanning electron microscope and SEM-EDS-AMICS analysis technology, and the development distribution mode and control factors of pore-lamellar fracture system were discussed. [Results and Discussions] The results show that the organic-rich laminated limestone mainly developed calcite-associated pores (intercrystalline pores, intergranular pores and dissolved pores), accounting for 32.48% of the total surface pore rate. The boundary between the two laminae is clear and the laminar fractures are well developed. The organic-rich laminated mudstone is most developed with clay mineral-associated pores (intercrystalline pores and intergranular pores), accounting for 37.51 % of the total surface pore rate, and there is also a good development of laminar fractures. [Conclusions] The pore-laminate fracture system of organic-rich laminated limestone is mainly composed of calcite intercrystalline pores, clay mineral intercrystalline pores and laminar fractures. The organic-rich laminated mudstone is mainly composed of clay mineral intercrystalline pores, organic pores and laminar fractures. The development of different pore-laminar fracture system in the two lithofacies is controlled by sedimentation and diagenesis. The depositional environments control the types of laminae and their combinatorial methods. In the process of diagenesis, the organic-rich laminated limestone is mainly affected by calcite recrystallization and dissolution, and the organic-rich laminated mudstone is dominated by clay mineral transformation and thermal evolution of organic matter. It is of great significance to clarify the distribution pattern and development control factors of pore-laminar fracture system for guiding the exploration and development of shale oil in Jiyang Depression.
[Objective] The Permian represents a critical period of tectonic-sedimentary transition in the northern Ordos Basin. A detailed characterization of its complex source-to-sink processes is essential for revealing multi-provenance differential supply patterns and paleogeographic evolution.[Methods] This study systematically analyzes provenance signals and sedimentary filling processes in the northern Ordos Basin through outcrop observations, well-logging data, and detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology, aiming to clarify the paleogeographic framework constrained by source-to-sink systems and its implications for the closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean. [Results](1) Detrital zircon U-Pb ages reveal that the Alxa Block, Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt, and North China Craton contributed differentially during the Permian, with marked east-west variations. Multidimensional scaling (MDS) analysis divides the northern basin into three provenance zones: Alxa, western Yinshan, and eastern Yinshan. (2) The Permian depositional systems evolved from tide-dominated deltas to braided-river deltas, with sediment thickness and sandbody distribution showing a "thicker in the west and stronger in the north" pattern. Provenance supply intensity closely correlated with environmental changes. Enhanced lateral continuity of sandbodies in the Shanxi and Shihezi Formations reflects braided channel development under strong sediment supply.(3) Source-to-sink analysis indicates:Taiyuan Stage: Dominated by proximal weak supply.Shanxi Stage: Increased provenance mixing formed an east-west differentiated depositional pattern.Shihezi Stage: Significant uplift of the North China Craton basement led to dominant distal supply, with maximum sandbody thickness and spatial extent. [Conclusions]The inhomogeneity of the subduction/closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean drove the differential uplift characterized by "strong in the west and weak in the east" in the Xing'an-Mongolian Orogenic Belt and "strong in the east and weak in the west" in the basement of the North China Craton. This controlled the east-west differentiation pattern and evolution of the provenance in the northern part of the basin, which showed "mixed provenance in the west and cratonic basement in the east". The sedimentary system transformed from a tide-dominated delta in the marine-continental transitional environment to a continental braided river delta from the Taiyuan Stage to the Shihezi Stage. [Significance] The established paleogeographic evolution model, based on source-to-sink processes, provides a dynamic coupling framework for understanding multi-provenance-sedimentation responses and hydrocarbon exploration in large cratonic basins.
[Objective] The geological conditions in the hinterland Junggar Basin are diverse and the crude oil properties are complex. To address the issues of crude oil type classification and oil and gas source identification in this area, a study on the hydrogen isotopic characteristics of n-alkanes (δ2Halk) in the mixed-source crude oils from the hinterland Junggar Basin was conducted. [Methods] GC-MS, GC-IRMS, and GC-TC-IRMS techniques were employed to analyze biomarker compounds and conduct hydrogen isotope analysis of n-alkane monomers in 33 crude oil samples from different strata. [Results and Discussions] Three types of crude oil were identified in the hinterland Junggar Basin: Type I crude oil originated from the Jurassic coal-bearing source rocks (J1b), with the lightest hydrogen isotopic composition due to the significant input of terrestrial higher plant organic matter; Type II crude oil mainly originated from the Permian Fengcheng Formation source rocks (P1f), with Type IIA crude oil from lacustrine sedimentary environments in transitional marine-terrestrial settings, featuring a low Ga/C30H ratio and relatively heavy hydrogen isotopic composition, while Type IIB crude oil had a lighter hydrogen isotopic composition and a higher Ga/C30H ratio; Type III crude oil mainly originated from the Permian Lower Wuerhe Formation source rocks (P2w), with a light hydrogen isotopic composition of n-alkanes. [Conclusions] The combination of hydrogen isotopic analysis of n-alkanes and biomarker compound analysis can precisely classify crude oil types and clarify their sources, which is of great significance for oil source tracking and crude oil classification in the entire Junggar Basin.
Abstract: [Objective] The Oceanic Anoxic Event 1d (OAE 1d), took place during the late Albian of the Early Cretaceous, represents a significant perturbation in the global carbon cycle associated with a greenhouse climate. Although extensive research has been conducted on the characteristics and origin of OAE 1d in the western Tethys and North Atlantic regions, the paleoenvironmental response to this event in the eastern Tethys remains poorly understood. [Methods] This study focuses on the Lower Cretaceous Lengqingre Formation at the Youxia section in Dingri (southern Tibet) within the eastern Tethyan domain. Here, an integrated approach of mineralogical, petrological, sedimentological, isotopic, and elemental geochemical analyses, was employed to evaluated the paleoenvironmental response to OAE 1d and its distinction from coeval global patterns compared to contemporaneous global records. [Results] (1) Both bulk carbonate and organic carbon isotope data confirm that the Youxia section records the OAE 1d excursion, supporting the global signal of this phenomenon. (2) Thin-section observations and terrigenous input proxies (e.g., Si/Al and Ti/Al ratios) indicate enhanced input of siliciclastic materials during OAE 1d, likely linked to accelerated hydrological cycling and intensified continental weathering related to coeval volcanic activity. (3) Corg/P ratios and framboidal pyrite characteristics reveal that the Youxia section was deposited under oxic to suboxic bottom-water conditions during OAE 1d, markedly different from the anoxic conditions observed in the western Tethys. This highlights the spatial heterogeneity in marine redox conditions during this event. (4) The absence of organic carbon-rich sediments at Youxia is attributed to a combination of oxic environmental conditions, intense terrigenous input, and dilution effects induced by rapid sedimentation rates. This suggests that organic carbon burial was suppressed by regional environmental controls in the Dingri region during OAE 1d. [Conclusion] The oxic-suboxic conditions and lack of organic-rich sediments in the eastern Tethys during OAE 1d underscore the regional heterogeneity in sedimentary and oceanographic responses to global Oceanic Anoxic Events. These findings provide critical insights into complexity of paleoenvironmental feedbacks during global Oceanic Anoxic Events.
The tight sandstone interlayer of the Chang 71-2 sub-member of the Yanchang Formation in the Qingcheng Oilfield is a typical sublacustrine fan deposit. However, the research on the difference of sandstone reservoir performance on the sedimentary microfacies scale is insufficient, which restricts the screening of high-yield blocks and the difference analysis of horizontal well production effects. Based on core, logging and seismic data, using thin section identification, scanning electron microscopy, micro-CT, nuclear magnetic resonance, high-pressure mercury injection and constant-rate mercury injection tests, combined with oil test and production test data, the differences in tight sandstone rock and ore, microscopic pore structure, oil content and mobility, and oil test in different sedimentary microfacies are analyzed. The results show that under the control of multi-stage slope break zones, multi-stage sublacustrine fan sand bodies accumulate in the relatively gentle semi-deep lake-deep lake slope toe zone, and frequently interact with organic-rich shale to form a large area of ' sandwich ' source-reservoir symbiosis, which constitutes the main geological dessert of interlayer shale oil in Qingcheng Oilfield. The sandstone interlayer can be divided into four sedimentary microfacies : channel, lobe, lobe side edge and slump body. The sandstone superimposed thickness of channel, lobe and lobe side edge is relatively large, and the logging interpretation is generally oil layer, which is the main target of horizontal well development. The reservoir space of channel, lobe body and lobe lateral margin is dominated by dissolution pores and intergranular pores. The cements are mainly ferrodolomite, ferrocalcite and quartz. The channel and lobe body have the characteristics of low content of interstitial materials and cements, high surface porosity, good physical properties and microscopic pore structure, high proportion of connected pore volume, large pore throat radius, and relatively high movable fluid saturation and oiliness. The saturation of movable fluid is closely related to the pore structure. Controlled by the microscopic pore structure, the channel has better microscopic pore throat parameters than the lobe, which is more conducive to the filling and seepage of oil and gas. Under the same thickness scale, the channel is easier to obtain high-yield industrial oil flow than the lobed body vertical well test, and the vertical superposition of the channel and the lobed body is a high-yield sedimentary combination box ; fine sublacustrine fan tight sandstone sedimentary microfacies characterization, optimizing the orientation and length of horizontal wells, and optimizing favorable microfacies combinations for development are the key to improving the drilling rate and development effect of horizontal well reservoirs.
[Significance] As a kind of autogenous clay mineral with a unique fibrous crystal structure,sepiolite plays an important role in the geological field with its excellent high adsorption and thermal stability.[Progress]The formation mechanism of sepiolite is complex and diverse, including direct precipitation,terrigene transport and sedimentation-diagenesis.This process is not only significantly affected by geological environment and climate conditions,but also intertwined with multiple factors such as element concentration and pH,which jointly shape the unique distribution pattern of sepiolite in nature.Sepiolite is mainly formed in the alkaline reduction environment rich in magnesium and silicon and poor in aluminum,and with the passage of time and the dynamic change of temperature and pressure,phase transition occurs and transforms into talc or montmorillonite and other minerals, thus forming a rich and diverse sedimentary-diagenetic evolution model.In terms of geological applications, sepiolite can efficiently adsorb a large amount of organic matter with its excellent adsorption properties,providing a material basis for the formation of unconventional oil and gas reservoirs, and significantly improving the quality of source rocks and hydrocarbon generation potential.In addition,sepiolite can also promote the dolomitization of high limestone,and then transform into high-quality dolomite reservoir,and breed two novel hydrocarbon accumulation modes:natural self-storage and lower and upper storage.By studying the thickness and distribution of sepiolite strata,we can infer the fluctuation characteristics of palaeogeomorphology, and then predict the favorable distribution area of oil and gas reservoirs,which provides important geological basis for oil and gas exploration.At the same time, the formation and distribution of sepiolite can also reflect various paleoenvironmental information such as evaporation system,water level change,climatic conditions and anoxic environment,and reveal major geological events.[Conclusion and progress]Therefore, sepiolite shows important research value in oil and gas exploration, paleogeomorphology reconstruction and paleoenvironment restoration.The future development trend of sepiolite will be to use sepiolite to obtain ancient environmental conditions,improve the ability to analyze seismic data of the thickness of sepiolite layer,and develop the exploration of oil and gas in sepiolite layer.
[Objective] After the end-Permian mass extinction, microbialites were widely distributed in South China, indicating a microbial bloom following the catastrophe. However, microbialites generally exhibit low paleo-productivity, which seems contradictory to the microbial explosion. This study analyzes the microbialites at the base of the Triassic Tianwan section in the Luodian area of Guizhou Province, focusing on the petrological characteristics of micritic pellets and their thermal metamorphic evolution and material sources of organic matter. It clarifies the respective influences of microbial-derived organic matter and seawater-trapped organic matter on pellet formation, aiming to provide empirical evidence for exploring carbon cycling mechanisms in post-extinction microbialite systems. [Methods] This study employs in situ micro-area analytical techniques including optical microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and laser Raman spectroscopy to conduct a detailed analysis of various types of peloids within microbialites from the Tianwan section. These methods reveal the distribution patterns and thermal metamorphic evolutionary characteristics of internal organic matter. [Discussions] Based on morphology and infill materials, various peloids were classified into six types. Raman spectroscopy-derived metamorphic roasting temperatures provide insights into the thermal history and transformation of these peloids. The organic matters in I, II, IV, and VI (MIP, RMIP, ISP, and AMIP) types of peloids show similar thermal maturity to that of primary cyanobacteria in microbialites and shell fragments, indicating a common diagenetic history and microbial origin. Among them, peloid I and peloid II exhibit low thermal maturation temperatures, with organic matter mainly derived from the photosynthetic and metabolic processes of primary cyanobacteria and other microorganisms. Peloid IV and peloid VI show moderate thermal maturation temperatures, with their organic matter formed through the combined processes of detrital micritization and biological detritus micritization. In contrast, peloids III and V (ADP and DP) exhibit significantly higher metamorphic temperatures, suggesting multiple thermal alteration events and a potential detrital or externally derived component, possibly from reworked organic-rich sediments or transported detrital material. [Results] In summary, after the end-Permian mass extinction, microbial blooms, especially cyanobacterial photosynthesis, led to the generation of large amounts of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the oceans. Due to frequent fluctuations in seawater redox conditions and rapid temperature increases, DOC was typically oxidized into CO2 and released into the atmosphere, with only a small fraction being preserved as particle organic carbon (POC) and deposited on the seafloor. Raman geothermometry analysis shows that most of the organic matter in the microbialite peloids, particularly those associated with bioclastic peloidal envelopes, originates from the metabolic activity of primary cyanobacteria, representing the original organic matter within the microbialite system. A small portion of the organic matter may have been sourced from long-stored terrestrial organic matter in seawater, which underwent multiple diagenetic thermal alterations and shows higher thermal maturation temperatures. The thermal maturation of organic matter and mineral recrystallization during diagenesis had a significant impact on the preservation efficiency of organic matter, ultimately resulting in a low total organic carbon (TOC) content in the microbialites.
[Objective] The Wuotuo village in Zongdi Town, Ziyun County, Southern Guizhou Province, developed an early Permian coral reef that is exposed with a thickness of approximately 45 meters and a lateral exposure of nearly 100 meters. The reef displays a positive relief. [Methods] The methods of paleontology and sedimentary petrology were systematically used to study the Gaozhai coral reef in Zongdi Town, Ziyun County, Guizhou Province. [Results] The fusulinids collected from the reef indicate an Early Asselian age. The primary reef-building organism is identified as the fasciculate colonial coral Fomichevella, while biotic compositions of the coral reef include foraminifers, brachiopods, gastropods, and calcareous algae. The Wotuo coral reef and its underlying and overlying strata contain a broad variety of microfacies types, including bioclastic wackestone-packstone, coral bafflestone, bioclastic packstone, bioclastic grainstone, phylloid algae-cement framestone, fasciculate coral framestone, bioclastic wackestone and foraminifer-fusulinid grainstone. [Conclusion] During the Early Permian, glacial-interglacial cycles were the primary factors influencing the variations in palaeoocean temperature and global sea levels. The vertical microfacies succession in this study provides a record of relative sea-level change. The decline of late Paleozoic glaciation, which resulted in the global warming and a relative rise in sea level, played a pivotal role in the development and flourishing of the coral reefs in southern Guizhou Province.
Abstract: In order to deeply understand the source properties of Quaternary mudstones in Sebei area of the Sanhu Depression in the Qaidam Basin, this paper focuses on sedimentary geochemistry and conducts analysis and testing of major, trace, and rare earth elements on core samples from different depths of the Quaternary in the Sebei area's Setan 1 and Setan2 wells (ST1 and ST2 wells). In general, the samples has low silicon (SiO2=48.17%), high aluminum (Al2O3=15.23%, aluminum index A / NK=2.54, aluminum saturation index A / NK = 1.59), rich magnesium and calcium (MgO=3.81%, CaO=7.91%), relatively rich iron (Fe2O3=4.99), low total alkali content (K2O + Na2O=5.94%), significant enrichment of Ba and Cu compared to UCC, Nb depletion, and other trace and rare earth elements comparable to the upper crust. Quaternary mudstones in Sebu area are less affected by sedimentary sorting, rewinding, weathering and diagenesis and its elemental features can effectively indicate the source and tectonic background. The results show that the characteristics of the two well samples are relatively consistent. The F1-F2, Co / Th-La / Sc, La / Th-Hf, La / Yb-Σ REE discrimination diagrams, rare earth right-dip flat distribution pattern and related parameters all show that the sedimentary source of Quaternary mudstones in the study area is mainly derived from the upper crust felsic sedimentary rocks and igneous rock sources. (SiO2/ Al2O3) - (K2O / Na2O), (K2O / Na2O) -SiO2, [K2O / (Na2O + CaO)] - (SiO2 / Al2O3), Ti / Zr-La / Sc, La-Th-Sc, Th-Co-Zr / 10 and Th-Zr / 10 ternary phase diagrams and related parameters determine that the source area is an active continental margin and continental island arc environment. The potential source areas of Quaternary sediments in the Sebei area of Sanhu Depression mainly include the eastern Kunlun orogenic belt on the south side of the depression and the south Qilian orogenic belt on the north side of the depression.
[Significance] Mires not only serve as the fundamental environment for coal deposition throughout geological history, offering invaluable insights into Earth’s history, paleoclimate, and environmental evolution, but also hold significant importance in the global carbon cycle. Numerous geological scholars have conducted a wealth of research on mires. Understanding the research fronts and trends in mire-related studies within coal geology can guide future research. When writing research papers and using professional terminology, scholars may confuse or misuse terminology due to the diverse concepts and English expressions of mires, thus making it particularly crucial to clarify and accurately apply mire-related terminology. [Progress] Based on the data from “Web of Science”, using common English terminology related to “mire” as search keywords. PRISMA flowchart was utilized to screen out 7,479 relevant articles, conducting an investigation on the temporal evolution and international distribution of mire research in the field of geology. Employing VOSviewer 1.6.20 to conduct keyword co-occurrence analysis on 726 research papers focused on mires in coal geology (selected from 7,479 articles), a deep exploration was further carried out on the research fronts of mires in coal geology. Subsequently, by integrating English definitions of mire-related terminology with research fronts on mires in coal geology, suggestions were offered for simplifying the application of mire-related terminology. The following conclusions have been made: (1) From 1943 to 2023, a total of 123 countries and regions worldwide have participated in mire research, with the 2000 marking a significant turning point when mire studies gained momentum and became a hot topic. Since then, the number of research publications on mires in geology has generally exhibited an upward trend, with scholars from leading research countries engaging in frequent exchanges and academic discussions. Usage frequencies of English mire-related terminology vary across countries, reflecting distinct research emphases on different mire types. (2) By integrating meta-analysis, bibliometrics, and visualization techniques, the research fronts on mires in the field of coal geology are systematically reviewed and summarized. Research themes linked to mire in coal geology include coal depositional environments and their evolution, paleo-wildfire, atmospheric deposition, carbon accumulation, paleoclimate, and paleoecology. (3) “Mire” should be considered as a general terminology for mire-related concepts. When there is a need to emphasize the spatial distribution of mires, “fen” is an appropriate terminology for low-lying mire, and “bog” should be used instead of “mire” for raised mire. When the ecological or vegetative characteristics of mires need to be highlighted in research, it is recommended to use “swamp” or “marsh”. [Conclusions and Prospects] The results offer valuable insights for understanding the developmental trajectory of international mire research, identifying research fronts of mires in coal geology, and standardizing the application of mire-related terminology in English. Future research on mires in the field of coal geology should actively and effectively leverage big data or machine learning techniques including simulation modeling, database construction, statistical data analysis, and image recognition classification. Additionally, a multidisciplinary approach integrating geochemical, organic petrological, coal petrological, and mineralogical methods should be systematically employed throughout the research process to ensure comprehensive insights.
[Objective] In the Yangtze Block, South China, many places have been found with well preserved sedimentary records of Neoproterozoic “Snowball Earth” (Cryogenian), including the sediments from Sturtian glaciation (ca. 720 ~ 660 Ma, equivalent to Chang'an glaciation and Gucheng glaciation, Nanhuan Period), nonglacial interlude (ca. 660 ~ 649 Ma, Datangpo Age ), and Marinoan glaciation (ca. 649 ~ 635 Ma, Nantuo glaciation). The Neoproterozoic glacial deposits in Gangchang-Yuanba section, Hanzhong area, north margin of the Yangtze Block, previously called “Nantuo tillite”, were formed above the Tonian Liantuo red coarse clastic rocks, and below the Ediacaran Dushanshituo dolomite. In order to clarify the tillite age, how they formed and filled in the small rift basin between the north margin of Yangtze Block and the south margin of Qinling Orogens. [Methods]The field observation and measurement were carried out in the section. Based on it, zircons selected from the bottom tuff layer and upper sandstones were conducted U-Pb dating analysis (LA-ICP-MS).The detailed features of the sedimentary rocks and their regional correlation were also discussed in this paper. [Results and Discussion] Two sets of tillites were first identified within the Neoproterozoic glacial sedimentary rocks in this region, and both were formed from continental glacier. Several layers of sandstones and siltstones were filled between them and above. Zircons from the bottom tuff yield a youngest mean concordant age of 719 ± 11Ma, indicating the beginning of glaciation in this area. Considering with the lithological succession and sedimentary structures, these Cryogenian deposits are thought to be formed in the Sturtian glaciation, corresponding respectively to the Chang'an glaciation and the Gucheng glaciation. The timing of this glaciation event and the sedimentary associations are not only consistent with the contemporaneous sediments in adjacent Zhenba and Chengkou areas, but also show similarities to the Sturtian sediments widely distributed in other parts of South China.
[Objective] The Carnian Pluvial Episode ( CPE ) had a significant impact on the climate of the Late Triassic, and the warm and humid climate was conducive to the formation of fine-grained sediments and the enrichment of organic matter. Based on the study of CPE event during the sedimentary period of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin, the response characteristics of CPE event to the enrichment of thick organic-rich black shale in Chang 7 member are revealed. [Methods] In this paper, based on the comprehensive analysis of ZK903 drilling data, the characteristics of paleoclimate, paleoredox, paleosalinity and the source of organic matter in ancient lakes from Chang 7 to Chang 8 members of Yanchang Formation were discussed in depth with the data of biomarkers as the core, combined with various analytical methods such as clay minerals, trace elements and organic carbon isotopes. The organic matter enrichment model under the influence of CPE event in the study area was established. [Results] The vertical difference of sedimentary environment in Ordos Basin is obvious. The lithology of the Chang 8 to Chang 73 members in the study area changes from sandstone to black shale. The sedimentary period is significantly affected by CPE event, and the enrichment of organic matter gradually increases. The average TOC of Chang 73 member is 9.6 %. The changes of Sr / Cu and Sr / Rb values and clay mineral content indicate that the climate type in the study area changed from hot and dry to warm and humid under the influence of this event. The values of V/Cr, U/Th, Pr/Ph and Ts/(Ts+Tm) in terpane indicated that the redox environment changed significantly during the sedimentary period of Chang 73 member in the study area. Combined with Sr / Ba and gammacerane index (GI), it shows that under the influence of CPE events, the temperature and precipitation in the study area increased, the water surface of the lake increased, and the stability of the water body increased, which aggravated the stratification of the water body. The lake showed a fresh water reduction environment. The values of ∑C21-/∑C22+ and C27/C29(aaa)R in biomarkers increased significantly in Chang 73 member, indicating that the source of organic matter was dominated by low aquatic organisms such as algae. [Conclusions] The CPE event significantly affects the paleoclimate background of the study area and the sedimentary environment of the ancient lake water body. The development of fine-grained sediments in a stable stratified environment of water body also provides good productivity and preservation conditions for the enrichment of organic matter in this area, and promotes the deposition of organic-rich black shale, that is, oil shale.
[Objective] The uplift of the Tibetan Plateau is a direct expression of the geodynamic processes within Earth's interior caused by the collision of the India-Eurasian plates, significantly impacting the earth's critical zone. Investigating the uplift history of the plateau is essential for elucidating the deformation mechanisms of the continental lithosphere and remains a central scientific issue in deciphering Earth's multiple spheres interactions. Despite extensive studies, there remains intense debate regarding the uplift and expansion of the plateau. The timing of the uplift in the northern Tibetan Plateau is considered pivotal for resolving these controversies. The Eastern Kunlun Mountains, as a crucial geomorphic boundary in northern Tibet Plateau, form the southern margin of the northern plateau and serve as a critical conduit for the northward propagation of collision-related stress. Thus, the Eastern Kunlun Mountains is an ideal area to study the uplift processes of northern Tibetan Plateau. However, the timing of the initial uplift of the Eastern Kunlun Mountains remains highly debated. [Methods] A comprehensive low-temperature thermochronological analysis of the bedrock in the Eastern Kunlun Mountains to constrain its Cenozoic uplift history. To this end, results from 37 low-temperature thermochronology studies in the region were integrated, including 203 apatite fission track data points and 142 apatite (U-Th)/He data points. During the dataset compilation stage, the sample selection criteria of low-temperature thermochronology were strictly followed, and a series of rigorous data screening strategies were established to minimize disturbances from experimental errors, sample characteristics, and complex thermal histories, thereby enhancing the accuracy and reliability of the dataset. The analysis involved several steps: first, the low-temperature thermochronological age distribution were visualized; second, the relationship between mean track length and age was established; and third, thermal history modeling results were compiled. By integrating these methods, one can construct a detailed and comprehensive low-temperature thermochronology framework that serves as the basis for assessing the Cenozoic uplift history of the Eastern Kunlun Mountains. [Results and Conclusions] Since the Late Cretaceous, the surface rocks of the Eastern Kunlun Mountains have generally remained in a relatively stable or slowly cooling state, within the apatite fission track partial annealing zone and the apatite (U-Th)/He partial retention zone. During the Paleogene, the Eastern Kunlun Mountains did not form a significant topographic barrier, and the drainage systems between adjacent basins were likely interconnected. Although, the possibility that sporadic highlands in localized areas of the Eastern Kunlun Mountains provided sediment sources for adjacent basins cannot be entirely excluded, the data indicate that initial widespread uplift of the Eastern Kunlun Mountains did not occur until approximately 20 Ma. At this time, a rapid uplift event took place, with the displacement of rocks relative to the surface estimated to be no less than the length of the rock column recording early Miocene apatite (U-Th)/He (22~17 Ma) and apatite fission track (23~15 Ma) age components, approximately 2 km. This finding provides new evidence for understanding the disintegration timing of the Paleo-Qaidam Basin, the paleoelevation history of the northern Tibetan Plateau during the early Miocene, as well as the uplift processes and dynamics mechanisms involved.
Abstract: [Objective] Discharge regulates the sedimentary evolution and morphological scale of braided rivers; however, the degree of its influence on braided channels, bars, and internal architecture has not been systematically analyzed.[Methods] Five groups of three-dimensional sedimentary numerical simulation experiments with different flow rates were carried out using Delft3D software to explore the evolution, morphological patterns, and scale differences of braided channels and bars under various flow rates, reproduce the internal architecture patterns of multi-type bars in braided rivers with different flow rates, and summarize the sedimentary characteristics and evolution of sandy braided rivers.[Results and Discussions] (1) The evolution rate of sandy braided rivers positively correlates with discharge, which also influences the co-evolutionary process of braided channels and bars. In low-discharge braided rivers, bars primarily accumulate downstream and overlap as they migrate downward. This pattern makes it difficult for the bars to be divided or re-merged by the channel. In contrast, high-discharge braided rivers typically exhibit lateral accumulation, leading to complex stacking. This results in a more frequent dynamic equilibrium process of bar merging and fragmentation. (2)Discharge control braided channel plane style and channel depth. As discharge increases, the braided channel becomes wider and deeper, which results in a reduced overall number of channels. However, the chute of the channel bars becomes more developed. In contrast, lower-discharge braided channels are shallower and primarily consist of narrow, numerous, and relatively fixed interwoven river networks. (3) The discharge affects the shape, architecture, and scale of channel bars. As discharge increases, a larger portion of the channel area becomes active, resulting in a greater hydrodynamic force on the bars due to the transformation of water flow. Consequently, there is a smaller proportion of preserved bars. With higher flow rates, the degree of transformation also increases, leading to collisions among multiple unit bars and compound bars, which creates more complex overlap relationships. Large-scale compound complex bars and sidebars can develop extensively, especially at the contact points where chutes form between the bars.(4) By comparing the effects of high and low hydrodynamic forces on the internal growth of braided rivers, we find similarities and differences in how channel bars form. Both types of bars have a lobate shape and consist of multiple layers of sediment accretion. These layers include downstream accretions at the core, aggradational accretions that are layered above and extend over a long-range, which are thin and have a small dip angle, as well as lateral accretions deposited on the sides or chutes. The lateral accretions are characterized by high inclination, greater thickness, and smaller scale.The key difference is that as discharge increases, the proportion of downstream accretions within the bar decreases, while the proportion of lateral accretions increases.(5) The flow rate positively correlates with the inclination angle, length, width, and thickness of the accretions, but negatively correlates with the length-to-width ratio and width-to-thickness ratio. [Conclusions] It is proposed that the flow rate is directly proportional to the size of the accretions within the channel bars of sandy braided rivers. This relationship clarifies the sedimentary characteristics and scale differences of sandy braided rivers influenced by flow rate, providing an essential basis for understanding the architecture of complex underground reservoirs.
Abstract:[Objecive]A set of typical gravity flow sedimentation were developed in the Ordovician Lashizhong Formation of the western margin of Ordos Basin.To investigate the formation process of gravity flows in the three member of the Lashizhong Formation, summarize the sedimentary characteristics and evolutionary pattern, and establish a sedimentary model based on these findings.[Methods] The analysis was conducted through methods such as outcrop observation, rock thin section examination, and paleocurrent measurement. [Results]The results show that there are eight kinds of lithofacies and six lithofacies associations are developed in the study area, namely horizontal bedding shale(A1), lens-shaped massive bedding calcirudyte(B1), lens-shaped parallel bedding sandstone(B2), lens-shaped cross bedding sandstone-siltstone(B3), wedge cross bedding sandstone-siltstone(C1), bedded graded bedding sandstone-siltstone(D1), Bedded parallel bedding siltstone (D2)and Bedded pebbly sandstone(D3), indicating channel axis deposition(B1), vertical aggradation channels(B2,C1,A1), distributary channels(B3,C1,A1), proximal lobes(D1,A1), distal lobes(D2,A1)and mass transport deposits(D3); The lower part of the three-member successively develop the channel axis deposition, vertical aggradation channels, distributary channels, proximal lobes and distal lobes, and is divided into 5 stages; The middle and upper parts of the three-member develop the mass transport deposits, proximal lobes and distal lobes, and is divided into 7 stages. [Conclusion]The evolution of which is closely related to the type and energy of gravity flow. At the initial stage, gravity flow is dominated by debris flow, with the weakening of the debris flow energy, the turbidity current dominates, the vertical aggradation channels are developed through multi-stage periods of erosion and sedimentation. With the further weakening of the turbidity flow, the distributary channel and lobes are developed. Tectonic movement can increase the sand content of sediment supply, leading to the initial development of massive transport deposition first and then large-scale lobes with higher sand content were developed. The vertical evolution of gravity flow sedimentation is predominantly governed by a combination of factors, including relative sea-level fluctuations, sediment supply and its compositional characteristics, as well as tectonic movements. An initial rise in sea level followed by a subsequent fall suggests a corresponding decrease and then increase in the scale of gravity flow development. Variations in sediment supply types give rise to diverse sedimentary units. These include channel axis deposition predominantly composed of calcirudyte, as well as vertical aggradation channels, distributary channels, proximal lobes, and distal lobes mainly consisting of fine sandstone and siltstone. Moreover, the magnitude of sediment supply significantly impacts the morphological features, dimensions, and sand-to-mud ratio of these sedimentary units. During the depositional period of the Lashizhong Formation in the western margin of the Ordos Basin, tectonic activity was relatively subdued. This tectonic quiescence facilitated the formation of a channel-lobe system that, in comparison to the scale typically encountered in exploration contexts, is relatively modest in size. The interplay of these factors—sea-level changes, sediment supply dynamics, and tectonic setting—collectively shapes the architectural complexity and distribution patterns of gravity flow deposits within the basin. Understanding these controls is crucial for accurate reservoir characterization and prediction in hydrocarbon exploration and production.This study can supple the understanding of gravity flow evolution in the study area and provide theoretical reference for oil and gas exploration.
Abstract: [Objective] The main controlling factors and exploration potential of different types of shale oil enrichment in the Chang 7 member of the Ordos Basin are discussed, and the next exploration direction is identified. [Methods] In this study, the formation conditions and exploration potential of shale oil such as petrology, geochemical characteristics and reservoir capacity of the Chang 7 shale were comprehensively studied using organic geochemistry, whole rock X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy, and rock pyrolysis experiments. [Results] The results show that: (1) The Chang 73 shale has high organic matter abundance, the best type, the highest maturity, and the greatest hydrocarbon generation potential. (2) The Chang 7 shale is dominated by inorganic pores and fractures, with the largest proportion of micropores, and the shale reservoir capacity is stronger than that of mudstone. (3) The enrichment of shale oil in the Chang 7 member is controlled by five factors : high-quality source rock, lithologic combination, fracture, mobility, and fracability. The distribution of high-quality source rocks controls the distribution range of shale oil, and the lithology combination controls the hydrocarbon expulsion efficiency and the enrichment type of shale oil. The hydrocarbon expulsion efficiency of the source-reservoir interbedded type is the highest, which is conducive to the enrichment of sand bodies; the hydrocarbon expulsion efficiency of the thick source-thin reservoir type is the lowest, which is conducive to the in-situ retention and enrichment of shale oil. The two-sidedness of fractures controls the enrichment degree of shale oil. The development of fractures is conducive to the enrichment of sandstone interlayer shale oil, and the underdevelopment of fractures is conducive to the retention and enrichment of pure shale-type shale oil. The mobility and fracability of crude oil control the high yield of shale, and the mobility and brittleness index of shale crude oil are better than those of mudstone. [Conclusion] The Chang 73 sub-member in the Jiyuan area is a favorable exploration block for pure shale-type shale oil. The Zhengning and Northern Shaanxi areas are favorable exploration blocks for sandstone-intercalated shale oil in the Chang 71 and Chang 72 sub-members. The Huachi area in Longdong is a favorable area for the exploration of both sandstone-intercalated and pure shale-type shale oil.
[Objective] The second member of the Lucaogou Formation (Lu2) of the Middle Permian in the Malang depression is the main source of lacustrine carbonate shale oil in the Santanghu Basin, however, the study on the coupling relationship between carbon-oxygen isotope composition and paleoenvironmental characteristics and organic matter enrichment is relatively weak. [Methods] In order to clarify the paleoenvironmental characteristics and the enrichment mechanism of organic matter, total organic carbon content, carbon-oxygen isotope and micronutrient of carbonate samples were analyzed in this study. [Results and Discussions] The results show that:①the carbon isotopes of the carbonate rocks in the second member of Lu Formation are all positive, and the oxygen isotopes are all negative, from bottom to top, the carbon-oxygen isotopes of Lu2 member show the characteristics of high-low-high, and have obvious response relationship with sedimentary cycle, paleoenvironment and paleoproductivity.②The lower part of the middle dessert is a deep water environment with drought, brackish water and strong reduction, and the paleoproductivity is low. The upper part is a deep water environment with semi-arid, brackish water and weak reduction, the paleoproductivity is high in arid, salt water, weak reduction-weak oxidation semi-deep water environment. [Conclusions] Based on the analysis of total organic carbon content and paleoenvironmental conditions, it is considered that the accumulation of organic matter is mainly controlled by paleoproductivity, and the reduction environment with high salinity contributes to the preservation of organic matter, the high-quality source rocks are developed in the upper and upper cycles of the middle sweet spot, while the lower cycles of the middle sweet spot are relatively poor.
[Objective] Xinying Bay, Hainan Province, retains a relatively complete sedimentary record of marine stratigraphy since the Pleistocene. Due to its closure and stability, it serves as a good window to reflect the paleoenvironmental changes since the Pleistocene in the Northern South China Sea. [Methods] Based on the analysis of whole rock major elements and Sr-Nd isotopes, the source of sediment material and the evolution of paleoclimate and paleoclimate in this area since Pleistocene were reconstructed, and the driving mechanism was discussed. [Results and Discussions] The borehole has three relatively obvious sections from bottom to top. The bottom U1 section has a relatively low εNd(0) value and a relatively high 86Sr/87Sr value. The middle U2 section has relatively high ratios of Al/Ti, K/Ti, Fe/Ti, and Mg/Ti. The results of provenance analysis show that the sediments of the borehole come from the intermediate source area, and the U1 section contains more older sedimentary materials, and the Sr-Nd isotope ratio is similar to that of the Red river sediments, while the U2 and U3 sections are similar to the Cretaceous-Permian feldspar granite in Hainan Island. The paleoenvironmental analysis shows that this region has experienced changes from dry cold to warm wet, and then to dry cold since the Pleistocene. [Conclusions] The sedimentary period of section U1 corresponds to the coldest MIS16 period in the Northern Hemisphere, which combined with previous chronological studies, and the dry and cold climate and relatively low sea level enable the clastic sediments of the Indochina continent to be transported to Xinying Bay. Then the East Asian summer monsoon strengthened, and the climate changed from cold and dry to warm and humid. As a result, the source area of U2 section was dominated by granitic rocks in Hainan Island because the sea level raised. The U3 section has undergone regional tectonic uplift, and the sedimentary source area is dominated by granite in the island.
Abstract: [Objective] The Late Triassic is a crucial period for the Mesozoic Qiangtang Basin evolution. However, the previous researches concentrated on the sedimentology of the Upper Triassic strata are rare in Qiangtang Basin, which is not conducive to elaborately analyzing the characterization of Late Triassic sedimentary evolution and predicting the distribution of source and reservoir rocks. [Methods] Based on the measured section, we synthesized the thin section, grain size of detrital particle and typical primary sedimentary structure to identify the sedimentary facies of the Jiapila, Bolila and Bagong Formations in the Jiangai Darina section and then establish the Late Triassic sedimentary evolution model in the central Qiangtang Basin. In addition, the whole-rock and clay minerals, physical properties, and total organic carbon (TOC) contents of sandstone and mudstone samples were analyzed to evaluate the characteristics of source and reservoir rocks. [Results] (1) In the Jiangai Darina section, the sedimentary facies of the Upper Triassic strata have experienced the evolution of the fan-delta facies→barrier-free coastal facies→carbonate ramp facies→neritic shelf facies→delta facies upward, and can be identified ten subfacies and eight microfacies totally. (2) The Upper Triassic strata in the study area constitute an upward deepening transgressive succession and then shallower regressive succession. Among them, the transgressive succession is mainly composed of the Jiapila and Bolila Formations, while the regressive succession is mianly composed of the Bagong Formation. (3) The sandstone samples from the Jiapila and Bagong Formations are ultra-low porosity and ultra-low permeability reservoir with secondary pores primarily. The mudstone samples of the Bagong Formation from the Jiangai Darina section are poor source rocks and non source rocks, while become better to north (Woruoshan section). We inferred that the depression between Jiangai Darina and Woruoshan may develop well source rocks and have a good exploration prospect based on the latest tectono-lithofacies paleogeographic data, but it still need to be confirmed. [Conclusion] These results would provide a valuable reference for the researches of Late Triassic sedimentary-tectonic evolution and oil and gas resource evaluation in Qiangtang Basin.
[Objective] Manganese (Mn), as a typical redox-sensitive metal element, shows a strong correlation between its enrichment in sediments and the redox conditions of the bottom water in basin. The western Hunan region hosts extensive Neoproterozoic marine sedimentary manganese deposits. A detailed study of the sedimentary redox conditions of these manganese deposits aids in elucidating their metallogenic mechanisms, constraining the marine manganese cycling during the mineralization period, and providing theoretical support for regional mineralization potential assessments. [Methods] This study involved mineralogical, geochemical, and inorganic carbon isotope analyses of 16 manganese ore samples of varying grades from the Datangpo Formation of the the Nanhua System from the Minle area in western Hunan. [Results] Mineralogical and carbon isotope analyses reveal that high-grade (MnO>20%) and medium-grade (10
【Objective】The trace element records of modern and ancient dunes in the southern part of the Mu Us Desert provide environmental information on their weathering, transportation and deposition processes. The aim of this study is to gain a deeper understanding of the sediment sources and climate environment in this area.【Methods】 Samples of modern and ancient dunes in the southern Mu Us Desert were collected, and the content characteristics and correlations of 14 trace elements including phosphorus (P), lead (Pb), and rubidium (Rb) were analyzed to explore the differences in trace element contents and spatial distribution characteristics among different types of dunes.【Results】 (1) The trace elements in modern and ancient dunes are mainly barium (Ba), strontium (Sr), and phosphorus (P), while the contents of arsenic (As), niobium (Nb), and copper (Cu) are relatively low.Their distribution patterns show certain regional characteristics. (2) The trace element contents in fixed dunes are significantly higher than those in mobile dunes, mainly due to the nature of the dunes and vegetation coverage; while the trace element contents in ancient dunes are higher than those in modern dunes, mainly influenced by sedimentary history, climate change, and special geomorphic positions. (3) The ratios of Sr/Cu, Rb/Sr, and Sr/Ba in modern and ancient dunes are comparable, indicating that they were formed in similar sedimentary environments.【Conclusion】 There are certain similarities and differences in the trace element contents of modern and ancient dunes and different types of dunes. The changes in trace element contents in ancient dunes can provide clues to the sources of modern dunes to a certain extent. The ratios of trace elements in modern and ancient dunes have certain implications for climate and environmental conditions.
[Objective] The beach facies dolomite reservoir of the Middle Permian Qixia Formation in the central Sichuan Basin exhibits significant potential for oil and gas exploration, but the systematic study on diagenetic sequence and pore evolution is relatively weak. [Methods] The petrological characteristics and pore genesis of the Qixia Formation were investigated through core observation, thin section analysis, cathodoluminescence examination, and image recognition techniques. This study aims to delineate diagenetic variations and pore evolution among different lithologies. [Results] In the Gaoshiti area, four types of rocks are identified within the Qixia Formation: micrite limestones, micrite grain limestones, sparry grain limestone, and residual grain dolostone. Four types of Reservoir space are observed: intergranular dissolved pores, intragranular dissolved pores, fractures and vugs. Each rock type has experienced distinct diagenesis: type of dissolution and its intensity vary across different lithologies. The two kinds of granular limestone are mainly dissolved by meteoric water, and the residual granular dolomite is more strongly dissolved by meteoric water, and on this basis, dolomitization and burial period dissolution occur. Recrystallization is more pronounced in residual grain dolomite whereas compaction and pressure dissolution is more evident in micrite grain limestone. The key diagenesis and stages influencing pore development vary among different types of rock: the pores of the two types of granular limestone are mainly formed by quasi-syngenetic dissolution, and then partially destroyed by compaction and cementation during the burial stage. The dissolution and dolomitization in the para-syngenetic stage are the key to the formation and preservation of the pores of the residual granular dolomites, while the dissolution and tectonic fracture in the burial stage are beneficial supplement, and the cementation in the shallow burial stage destroys the pores. [Conclusion] The difference of diagenesis caused the difference of pore evolution and formed four lithologies with decreasing pore development degree: Residual grain dolostone (plane porosity: 2.10 %), sparry grain limestone (plane porosity: 1.24 %), micrite grain limestone (plane porosity: 0.41 %), and micrite limestone (pyknotic).
The study of fine-grained sediment transport mechanisms is an important part of the "source-to-sink" system theory of fine-grained sediments, which is significant for restoring sedimentary environments, understanding the distribution of fine-grained sediments, and predicting unconventional oil and gas resources. Due to the fine granularity of fine-grained sediments, which makes them difficult to observe, and the rich variety of transport mechanisms, each corresponding to different sedimentary structures, there is currently a lack of summary on the characteristics of fine-grained sediment transport mechanisms. This paper synthesizes current research findings and systematically organizes the transport mechanisms and characteristics of fine-grained sediments, dividing them into three major categories: physical transport, chemical transport, and biological transport. Physical transport includes river flow, wind, bottom flow, plume flow and six types of gravity flow transport, triggered by wind, tides, earthquakes, floods, storms, and volcanic eruptions; dissolved substances such as clay minerals, dissolved organic carbon, carbonate minerals, and iron minerals, which are transported in colloidal solutions or true solutions, are influenced by environmental factors such as pH value, Eh value, temperature, pressure, ion concentration, or charge, and can be transported chemically; vertical upward transport, transport near the sediment-water interface, and comprehensive transport by multiple types of organisms are the three forms of biological transport of fine-grained sediments. The purpose of this paper is to clarify the transportation methods of fine-grained sediments, enhance the understanding of the transportation mechanisms of fine-grained sediments, and thus promote the development of fine-grained sedimentology theory. It provides a solid theoretical foundation and scientific basis for clarifying the distribution characteristics of fine-grained sedimentary strata and predicting the distribution of unconventional oil and gas resources.
Tidal forces have an important influence on the form and scale of Marine shelf deltas and the development and evolution of branch channels. The quantitative control mechanism of different amplitude tidal ranges on the dam body and branch channels of continental shelf deltas is a hot scientific issue. In this paper, a single factor control method is used to analyze the evolution of the key geologic bodies in the continental shelf delta under different tidal ranges by using Delft 3D hydrodynamic simulation software to set up four control groups: no, small, medium and spring difference. The experimental results show that the downcut depth and width of the branch channel decrease with the increase of the flow distance when there is no tidal effect. When tidal action is added, the number of distributary channels decreases with the increase of tidal range, but the downcut degree and width of distributary channels increase. The width-to-depth ratio of the branch channel ranges from 2 to 10 when there is no tidal action, and decreases to 0 when there is low tidal range. Under the influence of middle tidal range and spring tidal range, the width-to-depth ratio of the branch channel corresponds to 0 to 3 and 2 to 4 respectively. The results show that tidal action is beneficial to increase the broad-to-thickness ratio of sand body, and the delta morphology changes more stable with the increase of tidal range. The number of branch channels in the delta under the influence of tides decreases significantly, which is mainly due to the periodic influx and retreat of tides in the lateral direction, which promotes the formation of lateral channels and tidal channels. Under the influence of middle-spring difference, the lateral migration distance of the branch channel is shorter, the branch channel is more stable, and the dam body is more isolated from each other, which provides an important reference for reservoir configuration analysis of similar underground sediments.
During the Chang 7 period of the Yanchang Formation, Late Triassic in Ordos Basin, a set of continuously traceable shale was deposited, and the shale is currently the main stratigraphic strata for unconventional oil exploration and development. The shale oil reservoir at Chang 73 sub-member has features of fast lateral changing fast and vertical stacking, which make problems in practice such as unclear reservoir distribution, high exploration difficulty, and low drilling rate, etc. In order to clarify the distribution pattern of laminated-type shale oil reservoirs, we propose a shale oil reservoir distribution pattern controlled by seismic reflection characteristics of progradations and sedimentary paleogeomorphology by using seismic, geological, and logging data deeply. Firstly, through the latest 3D seismic data, the stratigraphic dip flipping method is used to recover sedimentary paleogeomorphology. Then, we mark the seismic reflection of lacustrine mudstones and make seismic stratigraphic comparison and division, and propose a four stage progradational clinoforms and distribution patterns of shale oil reservoir based on the sedimentary paleogeomorphology. Finally, the deep-water gravity flow sedimentary process of the Chang 73 sub-member laminated shale oil reservoir is inferred from above conclusions, and the inspiration of this research for unconventional oil and gas exploration and development in the Ordos Basin is discussed.
[Objective]Distributive fluvial system (DFS) are widely developed in modern and ancient sedimentary strata and are important hydrocarbon reservoirs. Multiple DFS interacting with each other and evolving axial rivers may be developed in narrow, shallow, narrow lacustrine basin with low accommodation. [Methods]Reproduced the deposition process through flume simulation experiments, and used a high-precision 3D scanner with a self-developed program to visual analysis the deposition area in three dimensions, to clarify the stage-by-stage evolution characteristics of the DFS. [Results and Discussions]1) with the expansion of the DFS scale, the water flow on the surface of the DFS gradually aggregates, and the initial flow pattern is sheet flow, then evolves into unrestricted flow, and finally restricted flow; 2) as the basin can accommodate less space, the axial water flow in the basin gradually aggregates into axial river, and the axial river has a destructive effect on the two sides of the DFS and constantly breaks, and finally forms a Large-scale fluvial deposition; 3) When multiple DFS are developed in a narrow shallow lacustrine basin, the sedimentary sands are mainly concentrated at the DFS near the source and downstream of the axial river, and the longer the basin development time, the larger the scale of fluvial deposition. [Conclusions]This paper describes the developmental processes and sand body spreading patterns of multiple DFS and axial rivers developed in a narrow, shallow lacustrine basin with low accommodation and sufficient supply of material sources at the basin scale, which provides theoretical support for oil and gas exploration and the study of distributive fluvial system.
Abstract: [ Objective ] The Upper Paleozoic Yanghugou Formation to Taiyuan Formation in the northwestern margin of the Ordos Basin has a good prospect for oil and gas exploration. The strata are completely developed and continuous, with large thickness changes and various types of sedimentary facies. Defining the distribution characteristics of sand bodies and clarifying the law of sedimentary evolution directly affect the selection of preferred exploration zones for oil and gas. [ Method ] This paper takes the Yanghugou Formation to Taiyuan Formation in the northwestern margin of Ordos Basin as the target horizon. On the basis of previous studies, through typical field profile measurement, drilling core observation, paleocurrent direction analysis, logging data and test data analysis, the sedimentary environment and sedimentary facies type characteristics, sedimentary evolution and sedimentary model of the study area are studied.[ Result and conclusion ] The research shows that there are 19 lithofacies types and two sedimentary systems in the study area, including 4 sedimentary facies types, and 13 sedimentary microfacies are further divided. The Yanghugou Formation-Taiyuan Formation in the study area is mainly supplied by the two provenance systems of the Alxa ancient land in the northwest of the basin and the Yinshan ancient land in the northeast. The Dickinson triangle plot reveals that the tectonic background of the provenance area is dominated by the recycled orogenic belt. The characteristics of heavy mineral assemblages are clear. The northwestern margin of the basin has obvious affinity with the Alashan Group ( Ar3-Pt1 ), the Archean Jining Group ( Ar3 ), and the Wulashan Group ( Ar1-2 ). The ZTR index shows that the unstable minerals gradually decrease from north to south ; the analysis of paleocurrent direction also reflects the material sources from northwest to southeast and from northeast to southwest.On the basis of the above provenance analysis, paleo-sedimentary environment evolution and sedimentary facies type characteristics, it is clear that the main body of Yanghugou Formation-Taiyuan Formation in the study area is the coexistence stage of sea and land. During the sedimentary period of Yanghugou Formation, under the background of the revival of Helan aulacogen and the backlog of north-south tectonics, the sea water enters rapidly. The whole study area is controlled by the delta-clastic coastal sedimentary system. The northern source supply is sufficient, resulting in the development of tidal-controlled delta deposits in the north. Affected by tides and waves, tidal flat-barrier island-Desalination of lagoons-shelf sedimentary microfacies are developed in the south. During the deposition period of the Taiyuan Formation, the crust continued to sink and seawater invaded. During this period, the basin became the most widely distributed period of the sea area. The sedimentary environment was basically similar to that of the Yanghugou Formation. The overall performance was the coexistence of tidal-controlled delta, tidal flat, Desalination of lagoons-barrier island sedimentary environment, and the erosion range in the northern region was relatively reduced, the source supply continued to increase, and the tidal-controlled delta range extended wider to the south.
Abstract:[Significance] The study of the provenance of fine-grained sedimentary rocks is a crucial first step in the "source-to-sink" system theory of fine-grained sedimentary rocks. It is of great importance for restoring the ancient environment, understanding the formation mechanism of fine-grained sedimentary rocks, and predicting the distribution of unconventional oil and gas resources. Fine-grained sedimentary rocks are characterized by small particle size, complex composition, and difficulty in observation and research, with different material components corresponding to a variety of sources and origins. A review of the existing research results at home and abroad shows that there is currently a lack of systematic organization and summary of research outcomes regarding the provenance and origins of fine-grained sedimentary materials.[Progress] This paper synthesizes current research findings and categorizes the sources of fine-grained sedimentary rocks into three major types: terrigenous, endogenic, and volcanic-hydrothermal. It provides an in-depth summary and conclusion on the common sources and origins of fine-grained sediments, pointing out: (1) Clay minerals are of terrigenous origin, authigenic transformation from other minerals, transformation between clay minerals, hydrolysis of submarine volcanic materials, and biogenic mediation by extracellular polymeric substances; (2) Quartz mainly originates from the weathering of terrigenous materials, intra-basin biological activity, devitrification of volcanic ash materials, and authigenic formation; (3) Feldspar originates from the weathering of terrigenous detritus, input from volcanic-hydrothermal activity, and recent studies have also indicated that feldspar can be formed through microbial chemical processes; (4) Carbonate minerals are primarily endogenic, formed through chemical, bio-chemical, biological, and transport-deposition processes within the basin, and the input of terrigenous and volcanic-hydrothermal materials not only directly provides carbonate minerals for fine-grained sedimentary rocks but also promotes the formation of carbonate minerals within the basin; (5) Pyrite is mainly formed by the two ore-forming elements, iron and sulfur, through dissimilatory iron reduction and iron shuttling mechanisms, microbial reduction, and thermogenic reduction of sulfate within the basin; (6) Organic matter can be divided into terrigenous vitrinite, inertinite, and some liptinite, as well as endogenic liptinite, zooclastic organic debris, and secondary organic matter. Future research on the provenance and origins of fine-grained sedimentary rocks will develop in a multidisciplinary and high-precision direction, and there is still an urgent need for a systematic approach suitable for the study of the provenance of fine-grained sedimentary rocks.[Conclusion] This paper aims to clarify the provenance and origins of fine-grained sedimentary rocks, enhance the understanding of the sources and formation mechanisms of fine-grained sediments, and thus promote the development of fine-grained sedimentology theory. It provides a solid theoretical foundation and scientific basis for identifying the distribution characteristics of fine-grained sedimentary strata and predicting the distribution of unconventional oil and gas resources.
[Significance] Peat bogs play an important role in the global carbon cycle as a depositional carrier of paleo-wildfire events and paleoclimate information. By systematically sorting out wildfires types in peat bogs and clarifying the academic terminology related to wildfire products such as charcoal, the carbon source and sink effects of wildfires in peat bogs will be discussed in this study, which will be useful for the study of the carbon cycle in deep time. [Progress] Wildfire product charcoal, approximately equivalent to the inertinite in coal, is a relatively stable carbon store of plant incomplete combustion residues, which can provide a record of wildfire activities in the geological history of millennia to billions of years. Changes in charcoal material composition (e.g., polysaccharides and lignin) and microstructure (e.g., cell wall homogenization) can reflect the temperature range of paleo-wildfires. Wildfire types can be recovered and atmospheric oxygen content can be constrained using inertinite reflectance and inertinite content. The impacts of wildfires on the global carbon cycle include both short-term carbon source and long-term carbon sink effects. Wildfires lead to direct large carbon emissions and carbon release from deep peat burning. However, wildfire-driven persistent changes in soil microorganisms, aggregates, and organic matter can directly offset some of the carbon losses, and charcoal provides a stable carbon store. [Conclusions and Prospects] Based on the carbon cycle model of peatland under normal burial conditions, the influence factors of wildfire, soil aggregates, fungi and bacteria were introduced to propose a post-fire peatland carbon cycle model. Using the inertinite wildfire genesis and greenhouse gas emission models, and taking the carbon emission and carbon storage of wildfires in early Cretaceous peat (coal-forming) bogs in Northeast China as an example, the results show that the long-term (million-year time scale) carbon sinks of forest vegetation growth and peatland are fully capable of neutralizing the short-term (year time scale) carbon source effect brought by wildfires. In the future, when evaluating the deep-time carbon cycle response to wildfires, it is necessary to take into account the length of the time period and wildfires intensity, and improve the understanding of climate change and environmental evolution caused by wildfire in order to promote the in-depth integration of deep-time and present-day climate change and carbon cycle research.
Abstract (Objective) In marine strata of the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (T-OAE), the widespread siderites are believed to result from the low sulfate concentration and increased terrestrial iron supply. Similar large amount of siderites were also reported in paleolakes in the same period. However, the mechanism of lacustrine siderite and its connection with the T-OAE remain unexplored, which is crucial to better comprehend the lacustrine biogeochemical cycling in early Toarcian. (Method) Mineralogical and carbon isotope geochemical analyses were performed on the siderite samples from the lacustrine Anya section of the Ordos paleolake. By integrating major and trace element data, we investigated the sources of iron and carbon, as well as the sedimentary environment. This allowed us to explore the formation mechanism of siderites under the T-OAE climatic change. (Result) The coexistence of pyrites and siderites was observed under scanning electron microscopy. The values of inorganic carbon isotopes(δ13Ccarb) vary from ?11.25 to +16.32 ‰, and the range of organic carbon isotope(δ13Corg) values is from ?32.03 to +14.33 ‰. The rare earth elements (REEs) exhibited an enrichment of light REEs and the depletion of heavy REEs, with Eu anomalies ranging from 0.69 to 0.85. (Conclusion) The iron source of the Anya siderites is derived from terrestrial inputs. Carbon involved in siderite formation included HCO3- produced via the methanogenesis, as well as carbon released from organic matter decomposition and the methane aerobic oxidation, either bacterially in the suboxic zone, or archaeally below oxic-anoxic interface right after methane production. The pore fluids during siderite formation was suboxic to anoxic environment. During the T-OAE, intensified continental weathering and increased surface runoff input fluxed abundant iron ions into lake basins. The widespread anoxia, abundant organic matter content, and low sulfate concentrations in the lakes created favorable conditions for siderites, leading to the extensive siderite depositions. Future work is needed to further verify whether such T-OAE-related siderites is a regional influence or a worldwide phenomenon.
[Objective] To understand the distribution patterns of Cretaceous sand bodies in the eastern depression of the Doseo Basin, this study employs physical sedimentation simulation techniques. An experimental setup with a movable baseboard was designed to investigate the evolution mechanisms of the channel-lobe system in the study area and to develop an effective regional sedimentary model, providing theoretical support for future favorable zone predictions. [Methods] Building on previous research on lobe development and evolution and channel classification [17], this study introduces a new classification method for lobes. Lobes are categorized into four types: agglomerative, superimposed, erosional, and amalgamated. Additionally, to accurately describe the development features and evolution of each lobe type, the study further analyzes the internal structures of lobes and identifies various constituent units. [Results and Discussions] (1) A consistent overlapping relationship exists between channels and lobes, where the migration, evolution, or disappearance of channels leads to the formation of new lobes. (2) Within the channel-lobe system, three main evolution mechanisms are driven by hydrodynamic strength: erosion of existing lobes, formation of lobes dominated by sandy deposition, and formation of mud layers dominated by fine-grained deposition. (3) The characteristics of channels determine the type of lobe development, while lobe morphology is influenced by factors such as sedimentary slope, tectonic activity, base level, and sediment source conditions. (4) The connectivity of sand bodies is affected by the constituent units of lobes, their contact relationships, lobe properties, and the types of lobe complexes. Later channel evolution can improve sand body connectivity to some extent. (5) The eastern depression of the Doseo Basin exhibits two sedimentary models: deep-water and shallow-water delta systems. In the deep-water delta model, the channel evolution area is larger, and connectivity improvements are more pronounced. In contrast, the shallow-water delta model features larger lobe deposition areas and wider planar distribution of lobes. [Conclusion] The new lobe classification method and the channel-lobe system evolution mechanism are applicable to the study of sand body connectivity and sedimentary models in the study area, and they are expected to be widely used in future delta sedimentary simulation research.
Abstract: [Objective] In order to define the high-quality reservoir development model of Xu3 Member in the source rock stratum, which is the tight sandstone gas exploration in the Xu3 Member of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan Depression to provide theoretical guidance.[Methods] The data of core, thin section, scanning electron microscope, fluid inclusion, situ stable carbon and oxygen isotopes, porosity and permeability are integrated, and based on the basic characteristics of Xu3 Member tight sandstone reservoirs in Western Sichuan Depression and the types of diagenesis, the heterogeneity of the reservoirs and the development model of high-quality reservoirs are further analyzed systematically. [Results and Discussions] It was found that mainly lithic quartz sandstone and litharenite sandstone were developed in Xu3 Member, and the reservoir space was mainly composed of intragranular dissolution pore and fracture, with porosity <7% and permeability <1mD. So the sandstone reservoirs could be divided into types of intragranular dissolution pore and fracture- intragranular dissolution pore. The diagenesis of the Xu3 Member sandstones included compaction, cementation and dissolution, and experienced early humic acid, middle organic acid and late hydrothermal fluids during the evolution process. In addition, two types of vertical sedimentary cycle of sandstone with sandstone and sandstone with mudstone had been identified in the Xu3 Member. [Conclusions] The results indicated that the tight sandstone was altered by the early humic acid and middle organic acid continuously via the intergranular pore throat and fracture and in favour of reservoir formation. However, the late hydrothermal fluid just acted in the late large scale fracture and had insignificant effect on the reservoir quality. In addition, the high-quality reservoir of the sandstone with sandstone vertical sedimentary cycle mainly develops in the lower part of the cycle which characterized by relatively coarse-grain, but the high-quality reservoir of the sandstone with mudstone vertical sedimentary cycle mainly develops in the lower part of the cycle with relatively coarse-grain, and the upper part of the cycle which adjacent to the mudstone.
[Objective] The Danxia strata, a representative of Cretaceous continental red beds, offers key insights into red bed sedimentation and Cretaceous geological events through its climate signals. [Methods] This study examines fine-grained clastic rocks from the second and fourth members of the Changba Formation and the Jinshiyan Member of the Danxia Formation in the Upper Cretaceous Danxia Basin. Sedimentology and elemental geochemistry etc. were used to explore the sedimentary environment and paleoclimate significance during key Late Cretaceous stages (Cenomanian, Turonian, Campanian). [Results and Discussions] The results indicate that the fine-grained clastic rocks of these formations were deposited during a warm and humid climate phase, with suboxic to oxic water conditions. The water bodies were predominantly brackish, while localized high-salinity brackish and low oxygen environments (e.g., the fourth member of the Changba Formation) were associated with lake shrinkage and climatic aridification. Water depth variations exhibited trends of initial contraction followed by expansion, gradual contraction, and initial expansion followed by contraction, which align with the changes in sedimentary facies and environment. [Conclusions] The Upper Cretaceous terrestrial sedimentary records of the Danxia Basin illustrate the climatic evolution of intermontane basins, shaped by global climate patterns of the Late Cretaceous, as well as by significant influences from local topographic and geomorphic features.
[Objective] The Taiyuan Formation of Permian system in Ordos Basin has the characteristics of large thickness, wide distribution and rich types of oil and gas resources, showing great exploration potential. At present, the study of this formation is mainly concentrated in the eastern part of the basin, while the exploration and study of Taiyuan Formation in the western part of the basin need to be further discussed due to the complex and variable tectonic pattern and sedimentary evolution.[Methods] The detrital material source, tectonic setting and paleogeographic evolution of Taiyuan Formation in western Ordos Basin are systematically studied by means of outcrop observation, drilling sample collection, detrital zircon U-Pb dating and paleo-flow analysis. [Results] The sediments in the northeastern part of the study area (Group A) are mainly from the Yinshan orogenic belt under the collision-compressional tectonic background, with strong provenances. The delta plain, delta front, tidal sand ridge and tidal sand bar are successively developed in the middle of the basin. The sediments in the northwest (Group B) are derived from the Alxa block under the collisional compression and convergent orogenic tectonic background, and the delta plain, delta front and lagoon-tidal flat develop successively towards the middle of the basin. The sediments in the southern (Group D) area came from the North Qilian and North Qinling tectonic belts under the extension-subduction-collision tectonic environment of the Paleo-Tethyan Ocean. The central paleo-uplift of the Taiyuan Period was slow, the provenance-supply was weak, and the mainly developed barrier island-barrier tidal flat deposits. [Conclusions] The northern part of the study area is characterized by high uplift and strong provenance supply in the context of collision and convergence orogenic structures, and large tide-delta complex system, while the southern part is characterized by weak provenance supply in the context of tensile extension structures, and is dominated by tidal flat and lagoon. This study not only deepens the understanding of the sedimentary system and provenance supply mechanism in the western Ordos Basin, but also provides a new perspective and reference for the reconstruction of the tectono-sedimentary evolution process and paleogeographic pattern in the western Ordos Basin.
[Objective] A large number of trace fossils Thalassinoides developed in the Cambrian, Henan Province. By studying the morphology and distribution characteristics of different ichnospecies and analyzing their sedimentary environment controlling factors. [Methods] Based on lithology and ichnography, the morphology, size, disturbance depth and disturbance intensity of Thalassinoides in this area were combined with sedimentary environment parameters. [Results and Discussions] The dense network Thalassinoides suevicus features Y-shaped branches with enlarged intersections, develops in the intertidal zone where water is turbulent and oxygen is abundant.Sparse Thalassionides horizontalis Type 1, which is Y-shaped long branches with large diameters, is formed in the shallow water area in front of the oolitic beach with abundant oxygen and nutrients due to water turbulence. Thalassionides horizontalis Type 2, T-shaped short branches with smaller diamerters, occurs in deeper waters on the seaward side in front of the oolitic beach. The three-dimensional, boxed burrows of Thalassionides bacae, featuring vertical tubes, branches, and thick lining walls, developed in interbeach-confined seas and deep subtidal zones where oxygen and nutrients were deficient. [Conclusions] The variation in different ichnospecies and morphologies of Thalassinoides is controlled by factors such as water depth, water kinetic energy, nutrients and oxygen content of the sedimentary environment. The trace maker adopted different strategies to cope with the changing sedimentary environment.
[Objective] The formation of sedimentary systems within straits is intricately linked to the unique topographical constraints that influence both facies characteristics and sediment distribution patterns. While current research on shallow-water strait sedimentation focuses primarily on narrower straits (less than 50 km wide) dominated by tidal processes, wider straits present more complex dynamics. This study investigates how the Bohai Strait, a shallow strait with a width of 106 km, utilizes its unique topography to influence the distribution of modern sedimentary systems. [Methods] An extensive dataset of surface sediment grain sizes, combined with four shallow seismic profiles, was used to characterize the sedimentary environment. Additionally, a Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS) simulation was employed for winter (December 2020 – February 2021) to better understand the hydrodynamic processes influencing sediment dynamics within and surrounding the Bohai Strait. [Results] Our results reveal significant differences in sediment dynamics between the northern and southern parts of the strait. The northern region exhibits a high-energy environment dominated by erosion, while the southern region displays a lower-energy environment conducive to deposition. Surface sediment types vary spatially, with coarser grains predominating in the north and narrow regions, while finer grains are observed on both sides (east-west) and in the south. A large-scale, sandy flood-tidal delta appears around the Laotieshan Channel in the north. The asymmetric tidal currents flowing in and out of the channel are likely responsible for this feature, with no evidence of an ebb-tidal delta formation. In contrast, the southern part of the strait exhibits two distinct sedimentary systems:(1)Shandong Mud Wedge: This system lies along the Shandong Peninsula's coast, shaped by the substantial sediment supply from the Yellow River and the influence of coastal currents. (2)Scour Troughs and Sandy Tidal Deltas: These smaller features are attributed to the protective effect of islands present in the southern strait, combined with the abundant supply of fine-grained sediments. [Conclusions] This study highlights the critical role of the strait's complex topography of the confinement in shaping regional sediment transport dynamics and the resulting distribution of sedimentary systems.
Abstract: [Objective] The Ordovician Kukersite oil shales that composed almost exclusively of Gloeocapsomorpha prisca (G. prisca) alginite are an important set Paleozoic source rocks from Paleozoic around the planet, but they have only been sporadically detected and reported in the Tarim Basin in China. Therefore, rapid identification of G. prisca in source rocks is an important geochemical work. Kerogen can be used to trace the source rock quickly for its enrichment of the parent material of hydrocarbon generation. [Method] Thus the kerogen from Estonian oil shale was analyzed using sequential stepwise pyrolysis with 50 °C intervals from 310 °C to 610 °C to investigate its chemical constitutions. [Results and discussion] The results illustrated that the pyrolyzed hydrocarbons formed upon sequential stepwise pyrolysis are dominated by 5-n-alkyl-1,3-benzenediols probably reflect a major contribution of selectively preserved, highly resistant biomacromolecules from the outer cell walls of G. prisca. It is also characterized by high content of short-chain alkanes, but abnormal high carbon number (>nC29) n-alkane/enes appear at 560 ℃. Besides, the consistent formation of alkyl benzenes, alkyl thiophenes and alkyl ketones also appeared at the middle to high temperature points (460 ~ 560 ℃). All pyrolyzates have the characteristics of lower carbon number, alkyl side chains with a distinct distribution of weak odd-over-even carbon numbers. The extremely abundant and continuous generation of 5-n-alkyl-1,3-benzenediols and its homologues in the pyrolysis products can help to quickly identify whether the source rocks contained G. Prisca or not. In addition, the composition characteristics, product changes and product correlation of the pyrolyzates at different temperatures are helpful for the investigation of kerogen structure. The results of sequential stepwise pyrolysis suggested that the macromolecules of kerogen were formed mainly by polymerization of 5-n-alkyl-1,3-benzenediols in G. prisca. The units in polymer macromolecules including phenol rings, thiophene rings, and normal alkyl chains, are intermolecular connected by C-C and C-O bonds. [Conclusions] The distribution changes of different series of compounds obtained at different temperatures by sequential stepwise pyrolysis can be applied to other organic-rich oil shales, which may reveal the details of algal evolution and determine the various sources of organic matter of kerogen.
Abstract: [Objective] The Luojiawopeng Formation is a set of purplish red sand and gravel accumulation strata in the Lower Pleistocene Series in the southeastern margin of Songnen Plain. The clay mineral analysis of this formation is conducive to understanding the paleoclimate characteristics in this region and defining its stratigraphic age. [Methods] Whole rock geochemistry, XRD, SEM and HRTEM analysis of clay minerals in Luojiawopeng Formation were carried out to reveal the composition and transformation characteristics of clay minerals in this formation. Comparation were taken on the aspect of clay mineral composition, between the red clay in the Chinese Loess Plateau and Luojiawopeng Formation. [Results] The clay mineral composition of Luojiawopeng Formation is dominated by kaolinite (content of 57%~73%), followed by illite (ranging from 25% ~ 41%) and the content of biotite /vermiculite mixed layer minerals is the least (average 1%). Kaolinite shows pseudo hexagonal morphology, and high degree of euhedral and crystallinity indicate its authigenic origin, together with high illite crystallinity (average 0.55) and illite chemical index (average 0.50), together with high clay/quartz ratio all indicate intense weathering characteristic. The transformation process of clay minerals is illite → kaolinite and biotite → biotite /vermiculite mixed layer minerals → kaolinite, which is consistent with the significant kaolinization trend of constant element 4Si-M+-R2+ ternary diagram, combined with the high CIA value and hematite/goethite ratio of the formation, all indicates that this formation formed in a humid and hot climate environment with increasingly strong weathering. [Conclusions] It is speculated that the Luojiawopeng formation was formed in the humid and hot climate background, rahter than the moraine accumulation as previously reported, and the stratigraphic chronology of the formation may be in the humid and hot period when the East Asian summer monsoon prevailed before the early Pleistocene.
[Objective] The shale gas of the Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in the Sichuan Basin has good prospects for exploration and development. It is of great significance to reveal the characteristics of its sedimentary environment for the evaluation of shale gas resources in the Qiongzhusi Formation. [Methods] Taking the shale series of Qiongzhusi Formation in Chengjiaba section of northern Sichuan as the research object, based on detailed field geological survey, the whole rock X-ray diffraction and geochemical analysis were carried out, and the characteristic elements and ratio parameters were optimized to reveal the sedimentary paleoenvironment and conditions of organic-rich shale in Qiongzhusi Formation in northern Sichuan. [Results] (1) The first and second members of Qiongzhusi Formation are mainly gray-black or black mudstone and silty mudstone, with siliceous rock facies and siliceous shale facies, with horizontal bedding, which is a deep-water shelf facies. (2) The shale TOC content of Qiongzhusi Formation is relatively high, ranging from 0.22 % to 4.34 %, with an average of 2.68 %. (3) The geochemical characteristics of the elements show that the climate was warm and humid during the deposition of the black shale of the Qiongzhusi Formation, the paleoproductivity and deposition rate were high, and the water body was anoxic and highly retained. [Conclusions] It is considered that the formation of organic-rich shale in Qiongzhusi Formation is controlled by redox conditions, paleoproductivity, paleoclimate and deposition rate.
[Objective] There is a close relationship between the cathodoluminescence (CL) characteristics of carbonate minerals and their trace and rare earth element (REE) contents. This study aims to investigate the relationship between these factors. [Methods] Cathodoluminescence and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) were used to test carbonate rock samples from the Lower and Middle Ordovician on the southern margin of the Ordos Basin. Statistical methods and classification algorithms were applied to analyze the test data, and common REE indicators were used to evaluate the properties of diagenetic fluids. [Results] The study reveals that matrix dolomite exhibits weak to moderate red luminescence under cathodoluminescence, with both zoned and uniform luminescence. Dolomite cements, with high Mn and Fe contents, are often zoned or non-luminescent. ANOVA and Tukey's HSD post-hoc tests indicate that Mn, Fe, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb contents, and the Fe/Mn ratio significantly influence the cathodoluminescence of carbonate minerals. Non-luminescent and strongly luminescent groups are relatively easy to distinguish: non-luminescent minerals generally have Fe contents greater than 10,000 ppm or Mn contents less than 40 ppm. Additionally, the non-luminescent group with Fe contents over 10,000 ppm displays REE distribution patterns enriched in MREE, while the strongly luminescent group shows LREE depletion and low Fe/Mn ratios. Using comprehensive dimensionality-reduced parameters of trace and rare earth elements, in conjunction with Mn content, effectively distinguishes the extremely weakly luminescent, weakly luminescent, and moderately luminescent groups. The nature of diagenetic fluids during diagenesis impacts carbonate sediment composition, mineral content, and trace and rare earth element variations, directly influencing carbonate mineral cathodoluminescence. [Conclusion] By combining in situ trace element testing with various data processing methods, this study provides a more quantitative understanding of the impact of trace and rare earth element contents on cathodoluminescence intensity. These findings offer valuable insights for both domestic and international scholars studying the factors affecting cathodoluminescence.
The Ordovician Majiagou Formation in the southern Sulige gas field is mainly a karst reservoir with proved reserves of over 100 billion square meters of gas. In the process of development and production, the formation water is serious, the gas-water relationship is complicated, the gas-water distribution law and the main control factors are unclear, which restricts the natural gas production capacity release in this area to a large extent. Based on the analysis of formation water chemical characteristics, the formation environment of formation water is analyzed by using chemical parameters such as sodium chloride coefficient, desulfurization coefficient, sodium calcium coefficient, magnesium calcium coefficient and metamorphism coefficient, and then the gas-water distribution law is studied through the identification of single well water level, the correlation of well profile and the characterization of plane distribution characteristics. Finally, the main controlling factors of gas and water distribution are discussed in terms of source rock, reservoir heterogeneity and structure. The results show that the formation water in the southern part of the Sulige gas field has a relatively concentrated salinity distribution with an mean of 83598.7mg/L, a light acidic pH, and a CaCl2 water type. The formation water as a whole is characterized by low sodium chloride coefficient, low desulphurization coefficient, low magnesium calcium coefficient, low sodium calcium coefficient and high metamorphism coefficient, indicating that the formation is well sealed. It is beneficial to gas reservoir preservation, and the plane characteristics of each parameter are similar and controlled by karst reservoir. According to the genetic difference, spatial distribution and reservoir characteristics, the formation water is divided into water in the lower part of type I structure, isolated lensing water in type II structure and water retention in type III low permeability zone. The water in the lower part of type I structure mainly develops in the karst area and is controlled by the karst residual hill unit, and the water in type II lensing water is scattered in the plane, and the water in type III low permeability is difficult to identify due to the plane distribution of karst depressions and trenches. The distribution of formation water is controlled by three factors: source rock, karst reservoir heterogeneity and local structure of the same karst unit. The lack of hydrocarbon supply capacity of source rock is fundamental to the development of formation water bodies. The distribution pattern of gas and water is determined by the heterogeneity of karst reservoir, and the differentiation of gas and water is caused by local structure. The same karst unit has a unified gas-water contact.
[Objective] An suite of Neoproterozoic diabase dykes is extensively exposed in the Jinkouhe area, western Sichuan Province, offering crucial insights into the tectonic evolution of the western Yangtze Craton. These diabases bear key implication for understanding the early tectono-magmatic history of the Yangtze Craton and its relationship with the assembly and fragmentation of the Rodinia supercontinent. [Methods] SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronology and whole-rock geochemistry analyses were conducted on the Jinkouhe diabases. [Results] SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of the diabase samples yields an age of 823 ± 10 Ma (MSWD = 1.30, n = 10). The diabases are classified as tholeiitic basalt series, displaying Nb-Ta depletion and negative Eu anomalies. Their geochemical signatures are indicative of both island arc and intraplate basaltic affinities. [Conclusion] The Jinkouhe diabases are interpreted to may have been originated from partial melting of a spinel-garnet lherzolite mantle source, which was metasomatized by subduction-related melts. Together with regional geological data, it is proposed that these diabases were most likely formed within a post-collisional extensional setting, reflecting tectonic processes associated with the final amalgamation of the Yangtze Craton in the context of the Rodinia supercontinent assembly.
[Objective] In recent years, the exploration of new type of natural gas reservoirs in marine clastic rocks of Shiqiantan Formation in Shiqiantan Depression of Jundong Region has gained significant breakthroughs, but the depositional characteristics and patterns of Shiqiantan Formation are not clear, and the configuration of source and storage is not realized, which restricts the next step of exploration and deployment.[Methods] The sedimentary paleomorphology of Shiqiantan Formation was recovered on the basis of isochronous stratigraphic division and comparison, and different sedimentary phases were identified by combining seismic phases, continuous well sections and microscopic depositional features such as cores and thin sections, the evolutionary process of sedimentary system was constructed, and the sedimentary evolutionary model was established. [Results and Conclusions] The Shiqiantan Formationdevelops a complete three-stage stratigraphic sequence, which can be divided into the early transgression systems tract (ETST), the late transgression systems tract (LTST) and the highstand systems tract (HST) in combination with the paleogeomorphic slope folding. During the sedimentary period of the Shiqiantan Formation, the overall depression is a narrow and elongated sea trough running in a northwest southeast direction, with various types of ancient landforms such as rifted sea troughs, multi-level gentle slopes, fault controlled steep slopes, and eroded gullies. Identify sedimentary facies types such as nearshore underwater fans, fan deltas, slope fans, and basin floor fans through typical logging data, rock cores, and seismic facies characteristics. The ancient landforms have a significant controlling effect on the distribution of sedimentary facies. Fan deltas and nearshore underwater fans are mainly distributed near the southern fault controlled steep slope zone, while slope fans are mainly developed on the northern multi-level slope break gentle slope zone, and basin floor fans are mainly developed in the trough. The entire sedimentary process formed an evolutionary model of multi-stage "stacked tile style retrogradations" of submarine fan slope fan sedimentation under the background of rapid marine invasion and large-scale braided river delta sedimentation in HST. High quality mature source rocks are developed in the transgressive domain, and the basin floor fans and slope fans on the "source" and "source side" of the northern gentle slope zone can form a "finger shaped interaction" favorable source and reservoir configuration with high-quality marine source rocks, with superior storage conditions, making it a favorable target for the next step of hidden oil and gas exploration.
[Objective] The catastrophic failure of large submarine landslides can result in the deformation and destruction of thousands of square kilometers of seafloor, transporting hundreds to thousands of cubic kilometers of submarine sediments. This process dramatically reconstructs the seafloor topography of the continental shelf-slope region and has a profound impact on subsequent submarine sedimentation processes. [Methods] The topographic features of different large submarine landslides were qualitatively described using multibeam bathymetric and seismic reflection data, and the key geometric parameters of the submarine landslide top surface, such as area and volume, were quantitatively characterized. Based on the scale, morphological features, and formation mechanisms of the associated reliefs on the submarine landslide top surface, these landslides were separated into three categories: head evacuation zone, locally negative accommodation associated with internal fault systems, and locally negative accommodation associated with internal deformation blocks. The mechanisms of the three types of negative accommodation on the subsequent turbidity current system are then discussed separately. [Results] Firstly, the head evacuation zone is typically associated with hundreds to thousands of square kilometers of negative accommodation, which acts as a "funnel" during sediment transport along the continental margin, effectively capturing and concentrating subsequent turbidity currents while enhancing the transport efficiency of gravel and coarse sand and playing a crucial role in the accumulation of marine organic matter. Secondly, the striped negative accommodation associated with internal fault systems and the irregular negative accommodation associated with internal deformation blocks can regulate the sedimentation dynamics of subsequent turbidity currents, such as constraining flow direction, enhancing erosion intensity, and forcing channels to avulse. Finally, the negative accommodations associated with the submarine landslide top surface may produce synergistic effects, influencing the sediment filling and evolution of sedimentary basins and the distribution of sedimentary centers over millions of years. [Conclusion] The investigation of the morphological characteristics of submarine landslide top surfaces and their controlling effects on the subsequent turbidity currents sedimentary dynamic process can provide key geological information for clarifying the transport process of marginal sediments, identifying the distribution of sand-rich reservoirs in deep-sea sedimentary basins, and predicting the development range of catastrophic turbidity currents.
The existing body of research on bauxite oil and gas reservoirs is limited in scope, both in terms of its domestic and international dimensions. The discovery of a bauxite reservoir with high-yield industrial gas flow in the Taiyuan Formation in the Longdong area, southwestern Ordos Basin, represents a significant advancement in the exploration of bauxite gas reservoirs. Additionally, the recent identification of bauxite strata in the Benxi Formation in the Linxing area of the northeastern margin of the basin, through the test of actual production, suggests promising exploration potential. [Objective] In order to further explore the potential of natural gas exploration and the development of bauxite series in the Linxing area, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the fundamental geological characteristics of the sedimentary environment, the composition of the rock minerals, the characteristics of the reservoir pores and the structure of the bauxite series. In addition, it is essential to identify the factors that control the development of bauxite in the study area. It would be beneficial to ascertain which areas are most conducive to such activity. [Methods] In this study, a comprehensive analysis was conducted on the sedimentary environment, reservoir characteristics and sedimentary model of the Benxi Formation bauxite rock series in the Linxing area. This analysis was based on a synthesis of logging and seismic data, X-ray diffraction, casting thin sections, scanning electron microscopy, major and trace elements, high-pressure mercury injection, N2, CO2 adsorption and conventional physical properties, and other experimental methods. [Results and Discussions] The bauxite rock series in the study area is characterised by a high concentration of diaspore and clay minerals, exhibiting a distinct three-stage vertical structure. The lower portion is rich in iron, the middle contains a higher aluminium content, and the upper section has a lower iron concentration. The pore types observed in the bauxite reservoir include dissolution pores, intercrystalline pores, organic pores and microfractures. The dissolution pore represents the predominant reservoir type, with pore sizes typically ranging between 2 and 50 nm. The sorting and connectivity of the pores are relatively good. The average porosity is 3.64%, with an average permeability of 7.24 × 10-3 μm2. [Conclusions] A comprehensive analysis indicates that the development thickness of bauxite rock series is contingent upon the sedimentary environment and karst paleogeomorphology. The shallow water sedimentary environment, characterised by high temperatures and humidity, low oxygen levels and alternating marine and terrestrial conditions, provides optimal conditions for the formation and preservation of bauxite rock series. The slope, or buried pit, represents a crucial area for the exploration and development of bauxite rock series. This understanding is anticipated to provide a geological foundation for the exploration and development of natural gas in bauxite rock series with comparable geological backgrounds in this region.
[Objective] To clarify whether the western edge of the Kaijiang-Liangping Trough and the eastern edge of the Pengxi-Wusheng intra-platform depression intersect in the north during the Late Permian Changxing Early Triassic Feixianguan period in northwest Sichuan, the sedimentary facies distribution of each layer in the region was constructed, and the sedimentary filling evolution process was analyzed. [Methods] Based on the latest drilling, field outcrop, and seismic data, this article systematically analyzes the distribution of lithofacies and paleogeography during the Changxing-Feixianguan period, as well as the evolution process of sedimentary filling, on the basis of stratigraphic and sedimentary facies division and comparison. [Results and Discussions] The intersection area of Changxing Formation and Feixianguan Formation can identify six types of sedimentary facies: shelf basin, slope, platform edge, open platform, restricted platform, and evaporative platform; Based on the sedimentary records of the front slope of the platform, it is clear that the western edge of the Kaijiang-Liangping trough and the eastern edge of the Pengxi-Wusheng intra-platform depression are merged to form a unified platform edge belt in the northwest Sichuan Majiaoba Shangsi area. The platform edge belt and the front slope show a northwest pointing interdistribution, rather than a smooth belt distribution; The intersection area of the two troughs in the Changxing Formation presents a sedimentary pattern of two troughs sandwiched by a platform from southwest to northeast. In the northwest direction of the platform edge zone, there are finger shaped distribution of platform edge biological reefs and shoals, which have the characteristics of developing bioclastic shoals in the first section of the platform edge zone and developing biological reefs and shoals in the second section of the platform edge zone; The sedimentary period of the first and second members of the Feixianguan Formation inherited the overall sedimentary pattern of the Changxing period. However, in the early stage of the Feixianguan Formation, only local platform edge oolitic beaches were formed due to sea flooding. In the late stage of the Feixianguan Formation to the Feixianguan Formation, platform edge oolitic beaches gradually developed and expanded in scope, and overall had the characteristic of eastward migration. The slope in front of the platform was prone to sliding and sedimentation; During the sedimentation period of the Feisan section, the sea trough gradually filled up, and the finger shaped platform edge zone disappeared, leaving only a small amount of lagoons and only developing ooid shoals in the Majiaoba area; The Feisi section deposited its entire area and filled it up, forming an evaporative platform facies. The platform margin zone in this region did not migrate northwestward along the finger shaped platform margin zone, but rather exhibited eastward migration characteristics. [Conclusions] The determination of Changxing-Feixianguan connectivity and the definition of five sedimentary filling evolution stages in Kaijiang-Liangping Trough and Pengxi-Wusheng intra-platform depression supplemented the understanding of sedimentary pattern and sedimentary filling evolution process in the intersection area of Changxing-Feixianguan trough, and formed a unique example of sedimentary filling evolution sequence in the transition area connected by two rows of cross-platform edge belts in the same period. It also provides ideas and references for oil and gas exploration in this area.
Abstract: [Objective] The provenance composition and evolution of the Lower Jurassic Badaowan Formation and Sangonghe Formation in the Dongdaohaizi Sag of the Junggar Basin are of great significance for the early Jurassic tectonic activity of the Karamaili orogenic belt in the provenance area. [Methods] Based on the composition of sandstone clasts, rare earth elements and detrital zircon U-Pb ages, the provenance characteristics and evolution process of the Badaowan Formation and Sangonghe Formation were analyzed. [Results] The results show that the Lower Jurassic sandstone in the study area is dominated by with an average content of 37.7% of rock fragments in thin sections, mainly tuff fragments and basalt fragments, and a small amount of metamorphic rock fragments.The Badaowan Formation shows no obvious differentiation between light (LREE) and heavy rare earth (HREE), while the Sangonghe Formation has the characteristics of slight LREE enrichment and HREE loss, and the age of detrital zircons in the Badaowan Formation mainly falls in the Permian and Devonian periods, while the age data of the Sangonghe Formation is mainly from the Carboniferous period, and there are obvious differences in age composition.[Conclusion] The analysis by synthesis of provenance characteristics, the parent rocks in the Lower Jurassic source area of the Dongdaohaizi Sag are dominated by medium-acid magmatic rocks and mafic magmatic rocks, and the tectonic background is mainly the transitional recycled zone of the recirculating orogenic belt, which is consistent with the mixed source formed by ocean-land subduction in the eastern Karamaili orogenic belt and the Karamaili orogenic belt after the closure of the ocean basin. The provenance of the Badaowan Formation to the Sangonghe Formation in the Dongdaohaizi Sag has undergone a conversion from the main source of oceanic crustal subduction to the closed source of the Carboniferous ocean-land, which has a good response to the increasing uplift process of the Early Jurassic of the Karamaili Orogenic Belt, indicating the continuous uplift and differential denudation process of the Early Jurassic of the Karamaili Orogenic Belt.
[Objective] Organisms are extremely responsive to the environments in which they live, and the traces they create are the result of interactions between organisms and environments, and to a certain extent reflect the characteristics of the depositional environment. Biological sedimentary structures are a powerful tool in understanding the ecology and depositional processes of modern coastal sedimentary environments. [Methods]The composition and distribution characteristics of modern biogenic traces in the tidal flat environments of the Pearl River Delta were studied by field observations and 3D reconstruction. [Results]The following key understanding was obtained after the study: the distribution of organisms in the supratidal, intertidal and subtidal varies greatly, and the biological traces are mainly distributed in the intertidal zone. In the supratidal zone, there are mainly Ligia oceanica and Uca arcuata, and the main traces created are Uca arcuata level feeding traces, excretion traces, trackways, and intra-layer I-shape dwelling burrows. Biological traces in the intertidal mud flat environment mainly include feeding, excretion, and trackways and I-shaped dwelling burrows at the level of Uca arcuata; crawling traces and Y-, U-, and I-shaped dwelling burrows at the level of Periophthalmus cantonensis; trackways and I- and Y-shaped dwelling burrows at the level of Orisarma dehaani. Biological traces in the mixed intertidal flat environment mainly include excretion traces and intra-layer I-, U-, and Y-shaped dwelling burrows of Perinereis aibuhitensis, Y-, U-, and I-shaped dwelling burrows of Ligia oceanica, and crawling traces of Vittina coromandeliana and Neritina pulligera. Biological traces in the sandy intertidal environment include feeding and excretion traces at the level of Ocypode cordimand and intra-layer I-shaped dwelling traces. The subtidal environment was not accessible for observation and no biological traces were found. [Conclusions] The research work on modern intertidal biological traces in the Pearl River Delta has not only supplemented the modern sedimentological data on tidal flat environments in the Pearl River Delta, but also provided modern empirical evidence for paleohermitology and paleoenvironmental reconstruction.
Abstract: [Objective] The abundant ichnofossils were developed in the Pinghu Formation and Baoshi Formation of the Eocene in Pingbei area, Xihu Sag. It is of practical significance for the division of sedimentary system in Xihu Sag to study the characteristics and distribution of its ichnofabrics and its indication of sedimentary environment. [Methods] Through core observations, the study identified ichnofossils and ichnofabrics in the Pingbei Area. The IDIPA technique was employed to objectively quantify ichnofossil abundance and accurately determine both the bioturbation index and the ichnofabric index. By integrating these findings with ichnological indices, this study summarizes the characteristics of the planar distribution and vertical evolution of ichnofabric in the study area. [Results and Discussions] (1) The research identified 6 ichnogenera of ichnofossils and divided them into 4 types of ichnofabrics, including Planolites ichnofabric, Thalassinoides ichnofabric, Teichichnus ichnofabric and Beaconites ichnofabric. (2) The study area features a high landform in the northwest and a low landform in the southeast. Seawater invades from south to north, and the sedimentary environment transitions from the subtidal zone to the intertidal zone, and finally to the supratidal zone, where the highest terrain is located in the northwest. The evolution pattern of the corresponding ichnofabrics follows the sequence Thalassinoides → Teichichnus → Planolites → Beaconites, consistent with the results of regional sedimentary zoning and paleoclimate analysis. (3) From the Pinghu to Baoshi Formation in the study area, it was found that the increase in the size, diversity, and abundance of ichnofossils. The tiering transitioned from simple and shallow to complex and deep. The variety of organisms and the degree of bioturbation increased, and the biological habits evolved continuously, indicating that the sedimentary environment changed from from anoxic to oxic. [Conclusions] Based on the characteristics of ichnofossils, ichnofabrics, and sedimentary structures, the response relationship between the ichnofabrics and the sedimentary environment was established in the Pinghu Formation and Baoshi Formation in Pingbei area. The research results provide new evidence for the changes in sedimentary environment from the perspective of ichnology in the Eocene of Xihu Sag.
Abstract: [Objective] Research on the weathering process of the aggradation red earth in subtropical China has long been crucial for understanding the evolution of the Quaternary environment. However, a comprehensive knowledge of the weathering environment of the aggradation red earth is hampered by the infrequent reporting of research on the weathering characteristics of the aggradation red earth at the spatial scale. [Methods] Based on a systematic analysis of the weathering characteristics of the aggradational red earth sections in southern China, this study focused on the Jinqu Basin, where non-zonal factors have a significant impact. The research primarily explored the chemical weathering characteristics and formation mechanisms of red earth within the basin, to deepen our understanding of the weathering features of aggradational red earth. [Results] The study shows that: 1) On a large scale, the weathering intensity of aggradational red earth in southern China is strongly correlated with hydrothermal conditions, with weathering intensifying as latitude decreases. However, the chemical weathering of red earth in certain locations or specific sections does not entirely conform to the latitudinal zonality in the mid-subtropical region between 25?N and 31?N, where aggradational red earth is widely spread. 2) The geochemical composition of aggradational red earth in the Jinqu Basin exhibits good consistency, with minimal differences in element enrichment or depletion among samples. However, there is regional variability in the degree of chemical weathering in the developmental stages of vermicular and typical red clays following the stagnation of vermicularization in the Jinqu Basin, compared with the chemical weathering characteristics of other aggradational red earth sections at the same latitude. 3) Influenced by a combination of factors such as provenance, topography, and local climate, the weathering characteristics of the aggradational red earth in the Jinqu Basin exhibit certain non-latitudinal zonal features. [Conclusion] The weathering characteristics of the aggradational red earth in southern China primarily follow a latitudinal zonal pattern under the large-scale monsoon evolution pattern. However, owing to the influence of non-zonal factors including topography, water, and differences in the geographic features of potential provenance, the chemical weathering of aggradational red earth also exhibits certain non-zonal characteristics within the mid-subtropical region between 25?N and 31?N. The relatively small and enclosed basin terrain of the Jinqu Basin, along with local microclimate conditions and contribution of bedrock weathering products to the red earth provenance, plays a significant role in interpreting the chemical weathering information of the red earth. Therefore, it is crucial to consider regional impacts while discussing the chemical weathering characteristics in different areas.
Abstract: [Objective] Climate change caused by astronomical orbital parameters is closely related to biological turnover and sedimentary evolution of the ocean and lakes, which in turn affects the organic matter enrichment in the strata. The late Paleozoic coal-bearing rock system in North China is dominated by coal, mudstone, siltstone, sandstone and tuff observed in a number of depositional cycles in the vertical direction. It is also an important system for current oil and gas exploration and development. The aim of this study is to systematically reveal the influence of the astronomical orbital cycle on organic matter enrichment in this coal-bearing system. [Methods] Natural gamma logging sequences were obtained for four wells (sampling distance 0.05 m) and continuous mineral elements for one well (sampling distance 1 m) in western North China. Astronomical cyclotron time series data and elemental geochemical analysis of typical samples were used to clarify the pattern of organic matter enrichment in stratigraphic cyclotrons at different scales. [Results and Discussions] (1) Six 1.2 Myr ultra-long obliquity cycles and eighteen 405 kyr long eccentricity cycles are recognizable in the Carboniferous–Permian Benxi, Taiyuan and Shanxi Formations. (2) Using Mg/Ca, SiO2/Al2O3, Fe/Mn and V/(V+Ni) ratios as paleoclimate and paleoredox proxies, six long-period variations and 18 medium-period variations were identified, all corresponding with ultra-long obliquities and long eccentricities. (3) Comparative analyses of paleoenvironmental restoration and organic carbon content during the depositional period of the Benxi–Shanxi Formations show that paleoclimate evolution and organic matter enrichment are basically synchronized and controlled by the astronomical orbital cycle, and that during periods of increasing ultra-long obliquity or long eccentricity the climate is warm and humid and the reducing nature of bodies of water is enhanced, which promotes organic matter enrichment. [Conclusions] The above results reveal Carboniferous–Permian climate change in North China influenced by the astronomical orbital cycle and the development of a constrained organic matter-rich stratigraphy, and find that the paleoclimate change during the same period was obviously constrained by the long eccentricity. The findings can be used as a reference for the study of global climate evolution and organic matter enrichment mechanism in the Permian.
[Objective]The Lower Triassic Feixianguan Formation in Sichuan basin develops thick oolitic beach reservoirs, which is the key layer of current oil and gas exploration. As the reserve strategic replacement field of Sichuan Basin, the sedimentary system, reservoir characteristics and favorable zone distribution of Feixianguan Formation in Tieshanpo and Qilibei areas are not clear, which restricts the deployment of oil and gas exploration in this area. [Methods]Based on the comprehensive analysis of core, rock slice, logging and seismic data, the sedimentary facies types, evolution rules and favorable reservoir zones of the Lower Triassic Feixianguan Formation in Tieshanpo and Qilibei areas were studied. [Results]The Feixianguan Formation in the study area develops a rimmed platform model, which can be subdivided into five sedimentary facies:restricted platform, open platform, platform edge, slope and basin. The platform margin is the favorable facies belt for the development of oolitic beach. The development of oolitic shoals in the area has obvious aggradation-lateral accretion characteristics, which are mostly superimposed in 2 to 3 periods vertically, and are distributed in ssq2 to ssq4 periods, with the largest scale in ssq2 period. Horizontally, the beach body is unstable and has a tendency to migrate into the basin; The reservoir rock types are mainly (residual) oolitic limestone, (residual) oolitic dolomite and powder crystal-fine crystal dolomite. [Conclusions]The platform margin oolitic beach is a favorable microfacies for reservoir development in Feixianguan Formation, and the porosity and permeability conditions are good. The area of wells Po5-Poxi1-Po2-Po1 in the Tieshanpo area is a favorable reservoir development zone, and the area of wells Qilibei1-Qibei102 in Qilibei area is a potential favorable reservoir development zone.The spatial and temporal distribution and migration law of beach bodies in different areas of the fourth-order sequence framework and the prediction results of favorable reservoir zones can provide a basis for deepening the exploration and development of oolitic beach reservoirs in this area.
Fluvial deposit is widely developed in natural strata, and meandering river deposit is an important part of fluvial deposit. Due to the frequent channel migration during the development of meandering river and the development of a large number of lateral deposits, the superposition relationship of sand bodies inside the point dam is complicated, so the analysis of the evolution process of meandering river has been the focus of sedimentological research. The analysis of controlling factors of meansional river morphology is of great significance to the study of paleoclimate evolution, continental weathering intensity and the exploration and development of oil and gas reservoirs. Previous scholars summarized the initial conditions for the generation of a zigzagging river by observing modern river sediments, and studied the effects of different clay mineral content, vegetation cover and initial saturation of river bed on the development of a zigzagging river. However, the development period of river sediments in nature is too long, and the dynamic sedimentation process of river cannot be well observed through field investigation and dissected outcrop, and the recording process is susceptible to interference by environmental factors. And lack of quantitative data support. In this paper, the effects of channel migration and dam body development on meander river development under single factor conditions were studied through flume sedimentation simulation experiments. In this study, three sets of experiments under different particle size, flow and clay mineral content were set up, and high-precision 3D laser scanner was used to convert the data into an elevation model for quantitative study of profile structure and bed sediment changes. The experimental results show that: (1) the particle size of the source sand directly affects the curvature of the meander river. Under the condition of constant clay content and constant flow, the smaller the particle size of the sand, the greater the curvature of the meander river formed. There are obvious differences in the structure of bank collapse sand bodies under different particle size conditions; (2) When the discharge affects the sediment transport balance and the flow impact force on the riverbank during the development of meandering river, when the sediment input rate and transport rate are in dynamic equilibrium, the riverbank maintains outward expansion and erosion, and the channel develops into meandering river form; (3) The addition of clay minerals to river banks can improve the permeability resistance of river banks. Under the condition that the source sand grain size and flow rate remain unchanged, the higher the clay mineral content, the lower the width to depth ratio of river channels.
[Objective]The research on sandy braided river delta has lots of achievements, but the sedimentary characteristics and evolution laws of sandy braided river delta keep different views, especially the understanding of mouth bars and distributary sand bars needs to be further study.[Methods]Based on the underground reservoir data, the paper uses the Delft3D software to show the growth and evolution process of the sandy braided river delta into the lake, summarizing it’ s sedimentary characteristics and evolution laws.[Results]The evolution of sandy braided river delta has three stages.In the early stage,the delta grows fastest, and the average diameter growth rate was greater than 6m/step. Sediments are carried into the lake and quickly unloaded, forming a large flower-shaped mouth bar under the water. In the middle stage, the delta plain keeps growing, the delta front keeps large,accounting for more than 50% of the delta. Contiguous sand bodies are built. In the late stage, the delta grows slowly, the average diameter growth rate is maintained at 1m/step.The front area is small, less than 20 % of the overall area.The delta plain has many distributary channels and ditches.There are many ways to transform the distributary sand bars.The delta front sand bars have different degrees of superposition relationship and rhythm combination characteristics, and the distributary sand bars are built on the residual mouth bar.[Conclusions]The sedimentary model of sandy braided river delta was established, which can provides reference for the genetic identification of distributary sand bars and mouth bars for the better study of underground reservoir architecture.
Abstract:[Objective] In this paper, the effect of seasonal lake level changes on the sedimentary characteristics, growth process, and sedimentary architecture of the bar fingers in shallow delta fronts is clarified. [Methods] Based on the modern mud and sand and hydrological data of the bar fingers in the Ganjiang Delta, the sedimentary numerical simulation software Delft3D, which is commonly used in China and abroad, is used to carry out numerical simulation of the sedimentation of the bar fingers under seasonal lake level changes and constant lake level conditions, and to compare the differences in sedimentary architectures. [Results] The study shows that under the condition of seasonal lake level changes, the bar fingers exhibit the following sedimentary architecture and growth evolution characteristics: (1) There are few bar fingers, small curvature, with an average value of about 1.42, long length, with an average value of about 9.2 km, thick in the middle, thin at the edge, with a thickness difference of 15.4 m, there is no obvious confluence between the bar fingers, presenting a plane combination style dominated by bird-foot shape; (2) The bar fingers develop deep distributary channels, the natural levees are wide and thick, and the thickness of the single-stage accretionary body in the mouth bar is large; (3) Under seasonal lake level changes, the bar fingers grow stably. During the period of lake level drop, the bar fingers undergo progradation, the distributary channels are mainly eroded-extended, and mouth bar deposits are formed at the front edge of the distributary channels. The distributary channels are also affected by the mouth bars and will undergo diversion and breach, forming multiple terminal distributary channels, while the natural levees are almost undeveloped; during the period of lake level rise, the bar fingers undergo retrogradation, the erosion of the distributary channels is weak, the distributary channels are abandoned and optimized, and the natural levees on both sides of the distributary channels accumulate and continue to thicken. Under the condition of constant lake level, the bar fingers show the following sedimentary architecture and growth evolution characteristics: (1) There are many bar fingers, with large curvature (average value is about 1.53), short length (average value is about 7.2 km), large overall thickness (maximum and minimum thickness differ by only 4.8 m), no obvious topographic difference, multiple bar fingers are constantly bifurcated and merged locally, forming a complex the bar fingers network, and the plane combination style of the bar fingers is mainly interlaced; (2) Deep distributary channels are also developed in the bar fingers, and the single-stage accretion body of the estuary bar is thick, but the most important difference is that there is no natural levee deposition; (3) The growth process of the bar fingers is relatively simple, mainly multiple the bar fingers grow simultaneously, intertwine with each other, and finally form an interlaced plane combination style. [Conclusion] Therefore, seasonal lake level change is an important formation condition for the bar fingers at the front of shallow deltas, which promotes the development of natural levees, improves the stability of distributary channels and the bar fingers, and plays an important role in controlling the sedimentary architecture and growth process of the bar fingers.
Some studies suggest that there is a causal relationship between climate and organic carbon enrichment, but the relevant reports mainly focus on high temperature, high insolation, marine transgression, and cyclical patterns. A comprehensive model establishing the coupling relationship between different climate conditions and the abundance of organic matter in basins from the perspective of the Earth system has not yet been developed. The main source rocks corresponding to large oil and gas fields in China are distributed in various geological periods. Source rocks from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic are mainly developed during periods of high-latitude greenhouse climate, while source rocks from the Paleozoic and Precambrian are mainly developed during periods of deglaciation at mid to low latitudes. The distribution of source rocks during the deglaciation spans four periods: the Neoproterozoic, the Ediacaran-Cambrian transition, the Ordovician-Silurian transition, and the Permian. The unique climate conditions during the deglaciation play a crucial role in the enrichment of organic carbon. The warming and climate fluctuations during the deglaciation, along with changes in ocean currents and volcanic activity, collectively lead to increased productivity of water and oxygen depletion, thereby promoting the accumulation of organic matter and the formation of source rocks. This relationship model between deglaciation climate and source rock reflects the control of the Earth system of oceans, land, and atmosphere on organic carbon enrichment under the influence of climate cycles. It can be used to guide the discovery of major oil and gas fields. However, the contribution of each factor to organic matter enrichment still needs to be quantitatively analyzed through the establishment of ocean-climate models and productivity models.
V/(V+Ni), V/Cr, U/Th, Uauto and Ce are the traditional redox proxies of Marine strata, but there are multiple solutions to the redox identification of lacustrine strata. Molybdenum(Mo) is a new redox proxies, but the fixation mechanisms of Mo under various redox conditions in lake environment are not well understood, which limits the application potential of Mo in the reconstruction of lake paleoenvironment. This article systematically tested surface sediment samples from Qinghai Lake, analyzed the planar enrichment characteristics of Mo, and explored the corresponding relationships between Mo content and continental input, grain size, element content, organic matter content of sediment and water environment. The preliminary results show that Qinghai Lake is an alkaline, suboxic and brackish water lake, and Mo element is slightly enriched in the sediments in deep water area. Continental input and grain size of sediment do not affect Mo enrichment. Mo can not be settled and enriched by adsorption of clay minerals and Fe oxyhydroxides in weakly alkaline-alkaline lake basin. Although Mn oxyhydroxides may adsorb Mo and settle, Mo will be re-released from the sediment into the water body as the sediment transforms into a reducing environment. There is a good correlation between organic matter abundance and Mo content, indicating that, at the deep part of lake, the hypolimnion becomes dysoxic. Organic matter adsorption and preservation are the main controlling factors of Mo enrichment in sediments.
The discovery of lithium mineralized bodies in multiple layers of the Permian-Jurassic layers in the northern margin of the Yangtze Block is of great significance to the investigation, development and utilization of sedimentary lithium resources. In order to clarify the provenance and tectonic setting of the parent rock in the source area of the lithium-bearing fine clastic rocks of the Jurassic Baitianba Formation, and to discuss the control of the paleo-environment on lithium enrichment, the typical lithology of the strata has been studied in detail, and the XRD and elemental geochemistry studies have been carried out. Results: The main element oxide discriminant function and LaN/YbN-ΣREE, K2O-Rb and La/Th-Hf diagrams show that the potential provenance region is a mixed provenance region of emerging medium-acid igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. The main element oxide discrimination function and the diagrams of La-Th, Ti/Zr-La/Sc, La-Th-Sc, Th-Sc-Zr/10 and Th-Co-Zr/10 show that the tectonic background of the sedimentary period was active continental margin, and some parent rocks in the source area were formed in continental island arc environment. Ga, Sr/Ba, Sr/Cu, C value, CIA, U/Th, Ni/Co and other paleoenvironmental indicators indicate that lithium-containing fine clastic rocks were deposited in a weakly reduction-oxidizing freshwater environment in a warm and humid climate. The A-CN-K and Th/ Sc-Zr /Sc diagram show that the parent rock of the source area has undergone moderate to intense weathering when the debris was first deposited. The comprehensive study shows that paleosalinity and paleoreduction-oxidation conditions control the enrichment of lithium to some extent, but the content of clay minerals in lithium-containing fine clastic rocks is the key to determine the enrichment of lithium. The lithium content level in the source area plays a leading role in lithium enrichment (" source "), and the sedimentary environment affects the lithium content in the formation (" storage ") by influencing the content of clay minerals.
[Objective] It is of great significance to study the relationship between climate proxies and climate factors in sandy surface sediments to determine the reliability and applicability of climate proxies. [Methods] In this paper, 32 surface sediments were collected on a large spatial scale in Otindag Sandy Land. Through the correlation analysis of chroma, Hm/Gt, magnetic susceptibility and modern climate factors (average annual precipitation and average annual temperature), the relationship between each index and climate factors and their environmental significance were discussed. [Results]The results show that the variation range of a* and b* is small, and the overall trend from east to west is increasing, in which the minimum value of a* is 3.87, the maximum value is 8.26, and the average value is 6.09. The minimum value of b* is 9.49, the maximum is 17.44, and the average is 14.24. a* and b* were negatively correlated with precipitation (correlation coefficients -0.88 and -0.77, P < 0.01), and positively correlated with temperature (correlation coefficients 0.89 and 0.82, P<0.01), indicating that both a* and b* could be used as effective proxy indicators of climate change. And a* is more sensitive to climate factors. The variation range of L* was small, and there was no obvious change rule from the east to the west. The maximum value was 59.54, the minimum value was 48.8, and the average value was 54.69. The relationship between L* and climate factors is not obvious, and its change is mainly directly affected by vegetation, and its indicative significance for climate is not obvious. The relative percentage content of hematite is between 8% and 19%, with an average of 14%, and the relative percentage content of goethite is between 6% and 9%, with an average of 7%. The value of hematite/goethite (Hm/Gt) ranged from 1.2 to 2.73, with an average value of 1.88, showing an increasing trend from east to west. The correlation between hematite and climate factors is higher than that of goethite. The ratio of Hm/Gt is negatively correlated with average annual precipitation (correlation coefficient is -0.85, P<0.01), and positively correlated with average annual temperature (correlation coefficient is 0.84, P<0.01), which reveals the sensitivity of hematite and Hm/Gt to precipitation and temperature. It can effectively reflect the changes of hydrothermal conditions in sandy land. The variation direction of low frequency magnetic susceptibility (χlf) and high frequency magnetic susceptibility (χhf) was the same, showing an increasing trend from the east to the west, and the variation amplitude was small in the east, but larger in the west, and the frequency magnetic susceptibility showed a decreasing trend from the east to the west. The magnetic susceptibility in this region does not show a good correspondence with climate factors. The source of sand material may be the main factor of its variation, indicating the complexity and particularity of the variation of magnetic susceptibility in sand.[Conclusions]Both a* and b* can be used as effective proxy indicators of climate in the study area, while L* is affected by vegetation, which leads to the ambiguity of its climate information. The correlation between hematite and Hm/Gt values and climatic parameters is good, which is an ideal index to indicate the change of water and heat in the sandy land. The magnetic susceptibility of the surface layer of the sandy land is less affected by the climate, and the more reaction is the complexity of the source information in the region.
[Objective] The end-Permian mass extinction event (EPME) led to a global decline in flora and biota. The thick coal seams, prevalent during the Permian, vanished following this event, resulting in a prolonged coal shortage throughout the Triassic. In the Sichuan Basin, following the EPME, spore plants that contributed to coal formation in the lowlands were lost, with no subsequent records of coal seam development. It was only during the early sedimentary period of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation (T3x1) that coal seams reemerged. In the Sichuan Basin, coal deposits resurfaced specifically in the T3x1. This section is characterized by thin coal seams and poor spatial continuity; In the middle to late stages of the Xujiahe Formation sedimentation,the thickness of coal seam sedimentation and its spatial distribution have strong regularity. At present, research on the Late Triassic paleoclimate in the Sichuan Basin mainly focuses on the middle and late stages of the Xujiahe Formation. However, there's a research gap regarding the paleoclimate during the initial coal-forming phase of the Late Triassic (early stage of the Xujiahe Formation). [Methods] To fill this gap, a focused study was conducted on the Norian T3x1 (specifically the Gongnongzhen and Wangjialiang sections) in the northwestern part of the Sichuan Basin. This study involved rock analysis of major and trace elements, combined with field outcrop descriptions and petrological analysis. The aim was to reconstruct the coal-forming paleoclimate and sedimentary environment, thereby exploring the environmental conditions crucial for the mechanisms of coal formation. [Results and Discussions] Research has shown that the sedimentary facies of the T3x1 in the Gongnongzhen section are mainly delta front subfacies, whereas those in the Wangjialiang section are chiefly delta plain subfacies. Weathering indices (CIAcorr, Rb/Sr) and climate indices (Sr/Cu and C values) of the T3x1 in the Gongnongzhen and Wangjialiang sections displayed an overall fluctuating trend: high-medium-high-medium-high. The humid and hot climates correspond to strong chemical weathering intensity, while the warm semi-arid/semi-humid climates correspond to moderate chemical weathering intensity[Conclusions] The paleoclimate during the initial coal-forming period of the Late Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Northwest Sichuan can be divided into two types: (1) hot and humid climates; (2) warm semi-arid to semi-humid alternated climates. In study area, coal seams are associated with hot and humid climates. Hot and humid conditions promote the reproduction of coal forming plants, providing abundant material sources for the formation of coal seams.The paleoclimate of dry to wet alternation during the T3x1 in Northwest Sichuan is closely related to the activity of the super monsoon. The high concentration of PCO2 combined with the influence of super monsoon activity jointly promoted the formations of humid climate and strong chemical weathering in the study area. Further research indicates that coal deposition requires not only a suitable paleoclimate but also an appropriate preservation environment. For instance, coal seams tend to be well-developed and preserved in the swamps of high-level system tracts.
[Objective] With the continuous breakthrough of oil and gas exploration and development technology, shale oil has become an important replacement field for petroleum resources in the future. At present, the exploration and development of shale oil in Chang 7 Member of Ordos Basin has made important progress, but the reservoir performance of laminae shale oil is rarely studied. [Methods] Taking the organic-rich shale of Changchang 7 member of Yanchang Chang in the southeast of Ordos Basin as the research object, the development characteristics, reservoir performance and oiliness of different shale types in the Changchang 7 member shale formation were studied by means of thin section observation, scanning electron microscopy, high-pressure mercury intrusion and nitrogen adsorption, so as to classify the types of shale laminae and clarify the occurrence characteristics of shale oil. [Results and Discussions] Laminae is developed in silty mudstone, argillaceous siltstone, siltstone, black shale and tuff in Chang 7 member of the study area, which can be macroscopically divided into three types: thick laminated shale (1cm
[Objective] Powdery~fine-crystalline dolomite dominated by residual granular structure and non-luminous under cathode rays is developed in the reservoir section of Maosan section-Wu section of the Permian of the Yuanba Tectonics in north-central Sichuan Province, and the mechanism of the genesis of this type of dolomite in the study area is not clear at the present time. [Methods] The dolomite genesis mechanism was studied based on the petrological characteristics of the reservoir combined with TIMA scanning of rocks, whole-rock X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, in-situ microzonation of major trace elements, strontium isotopes, and in-situ U-Pb chronology of dolomite. [Results] The study shows that: (1) the rock types of the reservoirs in Maosan Section 3 and Wu Section 1 are tuffs, dolomites and sedimentary tuffs. Tuff reservoirs mainly include mud crystal clastic tuff, bright crystal clastic tuff and cloudy tuff; dolomite reservoirs are semi-autogenous~autogenous powder~fine crystalline dolomite; sedimentary tuff reservoirs are mainly composed of volcanic clasts, charcoal, calcium and magnesium, sand clasts and metal minerals, etc. Volcanic clasts are glass clasts, basaltic and other clasts, and the main constituents of calcium and magnesium are dolomite and calcite. (2) The average values of trace elements of dolomite at the top of Maosan Section 3 and Wu Section 1 show extremely high Fe content (10,678.40×10-6), high Mn content (822.95×10-6), Si content (1,929.81×10-6), Al content (394.11×10-6), and high Na+K content (362.38×10-6), indicating that the fluids in the closed environment were formed by the volcanic fluids, which is the main component of calcium and magnesium, and calcite. Indicating that the rock-forming fluids in the confined environment are characterized by high salinity and high alkaline metal content. The 87Sr/86Sr in the matrix part of the dolomite and mud-crystal clastic tuff is within the range of seawater of the same period in the Maokou Group-Wujiaping Group, and it also has a low value of ∑REE, a loss of LREE, and exhibits the characteristics of negative anomalies of Ce (the average value of δPr is 1.03>1, and the average value of δCe is 0.96<1), and negative anomalies of Eu or no anomalies, which suggests that the dolomitization diagenesis fluid is similar to the seawater of the same period. seawater. (3) The U-Pb age of powdery to fine-crystalline dolomite in the Maosan section and Wu section is 245.36±1.08 Ma, and dolomitization mainly occurred in the shallow burial period.[Conclusion] It is concluded that the source of the dolomitization fluid in the powdery~fine crystalline dolomite of Maosan section and Wu section is the compaction and dewatering of clay minerals in the overlying muddy sedimentary tuff and tuffaceous mudstone sections of Wu section 1 and Wu section 2 during the shallow burial period. During this process, a large number of Mg2+, Fe2+, Al3+, and Si4+ ions were precipitated and transported to the granular tuff at the top of the Wu 1 and Maosan 3 Sections and accounted for by the seawater residual from the Maokou Formation to the Wujiaping Stage as the carrier.
[Objective] The Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang are located in the inner part of the Asia-Europe continent, in the transition zone between the westerly and monsoon circulations, and are sensitive to climate change. Academics have not yet united on the understanding of the Holocene environmental evolution in the region, and supplementing more high-resolution climatic records in the sensitive areas is the basis for clarifying this issue. [Methods]The study material was taken from the Middle Tien Shan Intermountain Basin, we reconstructed the vegetation and climate change processes in the study area since the Middle and Late Holocene, based on the AMS14C dating results and using sporadic pollen as a paleoclimate proxy. [Results and Discussions] 6369-3601 cal yr B.P. The period of Artemisia and Chenopodium was characterized by high content, positive pollen PCA axis 1 scores, and wet-dry fluctuations in the climate, with dryness as the dominant factor and abrupt climate change. 3601-2512 cal yr B.P. The period of spruce Picea content was characterized by elevated content, positive pollen PCA axis 2 scores, and cold-wet climate. 2512-1016 cal yr B.P. The period of Betula was characterized by increased content, positive pollen PCA axis 1 transitionscores, warm dry climate. [Conclusion] The three pollen zones indicate that the Middle and Late Holocene climate in the Zhongtianshan Intermontane Basin went through 3 phases of wet-dry fluctuations (off-dry)-cold-wet-warm-dry. Since the middle to late Holocene, the study area has received less solar radiation in summer, Weak evaporation from the North Atlantic sea surface and low water vapor carried by the westerly circulation, the climate has been arid. in the early Late Holocene, the westerly circulation shifted to the south, Superimposed negative phase of the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) transporting large amounts of water vapor and the climate was cold and humid. Then the climate became warm and dry due to the increase of solar radiation in the late winter. The abrupt climate change characterized by cold and dry conditions during 4766-3601 cal yr B.P. was a response to the "4.2 ka B.P." climatic event, which may have been caused by the weakening of the westerly circulation due to the weakening of solar radiation, the intensification of the cold in the middle and high latitudes, and the lowering of the SST in the North Atlantic Ocean.
[ Objective ] The Chang 7 member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin mainly develops semi-deep lake-deep lake subfacies, and deep-water gravity flow deposits are generally developed. [ Method ] Taking the Chang 7 Member in Fuxian area of the southeastern basin as the research object, based on the fine description results of centimeter-level cores from 13 coring wells, combined with particle size analysis and logging data, the types and characteristics, formation mechanism, distribution law and evolution model of gravity flow deposits in the Chang 7 Member were studied. Combined with oil test and production test data, the control effect of gravity flow on reservoir distribution was analyzed. [ Result ] The results show that the Chang 7 member in Fuxian area mainly develops three types of gravity flow deposits : sliding-slump, sandy debris flow and turbidity flow. The sliding-slump is characterized by the development of roll bedding, crumpled deformation structure, syndepositional stepped small faults and sliding surface, and is dominated by the mixed deposition of sandstone and mudstone. The sandy debris flow develops thick massive sandstone, mudstone tearing debris and mud-encapsulated gravel structure. The thickness of single sand body is between 0.3-3.5 m, and the cumulative thickness can reach more than 10 m. Turbidity flow develops flame structure and Bouma sequence, and incomplete A,B,D and E sections are common. The sand body is small in scale and limited in development. The thickness of single sand body is generally several centimeters to dozens of centimeters. [ Conclusion ] The Chang 7 member is divided into 6 typical logging facies combinations and 11 lithofacies types. The formation mechanism of gravity flow in this area is underwater slope break zone, volcano and earthquake. Along the source direction, the thickening of the stratum reflects the transition of the sedimentary environment from the delta front to the deep lake-semi-deep lake deposit ; vertically, three types of gravity flow overlap, dominated by sandy debris flow. The sandy debris flow in the gravity flow sand body has the best oil content, and the main body is oil spot-oil immersion.
[Significance] Cold seep activities have a significant impact on marine ecosystems and global climate change, and they are widely developed in the global active and passive continental margins. The fundamental process operating at seeps is the anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM), mediated by a consortium of anaerobic methanotrophic archaea (ANME) and sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB). This procedure will increase the alkalinity of pore water, forming a favorable precipitation environment for carbonate minerals. Cold seep carbonates are the products of submarine cold seep activities, and their geological and geochemical characteristics are often used to trace seepage fluid information and sedimentary environment changes. [Progress] The Taiwan Island is located in the collision zone between the Luzon Island Arc of the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian continental margin, which possesses complex geological structures such as extensive faults, providing appropriate conditions for the development of cold seeps. The cold seep carbonates in Taiwan area are mainly developed in Miocene to Pleistocene strata, which are ideal carriers for the study of ancient cold seeps. A relatively detailed study has been conducted on its fundamental geological and geochemical characteristics, including mineralogy, petrology, and carbon and oxygen isotopes. This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the geological occurrence, mineralogical and petrological characteristics, carbon and oxygen isotopes, rare earth elements geochemistry, and macrofossil contents of cold seep carbonates in Taiwan area. In addition, it explores the fluid seepage activities and depositional environment characteristics recorded by the cold seep carbonates in Taiwan area, combining the geological and geochemical features of cold seep carbonates from other regions globally. [Conclusions and Prospects] Cold seep carbonates in Taiwan area predominantly occur in blocky and chimney-like forms, which indicate two types of seepage activity. The blocky forms indicate prolonged periods of low-flux diffuse seepage, while the chimney-like forms represent shorter periods of high-flux convective seepage. The primary carbonate minerals in cold seep carbonates are dolomite and calcite, with a significant presence of framboidal pyrites. The size of the pyrite grains may be related to the redox conditions during sedimentation. The carbon isotope composition of cold seep carbonates indicates that the primary sources of carbon are biogenic and thermogenic methane, with additional influence from seawater or residual CO2 from methanogenesis. Notably, Pliocene cold seep carbonates exhibit the widest range in carbon isotope values, suggesting a greater diversity of carbon sources, potentially due to the complex geological structures in Taiwan area at that time. Furthermore, the δ18O values of cold seep carbonates from the Miocene to the Pleistocene in Taiwan area exhibit a progressively positive trend, suggesting these carbonates might have undergone a transition from gas hydrate formation to dissociation and release. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements illustrate that the sedimentary environment is dominated by reduction. The cold seep macrofossils are dominated by bivalve fossils, while they have few biological species in the Miocene and Pliocene, but more in the Pleistocene, which may be affected by water depth. In order to improve the in-depth understanding of the ancient cold seep systems in Taiwan area, future research can focus on in situ micro-scale carbon and oxygen isotope analysis of cold seep carbonates, Mo element and its isotope analysis of carbonate minerals, as well as the spatial differences in the growth of macrofauna of different genera of Lucinidae family, in conjunction with geochemical analysis.
Abstract: [Objective] In the middle and late stages of oil and gas field development, studying sand architecture is key to excavating residual oil and enhancing recovery. Precisely interpreting similar outcrops can provide a comparable prototype model for predicting underground reservoir architecture. [Methods] The shallow water delta profiles of the Yan'an Formation in the Kaokaowusu Gully and Gulf Mining Industry in the Ordos Basin were the research objects. UAV oblique photography was used to obtain massive outcrop image data, and then 3D digital outcrops were established. Detailed architecture interpretation of digital outcrops was carried out by combining field investigation and indoor analysis. [Results and Discussions] The developmental characteristics and evolutionary models of shallow water delta front architecture during the rising lake level were defined. When the lake level is low, mainly trunk-type distributary channels are developed, with widths of 23.3~48.4 m, thicknesses of 0.89~1.81 m, and width-to-thickness ratios of 26.74. The sandbody superimposition patterns are mainly overlay type. As the lake level increases, fork-type distributary channels, mouth bars, sand sheets, and subaqueous distributary bays gradually develop. The width of the mouth bar is 53.9 m, the thickness is 2.21 m, the width-to-thickness ratio is 24.39, and the superimposition pattern is mainly joint type. When the lake level is higher, mainly terminal-type distributary channels, mouth bars, and sheet sand architectural units are developed. The width of the terminal-type underwater distributary channel ranges from 4.7 to 40.6 m, the thickness ranges from 0.4 to 1.03 m, and the width-to-thickness ratio is from 11.75 to 24.56, isolated in the muddy deposit. [Conclusions] When the supply of material sources is relatively stable, the increase in lake level leads to an increase in accommodative space. The architectural units evolve from trunk-type distributary channels to terminal-type ones, depositing mouth bars and sand sheets. The size of the sand body decreases, but the width-to-thickness ratio increases. Overall, the sand-to-ground ratio decreases, spatial connectivity decreases, and reservoir heterogeneity is enhanced.
[Objective] The sedimentary environment of the Pearl River Delta is complex. with abundant Perinereis trace fossils. The characteristics,distribution and assemblage of Perinereis and their relationships with sedimentary environment and sediment properties are significant for the study of trace fossils and palaeoenvironment. [Methods] Based on sedimentary and ichnological methods, grain size analysis, salinity, turbidity, total organic carbon (TOC), X-ray scans, and three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction were applied to the modern biogenic sedimentary structures in different microenvironments of the Pearl River Delta tidal flat, discussed the composition,assemblage and distribution characteristics of Perinereis in tidal flat of Pearl River Delta, and analyzed the relationship between the biological assemblage and the sedimentary environments. [Results] 1) The Perinereis mainly lives in the tidal flat area of the tidal channel and the interdistributary bay in the Pearl River Delta. 2) The remains of the Perinereis mainly have grazing trails and dwelling trails, but the grazing trails on the layer are hard to observe, and the dwelling trails in the layer mainly have simple Y-shaped, I-shaped and U-shaped and complex network structures, and there are bulges at the joints. 3) The Perinereis is suitable for living in the tidal flat or tidal channel of the interdistributary bay with low hydrodynamic conditions, low salinity, low turbidity and rich total organic carbon content. [Conclusions] The spatial distribution of Perinereis’ neoichnology is imbalanced, and multiple environmental conditions jointly control the abundance of Perinereis’ neoichnology. The habitat of Perinereis is similar to the trace fossil Polykladichnus, which can belong to both the Mermia and Glossifunites ichnofacies, the trace fossil assemblage of this relic mainly appears in the channel and tidal flat area, and this study supplements the biological data of modern neoichnology of Perinereis.
Bauxite-type lithium-rich claystone deposits with great ore-forming potential have been found in the bauxite-bearing strata formed in different geological periods in the Yunnan-Guizhou area of southwestern China, but the current understanding of the material sources and lithium enrichment mechanisms of these bauxite-type lithium-rich claystones in these areas is still significantly insufficient. This study carried out a comparative analysis of the mineral composition, major trace and rare earth element composition of the bauxite-type lithium-rich claystone series of the Early Permian Daoshitou Formation in Yunnan and the Early Carboniferous Jiajialu Formation in Guizhou, and combined with the previous research results, systematically discussed the provenance characteristics and the limiting factors that caused the abnormal lithium enrichment of these two sets of bauxite-type lithium-rich claystones that formed in different ages but have extremely similar lithofacies characteristics. The results show that the difference in provenance characteristics between the Jiajialu Formation and the Daoshitou Formation lithium-rich claystones in Guizhou and Yunnan has a significant impact on their respective lithium characteristics. Generally, the formation of the Jiajialu Formation claystone with relatively low lithium content is closely related to the weathering and erosion of the impure dolomite of the underlying Loushanguan Group, and its original source may be the Mesoproterozoic-Middle Proterozoic intermediate-acidic magmatic rocks, and it is significantly affected by the magnesium-iron components. The formation of the Daoshitou Formation claystone with relatively high lithium content in Yunnan is significantly affected by the recycled material of the Ordovician sedimentary rock series, and the source connection with the underlying carbonate rock strata is weak. At the same time, its original source is obviously dominated by intermediate-acidic magmatic rocks. In addition, the lithium-bearing minerals in the lithium-rich claystones in the Yunnan-Guizhou area may be kaolinite or illite minerals, and the drainage of the basin during the sedimentary period and the coexistence effect of ions in the water body have played an important role in the enrichment of lithium in the clay. The relevant understanding of this study has important significance for deepening the ore-forming process and limiting mechanism of clay-type lithium deposits.
It is of great significance to study the variation mechanism of magnetic susceptibility and chroma of sediments in different environments for paleoclimate reconstruction. Based on the sampling and measurement of magnetic susceptibility and colorimetry of the surface soils in the western Qilian Mountains in northwest China, this contribution discussed the variations of magnetic susceptibility and colorimetry in terms of the precipitation, temperature and altitude, and established the functional relationship between magnetic susceptibility and colorimetry and climate factors and altitude. The results show that: (1) there is a nonlinear relationship between magnetic susceptibility and average annual temperature and precipitation, and there is a threshold value (~0℃, ~300mm), below which the magnetic susceptibility is inversely proportional, and vice versa; The magnetic susceptibility is negatively correlated with altitude in particularly at low altitude areas. (2) Chroma (brightness, redness, yellowness) has no obvious relationship with temperature and precipitation, and brightness has a significant negative correlation with altitude, and it is more sensitive in low altitude areas. (3) Compared with colorimetry, magnetic susceptibility can better reflect the climatic and elevation changes in the western Qilian Mountains. For altitude variation, the relationship between brightness and altitude is more significant at low altitude, followed by yellowness and magnetic susceptibility. The relationship between redness and brightness and altitude is more significant in high altitude area.
[Significance] The architecture of marine sandy beach-bar reservoirs is complex, and dominant seepage channels and barriers are developed inside the reservoirs. There is a lack of architecture models for underground reservoirs, which cannot effectively guide the recovery of remaining oil. [Method] In this paper, we have proposed the architecture pattern of marine sandy beach-bar reservoirs by outcrops, satellite photos and numerical simulation with the Hudson Donghe sandstone as the research objective. Under the guidance of the mode, the architecture of the Donghe sandstone reservoir is finely characterized. [Result] The results show that: the depositional architecture of a single sand bar inside composite beach-bar is controlled by many factors such as shoreline shape, coastal slope, wave direction, and height, multiple types of sandbars can be formed, such as conical bar, tight moon bar, positive linear bar, nonlinear inclined bar, and sandy beak bar. Based on the identification of single sandbar boundaries and guided by the architecture mode, 13 sandbars of different sizes were identified in the C1 layer of the study area, including five tight moon bar, seven forward linear bars and one oblique bar, there are differences in quantitative scale between different sanbars. The length of tight moon bar is about 1.5-3 km, the length of the oblique bar is about 4.5-5 km, and the length of the positive linear bar is more than 6 km. The sandbars exhibits both progradational and retrogradational stacking patterns, while the bars in C1 small layer exhibits progradational lateral separation and progradational lateral stacking patterns. The migration rate of the coastline affects the stacking relationship between the sandbars. The numerical simulation results and outcrop data indicate that there are differences in the development patterns of the internal accretion bodies. The distribution patterns of the internal interlayers include top accretion, top accretion-side accretion, and interval type. In the C1 small layer, three types of distribution patterns of the internal interlayers were identified. The internal interlayers in the No. 16 sandbar exhibit a two-stage distribution feature of "top accretion-side accretion", while the internal interlayers in the No. 19 sandbar exhibit a "side accretion". The angle distribution range of the top and side accretion interlayers is about 1-3 ° and 3-7 °, and the interlayers between dam No. 14 and 15 sandbars are distributed in an "interval" pattern. The development pattern of the interlayers inside the bars of Hudson Donghe sandstone reservoir is summarized. [Conclusion] Fine characterization of the internal architecture of marine sandy beach-bar reservoirs can effectively guide the recovery of remaining oil.
Abstract: [Objective] The high-resolution climate reconstruction of Liaodong Peninsula is important for exploring the evolution of regional climate environment and high-quality development. The aim of this study is to reconstruct the sedimentary environment and climate history by studying the sediments of the west coast of Dalian. [Methods] By analyzing AMS14C dating, lithology, and geochemical elements of the Laoyuwo (LYW) section to reveal the evolution of sedimentary environment and paleoclimate of the region. [Results and Discussions] The sediment is mainly composed of sand, silt, and gravel, which recorded sedimentary environment and paleoclimate evolution information from the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) to the Middle Holocene (18815–6802 cal.BP). The main chemical components in the profile are SiO2, Al2O3, K2O, and Fe2O3, the total content of which is 90.34%. The contents of major elements from large to small are SiO2 > Al2O3 > K2O > Fe2O3 > Na2O > CaO > TiO2 > MgO > P2O5 > MnO. The sedimentary records shows that the region experienced a dry and cold alluvial (18.8 cal.ka BP – late LGM), slightly warm and humid coastal intertidal (18.8–16.0 cal.ka BP), warm and humid coastal subtidal (18.8–16.0 aal.ka bp), warm and humid coastal subtidal((16.0–11.7 cal.ka BP), warmest and wettest coastal salt marsh (11.7–6.8 cal.ka BP), and dry and cold fluvial environment (6.8–0 cal.ka BP). The highest sea level around 6.8 cal.ka BP and the rapid climatic events during Younger Dryas (DY) and 8.0–9.0 ka are also responses in the sediment. [Conclusions] This study provides basic data and information for the Holocene climate reconstruction of Liaodong Peninsula, particularly for the sedimentary environment evolution history of the west coast of Dalian.
Gulong shale oil is an important replacement resource in the Songliao Basin, with an estimated resource amount of 15.1 billion tons. From the perspective of sedimentary and petrological characteristics, the most prominent feature of Gulong Qingshankou Formation shale is the extensive development of sand dikes, which is not found in shale oil reservoirs in other basins. Therefore, this is also an important information to explore the formation environment of Gulong Qingshankou Formation shale. The most peculiar thing is that in addition to sand dikes, there are two other special dikes in Gulong Qingshankou shale: pyrite dikes and cementite dikes. Pyrite dikes and cementite dikes are generally small in scale, with widths of 1-2 mm. Visible length several centimeters; Mostly curved like intestine, a few slightly curved. Multi-tilt output, tilt direction has a certain rule, 180° symmetry. The pyrite dikes in the shale oil reservoir of Qingshankou Formation in Gulong are formed by late pyritization of sand dikes. The cementation dikes are formed by gravity subsidence caused by density inversion and the formation kinetics of pyrite and tuff dike are also studied. The study of pyrite dikes and puffite dikes in the Gulong shale oil reservoir has three significances: first, the formation time, sedimentary environment, sedimentary process and sediment state of pyrite dikes and tuff dikes can be known; Second, the diagenetic compaction rate of shale can be known. Third, it can assist reservoir evaluation.
Abstract: [Objective] The level of oxygen content in shallow sea and atmosphere during the Mesoproterozoic (about 1.8-1.0 Ga) has been controversial.Due to the slow evolution of eukaryotes during this period, the redox state of the surface ocean and atmosphere has been considered to be a relatively stable hypoxic state. However, in recent years, more and more evidence shows that there are dynamic fluctuations in oxygen content during this period. However, due to the heterogeneity of time and space, people 's understanding of the global redox state during this period is still very limited.[Methods] In this study, the redox state of the shallow sea in the southern margin of the North China Craton was studied by analyzing the Ce anomaly, δ13C and Y/Ho indexes of carbonate rocks in the Longjiayuan ( 1.59-1.54Ga ) Formation.[Results] The results show that there are obvious negative Ce anomalies ( 0.53 ~ 0.94 ) and positive δ13C anomalies before and after 1.54 Ga in this area, accompanied by a significant increase in Y / Ho ( average 64 ), and later returned to normal levels.[Conclusion] It indicated that there might be a transient oxidation event. This oxidation event is consistent with the contemporaneous strata of the Jixian System in the northern margin of the North China Craton, indicating that the fluctuation of shallow sea oxygen content during this period may be widespread in the North China Craton. This study can provide direct evidence for the pulse oxygenation event in the Mesoproterozoic, and help to further determine the redox state of the shallow sea during this period and the effect of oxygen on the evolution of eukaryotes.
[Objective] Shallowing-upward sequences are extensively developed in shallow-water carbonate environments, and the identification of shallowing-upward sequences in deep-water carbonate rocks holds a unique advantage for analyzing the evolution of shallow-water carbonate sedimentary environments. [Method] This study focuses on the Late Cambrian Xixiangchi Formation in Xiuqi Town, Chengkou County, on the northern margin of the Yangtze Platform. Through detailed field sedimentological analysis and laboratory microfacies analysis, shallowing-upward sequences in carbonate rocks were identified. The compositional characteristics and vertical stacking relationships were analyzed, thereby exploring the Late Cambrian sedimentary environment evolution in the upper Yangtze region. [Results and Discussions] In the Xixiangchi Formation, 14 sedimentary microfacies have been identified, including MF0 argillaceous shale, MF1 micrite, MF2 bright crystal gravel limestone, MF3 bright crystal sand limestone, MF4 muddy siltstone, MF5 dolomitic microcrystalline limestone, MF6 gravel dolomite, MF7 bright crystal sand dolomite, MF8 sandy gravel grain dolomite, MF9 sandy sandy lithic grain dolomite, MF10 sandy dolomite, MF11 laminated dolomite, MF12 bamboo leaf-like gravel dolomite, and MF13 grain dolomite with dissolution pores. Based on the microfacies associations, six decimeter-scale upward-shallowing tidal sub-environments (C1-1 to C1-6) have been recognized within the Xixiangchi Formation, representing subtidal deposition. Additionally, six decimeter-scale upward-shallowing tidal-subtidal transition sub-environments (C2-1 to C2-6) and two decimeter-scale upward-shallowing intertidal-subtidal transition sub-environments (C3-1 and C3-2) have been identified. These decimeter-scale upward-shallowing cycles constitute three secondary sea-level cycles. These three secondary cycles, from bottom to top, combine to form one upward-shallowing sedimentary cycle within the Xixiangchi Formation, representing a rapid transgression followed by gradual regression. [Conclusions] Based on the identification of shallowing-upward sedimentary sequences and the analysis of their compositional characteristics and vertical stacking relationships, it is believed that the Late Cambrian Xixiangchi Formation was significantly influenced by high-frequency sea-level changes. It as a whole underwent an early rapid marine transgression, followed by a late slow regression, and experienced multiple episodes of secondary sea-level fluctuations. This resulted in a restricted carbonate platform sedimentary model characterized by mixed intertidal subfacies, chalky lagoon subfacies, and inner-shelf grainy shoal subfacies. This study further confirms a global late Cambrian sea-level regression event.
Abstract: J1b1 Formation in the Mahu slope area is a set of sandy (gravel) rock deposits of coal-bearing rock series close to the J/T unconformity. The shale rich conglomerate belt near the bottom of the J/T unconformity has obvious oil and gas thickened, and light oil and gas are mainly concentrated in the thin sandstone belt above the coal seam. There is still no research on the origin of oil and gas thickening zone in relatively deep buried area, the percolation mechanism of atmospheric fresh water to overlying strata on unconformity surface, and the origin of light oil and gas enrichment above coal seam of coal-bearing rock series. Therefore, based on the properties of crude oil and carbon isotope analysis of natural gas, combined with the data of burial history, thermal history, pore evolution history, and laser Raman spectrum analysis of hydrocarbon salt water inclusions, the genetic types of J1b1 natural gas and the origin and distribution of hydrocarbon thickening zone and light oil and gas zone are discussed. The results show that: ①J1b1 coal-bearing rock series can be divided into oil and gas thickening zone and light oil and gas zone according to the characteristics of oil and gas density viscosity. The former is mainly distributed in the upper wall of the fault zone, the fault zone, and the bottom of the slope zone adjacent to the J/T unconformity. The latter is mainly distributed in the thin sandstone zone above the coal seam in the slope zone, and the coal-derived gas content is high. ②The origin of the shale rich conglomerate oil and gas thickening zone at the bottom of the slope zone adjacent to the J/T unconformity is closely related to the atmospheric freshwater compacting-centrifugal flow oxidation degradation. The “YANSHAN normal fault-J /T unconformity -shale rich conglomerate assemblage”and the associated capillary imbibition of wetting water phase led to the formation of atmospheric freshwater compaction-centrifugal flow oil-gas thickening zone closely related to the unconformity in the slope area of relatively deep burial. ③The thin sandstone reservoir above the coal seam has the characteristics of “self-generated and self-stored (deinspiratory charging in J1b1 coal seam)” and “bottom-generated and upper-stored (hydrocarbon supply from P1f source rock)”, and has the advantage of light oil and gas enrichment. The coal seam desorption diffused upward through the positive fracture into the thin sandstone at the top, and the methane carbon isotope value was relatively light, which was different from the retained adsorbed gas in the coal seam (δ13C1=-48.2‰ in the former and δ13C1=-43.6‰ in the latter). The geological stratification effect caused by long distance migration of P1f source rock oil and gas further promotes the accumulation of light oil and gas in thin sandstone above the coal seam. The conclusion is that the upper thin sandstone belt of J1b1 is the first choice for exploration of light oil and gas enrichment belt. The quantitative lithological logging identification map of coal-bearing rock series with the combined restraint of CNL-IMP was established, and the effective reservoir distribution area of the upper thin sandstone of J1b1 with a thickness≥10m was identified in the Yanbei1 3D seismic zone.
[Objective] The redox states of the early Ediacaran ocean has always been a research hotspot. The formation process of sedimentary barite nodules is studied to explore the redox variation of the Ediacaran ocean immediately after the Snowball Earth event. [Methods] Analysis on sedimentary environments of barite nodules from calcareous mudstone of the lower Doushantuo Formation in Jinguadun section were developed via sedimentologic and petromineralogical methods. [Result and Discussion] Sedimentary beddings of the surrounding rocks are curved around the barite nodules, indicating that these nodules are probably classified to diagenetic nodules and formed in sedimentary soft muds during the early diagenetic stage. The barite, quartz and pyrite are the three top authigenic sedimentary minerals in the nodules. The mineral distribution is stratified in the barite nodules. Specially, the inner layer contains dense pyrite aggregates dominated by euhedral to subhedral pyrite grains and quartz minerals that grow interwoven together. From the core to the outer edge developed radial aggregates by barite and quartz. This study preliminarily demonstrates that the formation of authigenic sedimentary minerals occurring in different parts of the barite nodules probably precipitate in different redox zones. That is to say, the pyrite and quartz minerals in the inner nodule are formed in the sulfate reduction zone, then the formation location of nodules gradually transits from sulfate reduction zone to sulfate-methane transition zone. The Ba2+ sources in the barite probably originate from the methanogenic zone, where dissolution of labile and biogenic barite associated with organic matter occurs. The upward spreading Ba2+ ions react with downward diffusing seawater sulfate radicals and deposit barium sulfate in the upper front of sulfate-methane transition zone. [Conclusion] The formation process of the barite nodules is staged. Observation on barite nodules indicates that the depth of oceanic sulfate reduction chemocline has descende into the loose sediments beneath the interface of sediment and water body after the Snowball Event at about 600 Ma, due to the increase levels of the continental sulfate input at that time. Methane was partly oxidized in sulfate-methane transition zone, thus reducing the atmospheric emission of marine methane.
The formation and evolution of the Earth's crust is an important aspect of studying the early evolution of the Earth towards livable planets. The successive discovery of early basement rocks and their zircon age information in the Dabie region has made it an important place to study the early Earth. Compared with the limited exposure of basement rocks, the detrital zircons in river sediments can comprehensively reflect the geological evolution information of the source area, and are an effective means to explore the growth and evolution of continental crust. This article conducts U-Pb Hf isotope analysis of zircons in detrital sediments from three different rivers in the Dabie region. The U-Pb zircon age peaks obtained can be divided into four groups: 2676-2424 Ma, 2035-1812 Ma, 890-748 Ma, and 140-120 Ma. Based on the data in this article and previous research results, the following conclusions can be drawn: (1) The magmatic activity records in the Dabie region can be roughly divided into 10 stages and 5 cycles. The quiet periods are 3.0-2.9Ga, 2.4-2.1Ga, 1.8-0.9Ga, 0.70-0.14Ga, and the explosive periods are 4.0-3.0Ga, 2.9-2.4Ga, 2.1-1.8Ga, 0.9-0.7Ga, 0.14-0.12Ga, respectively. (2) The Dabie region mainly experienced four stages of metamorphic events, which occurred in the late Neoarchean (~2.5Ga), middle Paleoproterozoic (~2.0Ga), Triassic (0.24-0.20Ga), and Cretaceous (0.14-0.12Ga). (3) The Dabie region mainly experienced four stages of crustal growth events: initial crustal growth during the Mesozoic era, and massive crustal growth at 4.4-4.1Ga; The crustal growth at 4.1~3.9Ga is relatively slow, with no significant crustal growth; 3.9~2.8Ga sustained crustal growth; The crustal growth rate is relatively slow at 2.8~1.0Ga. (4) Compared to the magmatic, metamorphic, and crustal growth events in the Dabie and Huangling regions, there is a significant difference between the two before~2.0Ga, suggesting that the two were more likely independent micro landmasses before this time.
[Objective]The limestone-marlstone alterations (LMAs) are the important archives of climatic, hydrological, and geological events for geologists. But as a typical endmember of the LMAs, the knowledge about the genesis of the LMAs with eyelid-eyeball structure of the Member I of the Maokou Formation in the Sichuan Basin has not come to agreement widely. This not only seriously affects environmental researching of the LMAs with eyelid-eyeball structure, but also affects the efficiency of its exploration. Dolomitization is developed in the LMAs with eyelid-eyeball structure (mainly in the eyelids) of the Member I of the Maokou Formation of the DB1 well during the penecontemporaneous and early diagenetic phase can be used to constrain the depositional environments of carbonate rocks. [Methods] In this paper, petrological and geochemical analyses have been carried out in detailed, the process and the fluid properties of dolomitization has been discussed to constrain the process of LMAs with eyelid-eyeball structure. [Results and Discussions]Three types of dolomitization are developed in the Member I of the Maokou Formation, which are muddy dolomitic (EDM-I); limy dolomitic (EDM-II) and dolomitic marlstone(EDL). EDM-I has the highest degree of dolomitization, distinct bands of cathodoluminescence, a flat rare earth partitioning pattern, higher δ13C and δ18O values but lower Y/Ho values relative to seawater, it was dolomitized by penecontemporaneous seawater mixed with a small amount of meteoric freshwater during the penecontemporaneous phase. EDM-II has the middle degree of dolomitization, a left leaning rare earth partitioning pattern and values of δ13C, δ18O, 87Sr/86Sr, and Y/Ho similar to seawater, it was dolomitized by seawater with high Mg/Ca, which was induced by frequent sea-level rise and fall changes during the syn-sedimentary and penecontemporaneous phase. EDL has the lowest degree of dolomitization, a left leaning rare earth partitioning pattern, higher δ13C and δ18O values relative to EDM-II, and seawater-like Y/Ho values. EDL was dolomitized by the sealed seawater of the syn-sedimentary phase which has been alterated with the wall rocks in the early diagenetic stage. [Conclusions] The dolomitization of the LMAs with eyelid-eyeball structure by weakly evaporating seawater and seawater mixed with freshwater during the penecontemporaneous and early diagenetic phase requires that the LMAs deposited in a shallower water. The high mud content, high strontium isotope and rare earth element values, low carbon and oxygen isotope values and Y/Ho values of the eyelid-like marlstone relative to the eyeball-like limestone indicate that the depth of water for the eyelid-like marlstone is shallower than that of the eyeball-like limestone during they deposited. Therefore, it is inferred that the LMAs in the Member I of the Maokou Formation were produced under cyclic oscillation in the depositional environment, and their genesis may have been mainly influenced by sedimentary process.
[Objective]Mixed sediments were widely developed in Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Lixian Slope, clarify the mixed sedimentary characteristics and its control on reservoir is of great significance to determines the target area for exploration and development in the next step. [Methods]Based on core, thin section, well logging seismic, as well as laboratory analysis data, the mixed sedimentary types, distribution regularity, control factors, sedimentary model and high-quality reservoir’s formation mechanism in Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Lixian Slope were analyzed. [Results]There are two types of mixed sedimentary in the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in the study area, mixed sedimentary rock, mixed sedimentary strata, the mixed sedimentary rock can be divided into 6 types in three major categories, mixed sandstones, mixed mudstones and mixed carbonate rocks, the mixed sedimentary strata can be divided into 16 types in four?lithofacies assemblages, terrigenous rock-carbonate rock, terrigenous rock- mixosedimentite, carbonate rock-mixosedimentite, mixosedimentite. The Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Lixian Slope have typical mixed features, which can be divided into 8 mixed sedimentary microfacies, including underwater distributary channel, mouth bar sheet underwater diversion bay, mud flat,?sandy beach bar, carbonate beach bar, inner beach and the semi-deep lake mud,?the mixed sediments have the characteristics of rapid phase transformation in the lateral direction, multiple types of rock superimpose frequently in the vertical, the mixed sediments have different distribution characteristics?of different intervals. The mixed sediments were controlled by climatic and water environment, tectonic background and palaeogeomorphology, sediment supply?and lake level changes, two kinds of mixed depositional model are developed,lowstand period and high-stand periods. The mixed sediments plays a significant role in reservoir controlling factors, the sandy beach bar and carbonate beach bar where developed in high-energy facies zone are the favorable mixed sedimentary microfacies, the closed saline water environment is the foundation of reservoir formation, controlled the formation and distribution of high-quality reservoirs, sedimentary cycles controlled the development degree and distribution palace of high-quality reservoirs. [conclusion] the palaeogeomorphology highland in the southwestern are favorable areas for mixed beach bars development and exploration practice.
[Objective] The Qigebrak Formation developed abundant microbial carbonates, which are the favorable target for deep to ultra-deep oil and gas exploration. However, the existing stratigraphic division scheme of the Qigebrak Formation remains controversial, hindering the analysis of reservoir depositional evolution and distribution prediction. Further in-depth research and clarification are urgently needed. [Methods] This study focused on the Shiairik section in the northwest Aksu area of the Tarim Basin to define the depositional environment and sea-level change, and conduct a sequence stratigraphic division of the Qigebrak Formation based on the analysis of high-precision depositional facies and the Fischer plot. [Results] Ten main facies are recognized from the Qigebrak Formation and grouped into a carbonate ramp platform. Two subfacies; i.e., inner and middle ramp, are developed under this setting. The inner ramp consists of the tidal flat, lagoon, tidal channel, and grain shoals. Eight subtypes of peritidal cycles, two subtypes of shallow subtidal cycles and two subtypes of middle-ramp cycles are identified. Based on the stacking patterns reflected in the Fischer diagrams, analysis of orders of depositional facies and proportion of subtidal facies, the Qigebrak is divided into four third-order T-R sequences (SQ1–SQ4). Among these sequences, SQ1 only records the regressive system tract in the Qigebrak Formation, whereas SQ4 only preserves the transgressive system tract. [Conclusions] This study suggests that (1) it is reasonable to divide the Qigebrak Formation into four sequences; (2) the top of the Qigebrak Formation could have experienced the million-year-scale exposure and erosion, which would favor the formation of scaled reservoirs.
The saturated hydrocarbons of 26 coal measure source rock samples in the Upper Paleozoic of Ordos Basin were analyzed by gas chromatography and chromatography-mass spectrometry. According to the distribution characteristics of tricyclic terpanes (TT), the source rock samples in the study area were divided into three different types of distribution patterns. The C19TT is the main peak of the type I source rock, and the content of C19TT, C20TT and C21TT gradually decreases. At the same time, the Pr/Ph ratio is high and the content of C24 tetracyclic terpane is also rich in this type of sample. This kind of samples are mainly humic coal and carbonaceous mudstone, revealing the characteristics of lacustrine facies sedimentary environment. On the contrary, the tricyclic terpanes of type II source rocks are dominated by C23TT, and the contents of C19TT, C20TT and C21TT are gradually increasing, while the Pr/Ph ratio is low, and the content of C24 tetracyclic terpane is not abundant. In addition to coal-bearing mudstone, there are also humic coal and carbonaceous mudstone in these samples, and their sedimentary environment is quite different from that of type I source rocks. The distribution of tricyclic terpanes in type III source rocks is between type I and type II source rocks. On the one hand, the main peak carbon of tricyclic terpane is C23TT, on the other hand, the relative content of C19TT, C20TT and C21TT decreases in turn and shows the characteristics of stepwise distribution. In addition, the Pr/Ph ratio and the content of C24 tetracyclic terpane are between type I and type II source rocks. The results also reveal that with the increase of the thermal evolution degree of source rocks, the total amount of tricyclic terpanes shows an gradually increasing trend, but the distribution patterns of tricyclic terpanes in different types of source rocks have not changed significantly, in other words, the different distribution patterns of tricyclic terpanes in coal-bearing source rocks in the study area are less affected by the thermal evolution degree of organic matter, but mainly controlled by sedimentary environment and parent material type.
Qiangtang Basin, located in the most important oil & gas accumulation belt worldwide - eastern section of Tethys tectonic domain, has been listed as a strategic preparation area for oil & gas resources. However, there had been great arguments on the potential of oil & gas resources, which restricted the overall understanding of oil & gas exploration in Qiangtang Basin. Restoring the denudation history of basin in key tectonic periods and analyzing the burial history of source rocks is of great significance to deepen the hydrocarbon potential of leading source rocks and oil & gas resources in Qiangtang Basin. Based on the current data and previous research results, the main tectonic activities were analyzed and the denudation history of Qiangtang Basin in key tectonic periods were restored by using the structural-sedimentary extrapolation method. At the same time, the burial history of three sets of leading source beds in the Upper Triassic-Jurassic was analyzed by using the TSM basin simulation system. The results showed that: 1) Since the Late Triassic, Qiangtang basin had experienced four periods of tectonic movements: one period from the late Triassic to early Jurassic (210-180Ma)、the late Early Cretaceous (120-110Ma) and the Paleocene to the early Eocene (60-45Ma) and since the early Miocene; 2) At the first period (210-110Ma), Most areas of the basin was uplifted to the surface. The top of the Late Triassic Formation was denuded to form an ancient weathering crust, and then the volcanic rocks were deposited. The central uplift zone of the basin and the Northern Qiangtang were denuded most strongly; Between 120 and 110Ma, the basin strata were folded strongly, and the denudation was most intense in the central uplift zone and its two sides, and in the eastern part of the basin. The denudation is relatively weak in the middle and west of the North Qiangtang depression, and the south of the South Qiangtang. From 60 to 45 Ma, influenced by the long-range effect of the collision between the Indian continent and the Asian continent, the basin shortening rate is 11.9%, and the average uplift and denuded is about 700m. Since 23Ma, the basin continues to be affected by the north-south extrusion stress, and the whole basin escapes to the southeast direction. The basin's thrust faults continue to be active generally and more uniformly, and a number of normal faults or grabens were developed. The uplift rate of all parts of the basin is similar, and the uplift erosion is about 700m to some extent. 3) Influenced by the sedimentary thickness of the stratum and the differential denudation of multi-stage tectonic uplift, the maximum burial of the Upper Triassic Jurassic source beds in Qiangtang Basin occurred twice after the deposition of the J3-K1 Xueshan Formation and after the deposition of the Neogene Nkangtuo Formation and Suonahu Formation, respectively. The two main hydrocarbon generation periods corresponded to the two maximum burial depths and the subsequent tectonic uplift.
[Objective] In the western Sichuan Basin, the Middle Permian extensively features marine carbonate rocks, with dolomite being a focal point of geological investigation. However, the diverse and irregular distribution of dolomite types in the Middle Permian results in significant variations in dolomite characteristics across different regions. The rich variety of dolomite types described above constitutes an excellent set of natural gas reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin. [Methodology] To unravel the fluid dynamics of dolomites in the study area and reconstruct their diagenetic environments, the study extensively reviewed a substantial body of previous literature and references. samples from 16 well cores and 9 sections underwent a comprehensive analysis. Utilizing techniques such as microscopic thin section observation, cathodoluminescence, carbon-oxygen isotopes, strontium isotopes, and ICP-MS rare earth element analysis, the petrological and geochemical features were thoroughly investigated. [Results] The research findings can be summarized as follows: (1) Dolomite Types: Dolomites in the region can be broadly categorized into homogeneous dolomite and zebra-like dolomite. The primary type of homogeneous dolomite is granular dolomite, while zebra-like dolomite includes homogeneous dolomite with dark bands, predominantly filled with hydrothermal saddle dolomite. (2) Isotopic Analysis: Carbon Isotopes: Samples from the study area exhibit positive anomalies in carbon isotopes. Oxygen Isotopes: Oxygen isotope values show significant differences, with the filling material (saddle dolomite) exhibiting notably lower values than homogeneous dolomite. Oxygen isotope values in samples from southwestern Sichuan are significantly lower than those from northwestern Sichuan. (3) Rare Earth Elements: Rare earth element analysis reveals a negative anomaly in δCe and a positive anomaly in δEu, indicating that the oxidation conditions of the products were influenced by later-stage hydrothermal alteration. (4) Strontium Isotopes: Strontium isotopic values of homogeneous dolomite fall within the range of contemporaneous seawater. However, the filling material in southwestern Sichuan exhibits strontium isotopic values higher than the seawater range and significantly higher than homogeneous dolomite. [Conclusion] (1) Hydrothermal Modification: The diagenetic fluids responsible for the formation of homogeneous dolomite in the western to northern Sichuan region are primarily derived from contemporaneous seawater. Subsequent hydrothermal activities lead to modifications, resulting in the formation of hydrothermal saddle dolomite. Notably, the intensity of hydrothermal activity is more pronounced in the southwestern region and relatively weaker in the northwestern part of western Sichuan. (2) Diagenetic Environments: The diagenetic environments of dolomites in the study area encompass four types: marine diagenetic settings, shallow-to-intermediate burial diagenetic environments, and intermediate-to-deep burial diagenetic environments. The marine environment refers to an open-sea, grain shoal environment, predominantly developing fine to medium-crystalline dolomite. Inclusions exhibit a uniform temperature below 85°C. Shallow-to-intermediate burial environments, with burial depths ranging from approximately 800m to 2000m, primarily foster homogeneous fine-crystalline dolomite and some medium-to-coarse-crystalline dolomite. Inclusions exhibit a uniform temperature above 112°C. Hydrothermal saddle dolomite mainly develops in intermediate-to-deep burial environments with burial depths exceeding 3000m, and inclusions exhibit a uniform temperature above 175°C. This comprehensive research provides nuanced insights into the diverse dolomite types and their diagenetic histories, contributing significantly to the broader understanding of sedimentary processes and geological evolution in the western Sichuan Basin during the Middle Permian period.
The dolomite evaporite symbiotic system is widely distributed during the Middle Triassic period in the Sichuan Basin, but its sedimentary characteristics lack systematic characterization. The development and distribution patterns and main controlling factors are still unclear. Based on drilling, core, and seismic data, this article characterizes the sedimentary characteristics of the developed dolomite evaporite symbiotic system in the study area at multiple scales, elucidates the genetic mechanisms of different types of symbiotic systems, and further reveals their spatiotemporal distribution patterns and main controlling factors. The research results indicate that: (1) Four types of symbiotic systems are mainly developed in the Leikoupo Formation in the northwest Sichuan Basin: thick layer of dolomite with thin layer of evaporite, interlayer of dolomite and evaporite, thick layer of evaporite with thin layer of dolomite, and overlapping of thick layer of evaporite with thick layer of dolomite. They are respectively formed in gypsum containing lagoons, cloud containing gypsum containing lagoons, gypsum salt lakes, and gypsum salt basins. Among them, thick layer of dolomite mixed with thin layer of evaporite is widely distributed in the four periods of Leikoupo. Thick layer of evaporite mixed with thin layer of dolomite, and the overlap of thick layer of evaporite and thick layer of dolomite is the most developed in the central part of the Leisan and Leisi sedimentary periods of the basin. (3) The uplift of the Longmenshan Island Chain on the west side resulted in southeast compression of the basin, while the uplift of the Xuefeng Mountain on the east side restricted the southern migration of the Luzhou Kaijiang ancient uplift. The southern subduction of the Qinling Mountains jointly formed a nearly northeast southwest structural pattern in the Sichuan Basin, controlling the overall distribution of gypsum and symbiotic systems in a northeast southwest direction. (4) Affected by the significant uplift of the Luzhou Kaijiang ancient uplift, the later subsidence center of the Leikoupo Formation migrated to the west, and the gypsum sedimentary center and four symbiotic systems correspondingly developed from early dispersion to later concentration and migrated to the west. Under the constraints of different types of symbiotic systems, the paleogeography of the Leikoupo Formation was reconstructed for four periods. The above research provides a new understanding for the study of the symbiotic system of dolomite evaporite in the northwest Sichuan region, and also has a guiding role in the reconstruction of regional paleogeography.
Since 2019, CNPC has conducted exploration on the Upper Cretaceous Donga strata in the Trakes Slope of the Termit Basin, Niger. Several wells obtained industrial oil flows, demonstrating good exploration potential. Compared to the Paleogene fluvial-deltaic Sokor1 Formation, the detailed characteristics of the Upper Cretaceous marine sandstones of the Donga Formation have not yet investigated in detail. In the present study, based on seismic, wireline and mud logging data, 53 side wall cores and cutting samples from 4 wells were analyzed thin sections, casting thin sections, X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope, gamma-ray spectral logging, etc. This study investigate the reservoir characteristics of the DS1~DS3 members of Donga Formation, and analyze their controlling factors. The results show that rock types of DS1 member are fine-medium grained quartz sandstones with high component maturity, whereas that of DS3 member are fine grained lithic quartz sandstones with cements mainly of calcareous minerals. The quartz grains are sub-round to round with moderate to poor sorting. The matrix are mainly composed of kaolinite and calcites, and sandstones exhibit point and line contacts. The most common diagenetic process were compaction, cementation and dissolution, and compaction and cementation are obvious. The sandstones commonly experienced dissolution, and pore types are mainly intergranular pores with medium to ultra-low porosity and permeability. The high-quality reservoirs of the Donga Formation are mainly distributed in the DS1 member. Physical properties of sandstones become better from the west to east in Trakes Slope. The analysis results show that sandstones development in the Donga Formation is mainly controlled by three factors. Firstly, vertical distribution of sedimentary facies and sandstones were mainly controlled by sea level changes. The DS1 member, deposited in the early stage of marine transgression, mainly consists of distributary channel sandstones, whereas DS3 member, deposited during the highest sea level, is dominated by delta front sheet sandstones and distributary channel sandstones. The high salinity of sea water in this period resulted in high content of carbonate cement, and poor physical properties of reservoir rocks. Secondly, the stable gentle slope in the Late Cretaceous was favorable for the development of sand bodies, and the intense strike-slip fault activities in the Paleogene induced the formation of micro-fractures in reservoir rocks, effectively improving their physical properties. Thirdly, the rigid support of quartz sandstones was favorable for the preservation of primary pores, and the dissolution of unstable minerals such as feldspar and calcareous minerals improved the pore structure of reservoir rocks. The development of regional cap rocks of marine mudstones and shales is conducive for the formation of “self-generation and self-preservation” play in the Donga Formation. Compared with the low slope of the Trakes Slope, sandstones with better physical properties are well developed in the middle and high slope which are closer to the eastern provenance. They are favorable exploration areas for the Donga Formation.
【Objective】The carbonate-evaporite syngenetic system is widely distributed in the Cambrian of the Sichuan Basin, however, the developmental characteristics, depositional environments, depositional processes, and evolutionary modes of this syngenetic system are weakly studied, and the research methods need to be clarified urgently. 【Methods】The petrological characteristics of the symbiotic system, the state of the evaporites, the depositional environment of the symbiotic system, the depositional process and the evolutionary pattern of the symbiotic system are investigated based on the data of drilling cores, field sections, rock sheets and carbon and oxygen isotopes, and the isotopic signatures of Fe, Mn and S. 【Results】The results show that 1) the developmental characteristics of the symbiotic system, 2) the depositional environment, and 3) the evolutionary pattern of the symbiotic system are not well understood, but are not well understood. The results show that: 1) the carbonate-evaporite symbiotic system in the study area has developed five kinds of carbonate-evaporite symbiotic system rock assemblage sequences, including: carbonate rock and evaporite interbedded, evaporite sandwiched with carbonate rock, evaporite overlain carbonate rock, carbonate rock overlain with evaporite rock, and carbonate rock sandwiched with evaporite rock. 2) the geochemical features of the symbiotic system, including δ18O, mainly concentrated in -8‰~-9‰, and δ13C, mainly concentrated in -8‰~9‰; δ13C is mainly concentrated in -1‰~3‰; the results of using carbon and oxygen isotope values to calculate palaeosalinity and palaeotemperature show that the vast majority of Z values>120‰ and δ13C values>-2‰, and the palaeoseawater temperatures are in the range of 23.10~40.64℃; Fe is mainly concentrated in the range of 0~2000×10-5; and Mn is mainly concentrated in the range of 10-5~30×10-5, which indicates that in the Gautai Group During the Gaotai Formation, the depositional environment was a warm or hot paleoclimate and saline seawater environment, with a high degree of oxidation of the water body, and the rock-forming action in a relatively open system related to atmospheric water was experienced.3) Deposition of marine carbonate rocks and evaporites in a symbiotic system against the background of an arid and hot climate and a Ca-rich and low-SO4 calcite sea with a high degree of salinity The period of time can be divided into the sea level falling evaporite - dolomite deposition stage and sea level rising dolomite - evaporite - greywacke deposition stage; "tidal ping Sabuha mode" and "underwater condensed deposition mode" are two kinds of carbonate rock - evaporite symbiosis system development mode.【Conclusion】The carbonatite-evaporite symbiotic system carries the information of paleoenvironment, paleoclimate and paleohaline water chemistry during the depositional period, and also records the depositional process and evolutionary pattern of the symbiotic system. This study provides new ideas and understanding of the depositional environments and depositional patterns of the carbonatite-evaporite symbiotic system of the evaporitic environment of the marine phase of the Cambrian Gautai Formation.
Paleo-geomorphology has a strong control on the sedimentary system and reservoir distribution. This paper analyzes the single-well facies in Gaoquan Structural Zone of Sikeshu Sag, identifies the characteristics of the sedimentary and reservoirs of the Qingshuihe Formation, and then combines with the paleo-geomorphology of the pre-Qingshuihe Formation in Gaoquan Structural Zone, establishes model of the sedimentary evolution under the control of paleo-geomorphology, and clarifies the influence of micro-geomorphology on the distribution of high-quality reservoirs. The study shows that three slope breaks are developed in the Gaoquan Structural zone of Sikeshu Sag, with a near-northwestern-south-eastern trend. Each slope-folding zone can be divided into two types of paleo-geomorphology units, namely, grooves and platforms. Three phases of regressive fan deltas were formed on the three slope breaks during the lake transgression, and each phase of fan deltas can form 9-15m thick conglomerate reservoirs. On each slope breaks, the groove and platform control the mud content of the conglomerate reservoirs, and the brown conglomerate with high mud content is easily developed in the groove area, while the gray or gray-green conglomerate with low mud content is easily developed in the platform area. The conglomerate with low mud content is ready to form high-quality reservoir in the platform area.
Abstract: [Objective] In order to discuss the high-frequency sequence division and effect of high-frequency sedimentary cycle control reservoir in carbonate strata. [Methods] Used the Th/U ratio curve in natural gamma ray spectrum logging as the indicator curve, combined with Fisher diagram and lithological assemblage sequence, high frequency sequence of Ma51-5 sub-member of Majiagou Formation were divided quantitatively in Tao 7 block of Ordos basin. [Results] The research shows that the Th/U ratio in natural gamma-ray spectroscopy logging can be used as an indirect alternative index of astronomical orbit in carbonate strata. The high-frequency sequence can be effectively divided by quantitative and qualitative analysis methods such as spectrum analysis combined with Fisher diagram and lithologic lithofacies analysis. Ma51-5 sub-member in Block 7 can be divided into one third-order sequence, six fourth-order sequences and twenty fifth-order sequences. It is estimated that the average deposition rate of Ma51-5 sub-member is 5.03 cm/kyr and the deposition time is about 2.43 Ma. The gypsum pseudocrystal dolomite , which developed in the upper part of the intertidal zone and in the top of the high-frequency sedimentary cycle with upward shallowing, is the dominant facies belt for reservoir development. Near the high-frequency sequence boundary of the fourth-order sequence is the favorable interval for reservoir development. The frequent changes of sea level cause early karstification, which is the main driving force for the formation of karst model pores in the Ma51-4 sub-member and the basis of later supergene gas karstification. [Conclusion] Quantitative identification and division of high-frequency sequence is impotant for reservoir prediction in carbonate strata.
The Yuzhou area is the most highly studied on Upper Paleozoic coal-bearing strata of the southern part of North China Block, which has abundant sedimentological and stratigraphic paleontological research basis, however, due to the lack of absolute chronology data, the division of chronostratigraphy and regional large-scale stratigraphic correlation are affected. In this paper, a laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) was applied to date the U-Pb age of detrital zircon of two mudstone samples near the stratigraphic boundary of Taiyuan-Shanxi Formations and Xiashihezi-Shangshihezi Formations in Yuzhou area, and to determine their maximum depositional ages. The results show that: ①The 40 detrital zircons from the bottom sample of Shanxi Formation (ZK1006-5) constitute a continuous young component spectrum ranging from 283Ma to 343Ma, with the youngest single zircon age (YSG age) is 283±9.4Ma. The 18 detrital zircons from the bottom sample of Shangshihezi Formation (ZK2387-3) constitute a continuous young component spectrum ranging from 257Ma to 299Ma, with the youngest single zircon age (YSG age) is 257±6.8Ma.They can represent the maximum deposition age of the sample strata, indicating that the deposition time is no earlier than 283±9.4Ma and 257±6.8Ma. ②The deposition of Shanxi Formation and Shangshihezi Formation in Yuzhou area began in Kungurian and Wuchiapingian, respectively, which is consistent with regionnal biostratigraphic data. ③The Upper Paleozoic coal-bearing strata of the North China Block have obvious and large span of rock strata penetrating, and the overall performance is characterized by inward penetrating of the plate edge gradually through the new characteristics. Based on the previous studies on volcanic events in the Late Paleozoic basin of North China Block, it is concluded that the eastern margin of the basin was strongly active in which the same sedimentary period, and the induced magmatism, tectonic activity, biological succession and transgression may be related to the formation of the ancient continent of Laurisia land at the same time.
Aiming at the problem of unclear fan formation mechanism and sedimentary filling process under the condition of no well, from the perspective of source and sink system, three-dimensional seismic data were used to comprehensively analyze the denudation capacity and transport path of the source area of Bonan low bulge, and the sedimentary response characteristics and coupling mechanism of the large sublacustrine fan in the southeastern slope of Bozhong depression were clarified. The developmental model was summarized. The results show that: (1) The second of Dongying sequence is in the transition stage of lake basin fault depression, which can be divided into two tertiary sequences, in which the sublacustrine fan mainly developed in the highstand systems tract of the lower second of Dongying sequence; (2) The denudation flux in the eastern part of the Bonan low bulge is greater than deposition flux of the subestrustrine fan. The large subestrustrine fan is mainly influenced by the near province-source, and the braided river delta formed in the high part of the uplift does not pass through, and is discharged under the depositional break of the slope along five transport channels spreading from south to north. The coupling of near source supply, transport channel and sedimentary slope break formed a large contiguous lacustrine fan deposit. (3) The sedimentary filling of sublacustrine fan is controlled by the location of restricted palaeogeomorphology and the size of the space that can be accommodated. Among them, the early restricted paleogeomorphology formed A large space, and the fan sand body of the lake bottom was preferentially unloaded, forming three fan sediments, A, B and C. Due to the spatial limitations on both sides and the strong hydrodynamic conditions, the seismic facies showed the characteristics of chaotic downcut waterways and lateral migration superimposed, and the sand body formed was relatively rich in sand. With the inflow of gravity flow, the space that can be contained gradually decreases, and the gravity flow overflows along the recharge channel to the center of the open lake basin, forming two fan bodies D and E. Due to the dilution of water concentration and the change of paleo-geomorphology, the energy gradually weakens. The seismic phase has the characteristics of laminary-strong amplitude reflection, the channel features are not obvious, and the sand richness is moderate. The late source supply and energy are weak, and compared with the local erosion and reconstruction of the early fan, the earthquake shows weak amplitude reflection, which is dominated by the muddy channel. The large-scale sublustrine fan has the spatial and temporal distribution and evolution law of early restricted filling, mid-stage overflow adjustment and late erosion transformation, which constitute the development characteristics of transverse continuous and vertical multi-stage superposition. The three fan bodies A, B and C below the first stage have good sand-rich, shallow burial, good oil and gas migration and accumulation conditions, and good reservoer-cap combination. The sweet area of C-fan is large, which is an important target for lithologic reservoir exploration in Bohai sea in recent years.
[Objective] The previous regional geological data regarded the Sanjie sand and gravel section in Juren Town, Binxian County, Heilongjiang Province as the Luojiaweng Formation, but the study of its stratigraphic properties and sedimentary environment is weak, which greatly limits the in-depth understanding of regional surface processes recorded in this stratum. [Methods] From the perspectives of sedimentology, mineralogy, elemental geochemistry and U-Pb chronology of detrital zircon, the chemical weathering characteristics, source rock properties, sedimentary environment and tectonic setting of the provenance area of this section are discussed. [Results]The results show that the weathered degree of sand and gravel in the three sections is low, the sorting is poor, the roundness is good, and there is no obvious directional arrangement. The gravel lithology is mainly granitic rock (46.31%) and quartzy rock (28.19%), followed by syenite (0.2%), tuff (0.01%) and schist (0.01%). The heavy minerals were mainly sphenite (65.18%) and epidote (11.87%), but the other heavy minerals were less active. Elemental geochemistry reveals that the sediments in the three sections have a weak to moderate degree of chemical weathering, most of the sediments have undergone a primary cycle, and their parent rock type is felsic. According to the geochemical migration and enrichment of elements and the paleoclimate discrimination diagram, the sediment is revealed to be braided river sediment in arid oxidation environment. The zircon U-Pb ages are distributed in a narrow range (134.2~220.3 Ma, with a peak age of ~168 Ma), indicating the detrite contribution from Zhangguangcai Mountain, and indicating the subduction movement of Mudanjiang Ocean and the transformation of extensional environment after the subduction of the eastern oceanic plate to orogeny. Compared with the standard strata of Luojiawang Formation, there are significant differences in sedimentological characteristics, genetic types and geomorphologic characteristics of the three-section section. It is speculated that the formation time of the three-section section is later than that of the standard strata of Luojiawang Formation, and the time is roughly the same as that of Baitushan Formation. [Conclusion]This provides important indications for the division of the Quaternary strata in Harbin and the coupling relationship between regional structure geomorphology climate water system evolution.
C-6 Oilfield is one of the most principal oilfields of Caofeidian oil province with hundred million cubic metre of reserves. The third oil group of Guantao Formation (N1gⅢ), the main production zone of C-6 Oilfield, is sand-rich braided river deposit. The architecture and connectivity of braided river sandstone are the key geological factors affecting the development effect of the Oilfield. Calibrated with limited log data, intelligent fusion technology of multiple seismic attributes was introduced to finely characterizes the spatial distribution of the level-4 architecture units of the braided river reservoir. According to log interpretation, N1gⅢ of C-6 oilfield mainly develops two types of level-4 architecture units, namely, channel bar and braided channel, and braided bar is the best reservoir with high sandstone thickness and excellent physical properties. Based on seismic attribute extraction and correlation analysis with lithological and physical parameters, reflection intensity, relative impedance, sweet point, original amplitude, envelop were chosen as intelligent fusion seismic attributes with Deep Feed-Forward Neural Network (DFNN) algorithm under the supervision of porosity. The 3D attribute of DFNN fusion, representative of lithology and petrophysical property, largely improves the detecting ability of braided river sandstone unit and its boundary, and can be used to finely characterize the plan and section distribution of braided river level-4 architecture units effectively. A NE-SW braided flow zone was developed in N1gⅢ of C-6 oilfield, which could be internally sub-divided into 15 rhombic level-4 architecture units of the braided bar. Distributary channels, another level-4 architecture units, surrounded braided bar in a narrow strip. The level-4 architecture interface between the two units played as seepage barriers for fluid migration. The braided bars cut and overlapped one another vertically, forming “big bar and small channel” plan reservoir architecture pattern. The fine characterization results deepened the understanding of the reservoir connectivity of the braided river reservoir with sparse well pattern, which provided direct geological bases for the making of optimized adjustment plan of C-6 Oilfield.
The Middle Permian to Lower Triassic stratigraphy in the Fars region of the southern Persian Gulf harbors substantial oil and gas resources, making it a focal area for China's overseas exploration efforts. The current research lacks a comprehensive sequence stratigraphy and a macroscopic understanding of the sedimentary evolution of the entire oil-bearing succession. This study focuses on the Middle to Upper Permian Dalan Formation and the Lower Triassic Kangan Formation in the region. Utilizing data from individual wells, cross-sections, core samples, thin sections, well logging, and IHS and C&C databases, along with consideration of regional geological context and existing knowledge, the Middle Permian to Early Triassic in the study area is stratigraphically divided into sequences. The study provides an in-depth analysis of the characteristics and evolution of each sequence's sedimentary systems. The results indicate that the Dalan-Kangan formations in the study area exhibit six sequence boundaries and five maximum flooding surfaces. Based on the types of sequence boundaries and the development of maximum flooding surfaces, the Dalan and Kangan formations in the southern Persian Gulf are subdivided into five third-order sequences. The targeted lithology is predominantly carbonate ramp deposits, further categorized into inner ramp, mid-ramp, and outer ramp subfacies. The inner ramp can be subdivided into six depositional microfacies: Sabkha in the intertidal zone, tidal flat, lagoon, back-barrier, shoal middle, and shoal front. The study area represents an arid and hot shallow-water carbonate deposition environment. During the SQ1-SQ2 deposition period, a predominantly progradational sedimentary model is observed, while the SQ3 deposition period follows a retrogradational and aggradational model. The SQ4 deposition period returns to a progradational model, and the SQ5 deposition period is characterized by a retrogradational model.
[Objective] By analyzing the influence of the periodic change of earth orbit on the periodic change of climate, this paper discusses the climate change characteristics of the Lower Oil Sand Mountain Formation in Qaidam Basin, and establishes a high-resolution astronomical scale for the Lower Oil Sand Mountain in Qaidam Basin based on Milankovitch theory to identify and divide high-frequency sequences. [Methods] Firstly, Laskar algorithm is used to calculate the variation period of the earth's orbital parameters during the summer solstice at 35 north latitude from 14.5~23.8 Ma, and the Miocene cycle theory and Miocene cycle ratio in this sedimentary period are determined. Then, taking wells Xianzhong 39, Xianzhong 8-9 and Xianzhong 8-12 in Nanbaxian oil and gas field as examples, the natural gamma data are analyzed by frequency spectrum and continuous wavelet transform. Finally, according to the orbital period, the average sedimentation rate of the Lower Youshashan Formation is calculated, and the "floating" astronomical scale of well Xianzhong 39 is established. [Results] Through the analysis of frequency spectrum and continuous wavelet transform, the Neogene Lower Youshashan Formation is mainly controlled by eccentricity periods of 400 ka and 95 ka. The average sedimentation rate of the Lower Youshashan Formation is 0.094 41 m/ka, and the sedimentation duration is 7.2 Ma. Based on the 400 ka long eccentric period curve and 95 ka short eccentric period curve as benchmark curves, 18 fourth-order quasi-sequence groups and 72 fifth-order quasi-sequence groups were identified. [Conclusion] The results show that the climate change recorded in the Lower Youshashan Formation is obviously controlled and driven by cycles. Identification and division based on Milankovitch theory can reduce the influence of subjective factors, improve the accuracy of division results, and more accurately describe the climate change characteristics in sediments. These research results are helpful to deeply understand the evolution law of the earth's climate and provide important reference for oil and gas exploration and resource evaluation.
The East Mariana Basin of the West Pacific Ocean, which is located in the east of the Mariana Trench, south of the Magellan Seamounts, and north of the Caroline Seamounts, is an ideal area for the study of Asina aeolian dust deposits, but the sediment research of the East Mariana Basin is still weak. In order to reveal the sediment geochemical characteristics and provide background data for further sediment provenance, seabed mineral resources evaluation and climate-environment evolution research, element geochemistry of surface sediments in the East Mariana Basin was studied. Based on 28 pelagic clay surface sediment (0-10 cm) samples collected in the east part of the East Mariana Basin using the box sampler and gravity sampler, contents of major elements, trace elements and rare earth elements of the sediments were analyzed by ICP-OES and ICP-MS methods. Then, elements geochemical characteristics were analyzed, and their influencing factors and indicative significance were discussed. The results show that the contents of major elements in the pelagic clay sediments in the study area are roughly the same as those in the neighboring sea areas of the West Pacific Ocean. The distribution pattern of major elements (oxides) in sediments follows SiO2 > Al2O3 > Fe2O3 > Na2O > MgO > K2O > CaO > MnO > TiO2 > P2O5. The highest content of major elements is SiO2, with an average of 49.14%, followed by Al2O3, with an average of 15.85%. The highest content of trace elements was Ba, with an average of 770×10-6, followed by Cu, with an average of 289×10-6. The average of total rare earth elements ∑REE is 284×10-6, which is light rare earth-rich type, with the highest Ce, Nd and La contents. Principal component analysis of elements shows that the composition of chemical elements can be divided into four categories: The first type is closely related to rare earth elements, including rare earth elements ( except Ce ), P2O5, TiO2, etc., the second type is related to Fe-Mn micronodules, including Fe2O3, MnO, Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Ba and other metal elements, the third type is related to terrigenous debris, including Al2O3, MgO, SiO2, U, Hf, Th, Ce, etc., the fourth type is related to biological sources, including Cd, CaO, Mo. The elements combination indices (Si/Al, Fe/Al, La/Tb, Th/Sc, etc.) and the elements combination projection diagrams (La-Th-Sc triangle diagram, La/Th-Hf bivariate diagram) further reveal that the sediments sources are dominated by terrigenous materials, especially terrestrial aeolian dust materials. Meanwhile, the Chemical Index of Alteration (CIA) indicates that the parent rocks in the sediment source area are in low-medium chemical weathering conditions. The redox sensitive elements (Cr, Ni, V, U, Th, etc.) combination reveals that the bottom sedimentary environment in the study area is oxidation-weak oxidation environment. This study has some reference significance for understanding the influence of the Asian aeolian dust on the sediment provenance of the East Mariana Basin, revealing the sedimentary environment characteristics of the basin and the distribution of seabed mineral resources.
[Objective]Dengying Formation in Penglai area of central Sichuan has achieved a major breakthrough in exploration, but the fourth member of Dengying Formation has experienced multiple stages of oil and gas charging due to its large burial depth, old age and complex diagenetic evolution, the relationship between reservoir pore evolution and oil and gas charging is still unclear. [Methods]Based on drilling coring data, the petrological types, reservoir space characteristics, diagenetic types, diagenetic evolution sequence, pore evolution and hydrocarbon charging of the fourth member of Dengying Formation were studied by means of thin section observation, cathodoluminescence, in situ microelement analysis and fluid inclusion. [Results and Discussions]The reservoir rock types of the fourth member of Dengying Formation in Penglai area are mainly crystalline dolomite, granular dolomite and microbial dolomite. The types of reservoir space can be divided into three types: cave, pore and fracture. The main diagenetic types are syngene-parsyngenetic dissolution, epigenetic dissolution, buried dissolution, cementation and filling, tectonic rupture, silicification and compaction. Diagenesis in different stages jointly controls the evolution of reservoir pores in the four members of Dengying Formation, among which the constructive diagenesis is dissolution and rupture in different periods, and the destructive diagenesis is compaction and pressure-dissolution and cementation and filling.[Conclusion] The filling sequence of cement in the solution holes of the fourth member of the reservoir can be divided into: the first generation blade-like dolomite → the second generation powdery dolomite → the first stage bitumen → the third generation fine crystalline dolomite → the fourth generation medium crystalline dolomite → the fifth generation coarse crystalline dolomite → the sixth generation giant crystalline saddle-shaped dolomite → the second stage bitumen → the seventh generation quartz, fluorite and other minerals. According to the information of fluid inclusions captured by cemented fill of each stage, such as type, phase state and homogenization temperature, the oil-gas charging process of Dthe fourth member of Dengying Formation in Penglai Area was reconstructed: Paleo-oil reservoir charging in the middle and late Silurian period (the first phase of fossil oil reservoir) → late Caledonian paleo-oil reservoir destruction → Middle Triassic paleo-oil reservoir charging (the second phase of fossil oil reservoir) → Late Jurassic paleo-gas cracking in paleo-oil reservoir → the adjustment and formation of paleo-gas reservoir from Late Cretaceous to present, in which the late oil cracking gas → gaseous hydrocarbon charging is the main forming period of the fourth member gas reservoir of Dengying Formation.
[Objective]The reticulated laterite in southern China is a good geological carrier for Quaternary environmental changes, but there is currently relatively little microscopic research on bedrock reticulation,Not conducive to a comprehensive understanding of reticulation [Methods]Through micro-area analysis techniques, geostatistical and factor analysis, and other methods to conducted elemental geochemical analysis on the white vein micro-area of the bedrock and variegated?horizon in the Langxi profile. [Results]1) Element content in the white vein micro-area of sandstone: The content of iron group elements such as Fe2O3 (1.14-13.29%) and Mn (87×10-6 -3230×10-6) showed a trend of increasing from the center of the white veins to the periphery. However, the spatial distribution of other major elements and stable elements such as Ti (1294×10-6~ 2454×10-6) and Zr (171 ×10-6~ 197×10-6) showed the opposite trend. The spatial distribution of element content in the bedrock layer is basically consistent with that of the variegated?horizon. 2) Ti/Zr (bedrock layer: 7.23-12.89; reticulated layer: 12.82-21.84) and Ti/Al2O3 (bedrock layer: 0.013-0.018; reticulated layer: 0.044-0.062) were divided into two groups through cluster analysis and scatter plot.They have different provenance 3) The weathering of the bedrock layer (CIA: 86.37%~87.49%; SA: 5.23~5.76) is slightly higher than that of the variegated?horizon (CIA: 85.10%~86.07%; SA: 6.91~8.16;). The leaching intensity of elements such as Al2O3 (17.3%)、 Fe2O3 (73.91%) and MnO (76.68%)in the bedrock white vein micro-area and Al2O3 (15.78%) 、Fe2O3 (70.39%) and MnO (74.84%) in the variegated?horizon white vein micro-area showed a trend of decreasing from the center of the white veins to the periphery. 4) The common feature of factors in the white vein micro-area of the bedrock layer and the reticulated layer is that they are mainly factor 1, which reflects the leaching migration of iron and iron group elements in the white vein, as well as the relative enrichment process of constant elements such asAl2O3、SiO2and K2O and stable elements such as Ti and Zr. [Conclusion] The composition of the white reticulated interior of the bedrock layer and the variegated?horizon are non-spatially homogeneous, and the process of reticulation is a spatial process that extends from the center to the periphery.During reticulation, the leaching of iron and iron group elements dominates, but other elements also have a certain degree of migration, mainly characterized by strong leaching at the center of the reticulation and relatively weak leaching at the periphery. The reticulation process of the two is quite similar.
[Objective] The Paleogene Shahejie Formation around the Bozhong sag, Bohai Bay Basin is characterized by the development of mixed rock reservoirs, which are rich in abundant oil and gas resources. The unique biomass cavity pores in mixed rock reservoirs make the initial porosity of mixed rocks cannot be obtained by the conventional initial porosity recovery formula for mixed rocks, and there is a lack of initial porosity recovery methods for mixed rocks both at home and abroad, and the accurate recovery of the initial porosity is a key element in the study of the evolution of the reservoir. [Methods] In this study, modern snail samples were selected to determine the volume of snail body cavities using experimental and formulaic methods. Subsequently, a physical simulation experiment was conducted to simulate the filling conditions of snail body cavities in a real depositional environment. Finally, based on commonly used formulas for calculating initial porosity in reservoirs, a formula suitable for mixed rock reservoirs was derived. [Results and Discussions] Studies have shown that the species of snails is the biggest factor affecting the percentage of body cavity pore volume of snails. Different species of snails have different sizes of effective storage space, i.e., body cavity pore porosity; the main reason affecting the difference in body cavity pore porosity of the same species of snails is the size of the body cavity pore lumen. Taking the mixed rock sample from well QHD36-3-A at a depth of 3765.03m with a high content of fragmented bioclasts as an example, the initial porosity of this mixed rock at that depth was determined to be 51.68%. [Conclusions] In this paper, a new calculation method to find the initial porosity of mixed rocks is established based on the previous formula and combined with physical simulation experiments, which is of great significance for the study of mixed reservoir evolution.
Abstract : In order to deeply evaluate the natural gas exploration prospect and predict the favorable exploration zone and exploration target of the shore-shallow lake beach-bar sand body of the Quaternary Qigequan Formation in Tainan area, eastern Qaidam Basin, based on the comprehensive analysis of core observation and drilling ( logging ) data, combined with the analysis results of rock thin section, grain size-standard deviation, grain size cumulative probability curve, environmental sensitive grain size composition and other parameters, the grain size variation characteristics and hydrodynamic significance of the shore-shallow lake beach-bar sand body of Qigequan Formation in this area were studied in detail. The results show that : First, The sedimentary period of Qigequan in Tainan area is the sedimentary environment of shore-shallow lake. The beach-bar sand body is developed, the rock is loose, the cementation is poor, easy to break, and the grain size is fine. The lithology is mainly lithic feldspar fine sandstone-siltstone, the composition maturity is medium-poor, and the sorting roundness is medium-poor. Second,During the sedimentary period of Qigequan Formation, the cumulative probability curve of grain size of beach-bar sand bodies in the study area showed six patterns, mainly one-hop one-suspension type ( 64.4% ), followed by multi-segment type ( 11.9% ), and the third is two-hop one-suspension type ( 7.5% ). Third, During the sedimentary period of Qigequan Formation, the grain size-standard deviation diagram of beach-bar sand bodies in the study area showed four patterns, mainly multimodal ( 50.0% ), followed by bimodal ( 33.4% ), unimodal and trimodal ( both 8.3% ). Combined with the cumulative curve of grain size probability and paleogeomorphology analysis, four environmentally sensitive grain size components were determined, which represented suspension transport, wave, coastal current and storm wave, respectively. Among them, wave was the main hydrodynamic type controlling the formation and development of beach-bar sand bodies, and the average value of environmentally sensitive grain size components accounted for 27.9% of the total grain size. Followed by the suspension effect ( average of 15.3% ) and the coastal current ( average of 11.4% ), the storm wave effect is the weakest ( average of 2.3% ). Forth, Through the study of the plane distribution characteristics of the percentage content of environmentally sensitive grain size components, it is shown that the influence of waves on the formation and development of beach-bar sand bodies is weakened from the core to the wing of the anticline, while the suspension effect is just the opposite, and the influence of coastal flow on beach-bar sand bodies is concentrated on the east and west wings of the anticline.
[Objective] Recently, the shale gas exploration of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in the Sichuan Basin marked a significant breakthrough, which has aroused widespread attention towards the redox conditions and the organic matter enrichment mechanisms of the Qiongzhusi Formation during its sedimentary period. Redox conditions of water column play a pivotal role in controlling the enrichment of organic matter. The particle sizes and distribution of framboidal pyrites serve as powerful redox indicators. These proxies, when combined with relevant geochemical data, enable the reconstruction of the ancient oceanic redox environment. Furthermore, the assemblage of pyrite morphological characteristics may correspond to changes in redox conditions. However, a detailed comparison between the pyrite morphological characteristics and redox conditions revealed by other geochemical markers remains limited. [Methods] This study focuses on the black shale of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation from well W207 in the Sichuan Basin. We conducted a comprehensive analysis of the particle sizes and distribution patterns of the framboidal pyrites. Using this method, in combination with total organic carbon (TOC), total sulfur (TS), pyrite content and previously published iron speciation data, we aimed to reconstruct the paleo-marine redox environment of the Qiongzhusi Formation during its sedimentary period. On this basis, the relationship between the assemblage of pyrite morphological characteristics and redox condition changes is discussed. [Results and Discussions] The redox environmental evolution of the Qiongzhusi Formation can be divided into three stages, i.e., strongly euxinic, intermittently euxinic and dysoxic from the bottom to the top. The morphology of pyrite is abundant, mainly framboidal pyrites, accompanied by a few pyrite microcrystals and euhedral pyrites. The framboidal pyrites are generally small in size, ranging from 2.2 to 18.4 μm with an average value of 6.39 ± 1.7 μm. More than 80% of the particle sizes are in the range of 3 – 8 μm, reflecting that framboidal pyrites were mainly formed in the water bodies of the synsedimentary period. In addition, a robust positive correlation between pyrite content and TOC and TS contents was observed. Pyrite morphology varies in different redox conditions. Specifically, in euxinic environment, the pyrite content is notably high, mainly contributed by abundant framboidal pyrites. In this setting, spherulitic microcrystals are dominant, while pyrite microcrystals and well-defined euhedral pyrites with clear edges are rare. As the redox environment gradually shifted to a more oxidized state, there was a decline in both the pyrite content and the quantity of framboidal pyrites. Concurrently, the microcrystals of the framboidal pyrites evolved from octahedral to cubic forms. At this stage, the pyrite microcrystals and euhedral pyrites both increase in quantity, with the former often exhibiting aggregates and the latter featuring irregular edges. [Conclusions] In conclusion, the observed changes in redox conditions during the sedimentation of the Qiongzhusi Formation reflect a gradual oxidation process in the inner shelf areas of South China. This aligns with the rise in atmospheric oxygen level during the early Cambrian. Notably, sedimentary pyrite displays distinct variations in the distribution of particle sizes and the assemblage of pyrite morphological characteristics as a function of redox conditions. These differences can serve as valuable supplementary indicators for assessing redox conditions in subsequent studies.
Abstract: [Objective]Currently, research on the Early Jurassic Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (T-OAE; ~183 Ma) in the Ordos Basin mainly focuses on paleoclimate conditions, sedimentary environment evolution, and biodiversity changes, while the mechanisms of sulfur cycling during the T-OAE period in lakes remain unclear.[Methods]In order to further elucidate the sulfur cycling mechanism, Petrology and Geochemistry analyses were conducted on mudstone and black shale samples from the Anya section. The mechanisms of sulfur isotope fractionation during the T-OAE period were explored using major and trace elements and pyrite sulfur isotopes (δ34Spy).[Results and discussions]The pyrite in the Anya section samples mainly exists in the form of tetrahedral crystals, forming framboidal pyrite. The δ34Spy values of the samples exhibit anomalously positive values (ranging from 2.7 to 14.1‰, with an average of 8.3‰). Based on the variations in δ34Spy and total organic carbon (TOC) in conjunction with geochemical indicators (δ13C, TS, Corg/P, (La/Th)N), the evolution of the lake sedimentary environment during the T-OAE period was divided into four stages (high organic matter stages I and II, low organic matter stages I and II). [Conclusions] The δ34Spy values during the T-OAE period in the Anya section of the Ordos Basin coincide with atmospheric precipitation and surface runoff, indicating that the main source of sulfur in the lake is sulfate in the water mass. The sulfur isotopes of the samples are mainly controlled by the redox conditions of the lake bottom water and organic matter, and are independent of sedimentation rate and sulfate concentration. When the dissolved oxygen in the basin bottom water is low and the organic matter content is high, dissolved oxygen infiltrates into the sediment, activating anaerobic oxidants and promoting the reoxidation of H2S, resulting in positive δ34Spy values through Rayleigh fractionation. When the bottom water environment of the lake is oxygen-rich and the organic matter content is low, dissolved oxygen infiltrates into sediments, activating anaerobic oxidants and promoting H2S reoxidation, leading to a positive δ34Spy shift through the Rayleigh fractionation model. When the bottom water environment of the lake is oxygen-deficient and the organic matter content is high, the activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria is enhanced, promoting the MSR reaction and preferentially incorporating 32S, resulting in a negative δ34Spy shift. The sulfur cycle during the T-OAE period in the Anya section is mainly controlled by local/regional sedimentary environments, but the sulfur cycle is also influenced by global warming and intensified hydrological circulation during the T-OAE period
Significance The development mechanism of fine-grained rock laminae is important for paleoclimate reduction and unconventional oil and gas exploration, and has attracted significant attention in recent years. However, the formation mechanism and corresponding identification characteristics of laminae in lacustrine fine-grained sedimentary rocks are still unclear. Progress This article systematically summarizes the sedimentary properties and factors influencing the formation of laminae in lacustrine fine-grained sedimentary rocks, such as suspended sedimentation, distal dilution of gravity flow, bottom currents, volcanic hydrothermal fluid and microbial activities. Various sedimentary processes may form similar laminae in composition, lamina thickness, particle size, and morphology, but for genetic identification, significant differences are evident in laminae combinations, bioturbation and other sedimentary features. The formation and distribution of these laminae are controlled by two major factors: paleoclimate and paleogeography. Paleoclimate has a broad, complex control over laminae; paleogeography controls their distribution pattern. [Prospects] From the perspectives of theoretical development and practical application, there remain some outstanding issues in the study of laminae in lacustrine fine-grained sedimentary rocks. In future studies, effective methods for extracting and naming laminae should be developed for identifying their formation mechanism, integrating spatial changes and focusing on groundbreaking issues (e.g., paleoclimate interpretation, carbon burial, life evolution, Martian sedimentology) to meet the major needs of unconventional oil and gas exploration.
Significance The dolomite problem remains one of the most contentious and prominent issues in the field of sedimentology. Previous studies have demonstrated that the direct precipitation of ordered dolomite under low-temperature, inorganic conditions is challenging both in laboratory settings and modern natural sedimentary environments. The formation of dolomite is a kinetically controlled process, and several crucial factors have been identified, including the hydration of Mg2+, presence of sulfate inhibitor, nucleation sites, and ordering of cations. The role of sulfate in the formation of dolomite has garnered considerable attention, yet it remains a subject of substantial debate. The hypothesis that sulfate inhibits the formation of dolomite has long been widely accepted by geologists, serving as an explanatory framework for determining the evolution of dolomite abundance and seawater properties throughout geological history. With the advancement of research, particularly in ongoing investigations into the formation mechanism of microbial dolomite, a contentious debate has arisen regarding the role of sulfate, as several scholars have argued that the presence of sulfate does not inhibit low-temperature dolomite precipitation. The controversy regarding the role of sulfate arises from: (1) the large variation in SO
Significance Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, human activities have resulted in the sustained release of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. This has been primarily driven by the combustion of fossil fuels, and threatens profound climatic disturbances, environmental transformations and widespread biological crises. Similarly, the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM, ~56 Ma) represents a period of massive carbon release into the atmosphere, occurring at a rate strikingly comparable to current anthropogenic carbon emissions. It is of paramount importance to gain a comprehensive understanding of the processes and mechanisms that regulated carbon release during the PETM. Such knowledge can provide valuable insights into the impact of these emissions on the Earth’s habitability. Furthermore, these findings have significant implications for our attempts to gain an understanding of present-day and future climate change. It is consequently of the highest scientific importance to study this ancient climatic event, as it offers a natural experiment for evaluating the potential consequences of contemporary carbon emissions on global climate dynamics and ecological stability. Progress The trigger of the PETM has been the subject of considerable debate among scholars in the past few decades. Despite extensive research, the exact mechanism that instigated the massive carbon release during the PETM remains unresolved, although the findings of recent studies have indicated a temporal correlation between magmatism in the North Atlantic Igneous Province (NAIP) and the PETM. This evidence suggests that volcanic activity in NAIP was likely to be have been the trigger of the climatic perturbation. While this hypothesis adds to our insights into the triggering mechanisms of PETM events, our understanding of the exact cause-and-effect relationship between volcanic activity and climate fluctuations during this transition period remains incomplete. A significant challenge to a full establishing this relationship is the difficulty of accurately tracing volcanic activity in the sedimentary record during this period, due to the complex nature of volcanic products and their subsequent alteration over millions of years and the problem of identifying and distinguishing between different volcanic events. Recently, mercury (Hg) concentrations and their isotopic compositions in sediments have emerged as promising tools for tracing volcanic activity throughout geological history. However, in the present study, the focus on the Hg record of the PETM was largely limited to near-shore areas proximal to the NAIP eruption sites. Few studies have explored the Hg concentrations in sediments from open-ocean regions located at a considerable distance from the eruption centers, leaving a significant gap in our understanding of the broader extent of the influence of the NAIP. The spatial limitations of this study restricted our ability to fully assess the global impact of volcanic emissions on the Earth’s climate and ecosystems during the PETM. Conclusions and Prospects This paper provides a comprehensive review of the current state of research on the use of mercury deposition as a tracer of ancient volcanic activity during the PETM. It identifies existing research limitations and suggests key directions for future studies. It also reviews the possible relationship between the volcanic activity of the NAIP and the climatic events of the PETM, emphasizing the need for further interdisciplinary research to resolve outstanding issues and refine our understanding of this critical period in the Earth’s history.
Objective At present, research on the Early Jurassic Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (T-OAE; ~183 Ma) in the Ordos Basin primarily emphasizes paleoclimate conditions, the evolution of the sedimentary environment, and biodiversity changes. However, the mechanisms governing sulfur cycling in lakes during the T-OAE remain unclear. Consequently, further examination of the sulfur cycling mechanism is essential. Methods Twenty-eight samples were selected from the Anya section. Mineralogy and isotope geochemistry analyses were performed on mudstone and black shale samples from the Anya section. The mechanisms of sulfur isotope fractionation during the T-OAE were investigated using major and trace elements, as well as pyrite sulfur isotopes (δ34Spy). To avoid interference from marcasite and siderite, mineral morphology and energy spectra were examined using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Results The pyrite in the samples from the Anya section predominantly were tetrahedral and octahedral crystals, forming framboidal pyrite. The mineral surface exhibits a smooth texture without the presence of platy marcasite. The coexistence of radial siderite with pyrite is also observable. The δ34Spy values of these samples consistently display positive values, ranging from 2.7‰ to 14.1‰, with an average of 8.3‰. By analyzing the fluctuations in δ34Spy and total organic carbon (TOC), along with the use of geochemical indicators such as δ13C, total sulfur (TS), Corg/P, and (La/Yb)N, we delineated the evolution of the lacustrine sedimentary environment during the T-OAE into four distinct stages, comprising periods characterized by high (Stages I and II) and low organic matter (Stages I and II). Conclusions The δ34Spy values during the T-OAE in the Anya section of the Ordos Basin align with those of atmospheric precipitation and surface runoff, suggesting that sulfate in the water mass serves as the primary source of sulfur in the lake. Atmospheric precipitation and surface runoff mainly consist of dissolved sulfate ions exhibiting lacustrine sulfate isotope compositions between 0 and 10%. However, the samples from the Anya section include black shale, mudstone, sandstone, and other low sulfur source rocks, likely resulting in smaller sulfur isotope compositions within the lakes. It is improbable that the sulfur isotope composition of pyrite is inherited from lacustrine sulfate. The sulfur isotopes in the pyrite of the samples are primarily influenced by the redox conditions of the lake bottom water and the organic matter content/type within the sediment. When the lake bottom water is oxygen-rich and the organic matter content is low, dissolved oxygen infiltrates into sediments, activating anaerobic oxidants such as NO
Objective Carbon and oxygen isotopes are important geochemical indices of carbonate rocks, play an important role in revealing the characteristics of sedimentary and diagenetic fluids, and have become one of the basic means to study carbonate rocks. At present, a large number of studies on carbon and oxygen isotopes in limestone-dolomite have been conducted globally, but there are few studies on carbon and oxygen isotopes in sulfate-carbonate. In the sulfate-carbonate stage of the sedimentary sequence, there are still carbon and oxygen elements that can be tested, which makes this study possible. There are currently studies on carbon and oxygen isotopes of the plaster salt section of Huaying Mountain and the plaster bearing strata of Reichenhall Formation, Australia, but these studies are few and concentrated on surface samples. It is of great theoretical significance to study carbon and oxygen isotopes of drilling gypsum salt samples. Methods In the process of drilling a geothermal well in Doubei Village, Gaotan Town, Linshui County, and Sichuan, to the east of Huaying Mountain in Sichuan Basin, carbon and oxygen isotopes of paste salt interbedding cuttings of Jialingjiang-Lekoupo Formation were studied. Results (1) The δ13CPDB ranges from -4.68‰ to -0.12‰, with an average value of -2.86‰. The δ18OPDB of paste salt interbedding cuttings in the Daobei geothermal well ranges from -15.47‰ to -2.56‰, with an average value of -9.13‰, and the Z-value is lower than 120, which is inconsistent with the characteristics of marine sediments. The δ13CPDB and δ18OPDB values were significantly lower than that of the Triassic paste salt formation in Huaying Mountain and the Reichenhall paste salt formation in Australia; (2) According to the two calculation methods, the formation temperature is 28.18 ℃-111.71 ℃, the average value is 68.45 ℃ and 4.54 ℃-78.21 ℃, the average value is 38.91 ℃. The former was close to the present temperature of the formation, but the latter was lower, which may be related to the selection of δ18O in the calculation formula. Conclusions The carbon and oxygen isotopes of the underground salt-salt strata in this area are mainly affected by the thermochemical sulfate reduction (TSR) in the deep-buried stage before the formation fold and the massive inflow of surface fresh water after the formation fold, fracture and uplift. The high formation temperature and exchange of organic carbon before fold and the desalting of surface water after fold and fracture are the fundamental reasons for the low δ13C and δ18O of the gypsum salt layer in this area. However, there may be a little freshwater action and influence during the depositional stage.
Objective During the Cretaceous period, extreme greenhouse climate, global oceanic anoxia,and oxygen enrichment events occurred. The Cretaceous red beds that appeared during this period contain important information related to the paleoclimate and paleoenvironment that aid in our understanding of stratigraphic surface systems. Methods In this study, a set of red mudstones developed during the Cretaceous in the North Yellow Sea Basin of eastern China were taken as the object of study. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) analyses were conducted on the red and grey mudstones of the Middle Jurassic to Lower Cretaceous to semi-quantitatively and quantitatively analyze the composition and content of chromogenic minerals in the rocks. We also combined the ordinary thin section and scanning electron microscope methods to observe the characteristics of chromogenic minerals in the red mudstone, such as the morphology, distribution, and crystalline size of iron-containing minerals. The DRS second derivative method was used to calculate the contents of hematite and goethite in mudstone samples. The paleoclimate and paleoenvironment information of red mudstone during its deposition period was obtained by combining the content and ratio of iron oxides in the samples. Results XRD results show that the chromogenic minerals in the red mudstone are hematite and goethite, of which hematite is the main content. The highest content can reach 14%, whereas the grey mudstone does not contain hematite; hematite aggregates can be seen under the microscope in the red mudstone, and alteration phenomena can be seen in the local area; hematite can be seen as granular or plate aggregates under the scanning electron microscope; The DRS second derivative method calculated that the average content of hematite in red samples was 1.25 g/kg, and the highest was 2.62 g/kg. The average content of goethite was 0.62 g/kg, and the highest was 1.19 g/kg. Using the changes in hematite and goethite content, the climate was found to be relatively humid from the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous, and hot and dry from the Middle to Late Early Cretaceous. Conclusions Combined with the paleoclimate data of the North Yellow Sea Basin and its adjacent areas, the method of using iron oxides to reflect the paleoclimate changes in the study area was found to be feasible. A comprehensive analysis suggests that the chromogenic minerals in the red mudstone of the Lower Cretaceous have indicative significance for the paleoenvironment and paleoclimate.
Objective Chemical weathering is a key geological process that regulates the long-term climate of the Earth and participates in the global carbon cycle. It plays a key role in the evolution of terrestrial climate and paleo-climate reconstruction, shaping the surface morphology and sustaining life. Methods The chemical weathering characteristics of fine particle components (<63 μm) of 89 aeolian and fluvial sand samples from four major sandy lands in Northeast China (Hunshandake sandy land, Horqin sandy land, Songnen sandy land, and Hulunbuir sandy land) were analyzed to reveal the spatial distribution characteristics of chemical weathering in the Northeast sandy land. To evaluate the correlation between 13 different weathering indices and climate factors (annual average temperature and precipitation) and the main influencing factors controlling the chemical weathering degree of the Northeast sandy land . Results The results showed that when the same chemical weathering index (such as Chemical Index of Alteration, CIA) was used to reconstruct the chemical weathering characteristics of sandy land, the spatial distribution of different sandy lands was poor, the correlation between the same weathering index and climate factors was poor (r≤0.4, p>0.05). However, different weathering indices showed clear spatial distribution rules when reconstructing the distribution characteristics of chemical weathering in the Northeast sandy land, and the correlation with climate factors was better in different sandy lands (r≥0.6, p≤0.05), indicating that different weathering indices had different sensitivities to climate in different regions. Therefore, the chemical weathering measured by different indices in the Northeast sandy land is controlled by climate factors, but the correlation between chemical weathering intensity and temperature and precipitation of different sandy lands is still significantly different. In general, most of the chemical weathering areas reconstructed with different indices in the Northeast sandy land are in a low chemical weathering intensity, and the distribution range of chemical weathering high value is small, and there are clear spatial distribution characteristics. The intensity of chemical weathering in Hunshandake sandy land, eastern Horqin sandy land and Songnen sandy land is affected by precipitation factors. The temperature and precipitation changes are influenced by fluvial action, monsoon precipitation, geographical location, and vegetation coverage, which indirectly affect the occurrence of chemical weathering. The chemical weathering intensity in the west Horqin sandy land is mainly affected by temperature factors and controlled by terrain and higher average annual temperature. The chemical weathering intensity of Hulunbuir sandy land is weakly affected by temperature and precipitation factors, and non-climatic factors (such as terrain, wind erosion, physical weathering, and vegetation coverage) may weaken the influence of climate on chemical weathering. Conclusions In summary, the degree of chemical weathering in the Northeast sandy land is mainly controlled by climatic conditions (temperature and precipitation), but the sensitivity of chemical weathering represented by different chemical weathering indices to climate is significantly different in different sandy lands. Therefore, careful choices should be made when using chemical weathering indices of sediments for paleo-climate and paleo-climate reconstruction.
Objective Mangroves are an important coastal blue carbon ecosystem, with a strong carbon sink function that has a profound impact on the global carbon cycle. In recent years, the sources and burial characteristics of organic carbon in mangrove wetland sediments have become a hot topic at home and abroad. However, there are few studies on the sources and biogeochemical cycles of organic carbon in mangrove wetland sediments at high latitudes. Methods A high-resolution 210Pb chronostratigraphic framework was established in the Yanpu Bay mangrove research area using the 1.5 m deep column sediment collected from the mangrove as a carrier. The sediment accumulation rate (SAR), organic carbon accumulation rate (OCAR), potential sources of organic carbon, and their contribution rates were analyzed according to the characteristics of the total organic carbon content (TOC), carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N), median particle size (D50) and stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen (δ13C, δ15N). Results The sedimentation rate of mangrove sediments along Yanpu Bay is approximately 2.2cm/a, and a continuous sedimentary sequence of almost 70 years has been obtained. The particle size components are mainly silt and clay components. The proportion of different components of particle size and D50 remained unchanged with depth, and the activity of excess 210Pb was closely related to depth, indicating that the sedimentary environment was relatively stable. The average content of TOC is 1.63%, while the average content of TN is 0.10%. There was a significant positive correlation between TOC and TN (R2=0.238 09), and a significant negative correlation between TOC and δ13C (R2=0.472 69), indicating that the sources of organic carbon and nitrogen in sediments were consistent, and carbon sources with lower δ13C values were the main contributors to organic carbon in sediments. According to the vertical trend of TOC content, SAR and OCAR, the sedimentary record of organic carbon can be divided into three stages: the first stage is from 1955 to 1982, the second stage is from 1982 to 2014, and the third stage is from 2014 to 2021. The SAR values ranged from 52.03 to 233.61 g/(cm2·a), with an average value of 177.68 g/(cm2·a), OCAR values ranged from 112.78 to 473.97 g/(m2·a), with an average value of 286.65 g/(m2·a). TOC and OCAR showed no significant correlation (R2=0.095 78), while SAR and OCAR showed a significant positive correlation (R2=0.457 66). SAR of mangrove sediments may be an important factor that affects the burial of organic carbon in sediments. According to the distribution range of δ13C, δ15N and C/N values of mangrove columnar sediments, it is preliminarily concluded that the deposition of terrigenous organic matter is mainly contributed by terrigenous plants, C3 plants and organic matter in lost soil. Marine organic matter deposition is mainly caused by aquatic plants, marine phytoplankton and suspended organic particles brought by seawater perfusion. Among them, the contribution rate of mangrove litter was the highest (59.44%), followed by the average contribution rate of POM (25.91%), and the contribution rate of SOM and phytoplankton was relatively small. The contribution rate of POM is the largest, which is mainly affected by downstream seawater injection and the upstream runoff. The water conservancy facilities are the main limiting factor of the contribution rate of POM. Mangrove area and POM delivery are important factors that affect the burial of organic carbon burial in sediments. Conclusions Mangrove sediment organic carbon in Yanpu Bay is a mixed source of marine and land, and the sources of organic carbon and nitrogen in the sediment are consistent. Mangrove plant litter is the main contributor to organic carbon in sediments. Extreme weather, natural disasters, and water conservancy projects increase the complexity of sediment organic carbon sources. The sediment mass burial rate is the main factor affecting the organic carbon burial flux of mangrove sediments along Yanpu Bay. The sediment mass burial rate is mainly affected by extreme weather such as typhoon, and the use of upstream sluices and estuarine sluices also has a significant influence on it. Through reconstruction of the organic carbon burial records of mangrove sediments in Yanpu Bay, it is found that the burial of organic carbon in mangrove sediments is greatly affected by extreme weather and water conservancy projects, forming a phased deposition process.
Objective The First member of the Neogene Shawan Formation located at the eastern side of the Chepaizi uplift in the Junggar Basin displays significant carbonate cementation and strongly heterogeneous oil-bearing potential. The reasons for the development of the carbonate cements in the study area were thoroughly analyzed, and its effects on the physical properties and oil content of the reservoir are discussed. Methods The types, distribution, formation stages and genesis of these shallow-depth carbonate cements were studied by core observation and cathode luminescence (CL) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) examination of thin sections. Results At least three stages of carbonate cementation were identified. The first stage is mainly dominated by shell-like calcite and granular siderite. Polarized microscopy indicated that the edges of some mineral particles have been replaced, and at the later stage the influence of acidic fluids has resulted in poor connectivity of the cement. The CL showed the calcite as bright yellow. The carbonate cement formation was mainly influenced by paleoclimate and depositional water; in the study area there is also evidence of the presence of algae. The second and third stages are dominated by poikilitic calcite, which is most widely distributed in the second stage. Also, CL of the second stage shows the calcite cement as almost non-luminous, and with a high Mg content. The calcite cement in the third stage is seen as orange-yellow color under CL. Signs of corrosion at the boundary between the second and third stages are clearly seen under the polarizing microscope. In both the second and third stages, the effect of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion from Middle and Lower Jurassic source rocks in the Changji Depression is indicated. Organic acid fluid dissolved the early carbonate cements and acid-soluble particles, providing the main material source for the development of subsequent carbonate cements. It was found that the carbonate cement causes the poor physical properties of the Shawan Formation reservoir in the early stage. Subsequent injection of acidic fluid in the later stages increased the porosity and permeability of the reservoir to a limited extent. Continuous planar development formed thin interlayers of carbonate cement sealed by capillary pressure, restricting hydrocarbon migration and trap types in the reservoir by blocking their migration path, so that migration and accumulation of oil and gas only occurs along a few structural fractures. This has led to obvious oil heterogeneity in the sandstone within the study area. Also, where high-carbonate cement occurs over large areas, it overlies the sand body. Because it is mostly basement cementation, it may form a better cap layer, affecting the accumulation of oil and gas. Conclusions The types, distribution, formation and geological significance of the multistage carbonate cements are defined, providing support for continued exploration and development as well as the search for new exploration targets.
Objective Peperite is a transitional rock type formed by the syngenetic mixing of hot magmatic materials with wet and cold unconsolidated sediments, which has important paleoenvironmental implications. Methods Based on outcrop geological survey and microscopic petrological analysis, typical peperites are recognized in Ediacaran basic volcanic rocks in the northwestern Tarim Basin. These are mainly blocky peperites and fluidal peperites hosted by purplish-red sandy sediments. Results The peperites were mainly formed by the intrusion of magma into water-rich unconsolidated sandy sediments or by the flow of magma on the surface of water-rich unconsolidated sandy sediments. Of these, the thinner magmatic intrusion and the lower surface of the flood basalt mainly formed the fluidal peperites, and the thicker magmatic intrusion developed the blocky peperites. Conclusions The northern margin of the Tarim Craton was still in an intraplate rift setting related to the breakup of the Rodinia supercontinent during the early Ediacaran, and the development of peperite indicates that the basalt eruption in this area took place in a mainly littoral subaqueous sedimentary environment. With the end of volcanic eruption, the northern Tarim Craton transformed into a relatively stable passive continental margin basin or a cratonic basin during the late Ediacaran.
Objective There are many curvilinear ridges that have similar planforms as rivers in the northern and southwestern Qaidam Basin. To investigate their formation mechanism, we conducted research on the fabric of gravel layers to restore the paleo-sedimentary environment of curvilinear ridges. Methods Statistical and morphological analyses were performed on 21 sets of gravel samples from the curvilinear ridges and compared with the gravel layer sediments in the middle reaches of the Han River. Results The ratio of round and sub-round gravels in the curvilinear ridges area ranges from 71.6%-74.0%, and the ratio of discoid gravels ranges from 44.9%-54.0%. The correlation coefficients of the gravel morphological features between the distribution area of curvilinear ridges in the Qaidam Basin and those in the sampling area of the middle reaches of the Han River range from 0.685-0.703. Conclusions The gravels in the curvilinear ridges are fluvial deposits. If based on the modern hydrologic parameters of the Qaidam Basin, the paleocurrent velocity, paleo-discharge, and paleo-annual runoff rate of the river indicated by the curvilinear ridges are 0.217 m/s, 1.39 m3/s, and 0.144 0×108 m3, respectively. The paleo-discharge range of the curvilinear ridges of the Qaidam Basin reconstructed based on the channel width is 14-16 m3/s. Accordingly, the paleo-runoff depth is estimated to be approximately 2 m, and the corresponding paleocurrent velocity, paleo-discharge, and paleo-annual runoff rates are approximately 0.357 m/s, 14.28 m3/s, and 1.480 1×108 m3, respectively.
Objective Lacustrine fine-grained sedimentary rock mixed with clay, felsic, carbonate and analcite minerals, developed in the Fourth member of the Shahejie Formation of the Leijia area in the Western Sag of the Liaohe Depression in the Bohai Bay Basin, is the main carrier of oil and gas in the region. Owing to the complex composition and rapid lateral changes of mixed fine-grained rocks, the reservoirs are highly heterogeneous, which brings certain difficulties to the prediction of high-quality reservoirs. Methods Taking wells Lei 15, Lei 14, and Lei 61 in the Leijia area of the Western Sag as an example, and based on time series analysis method, high-precision carbonate U-Pb dating, and natural gamma ray (GR) logging data, the mixed fine-grained rocks of the Fourth member of the Shahejie Formation were analyzed using cyclostratigraphy. Results (1) The optimal sedimentation rates of wells Lei 15, Lei 14, andl Lei 61 were estimated by Correlation Coefficient(COCO), the optimal sedimentation rates increased sequentially and were 10.57, 11.4, and 13.93 cm/kyr, respectively. (2) We performed spectrum analysis on the paleoclimate proxy indicator (GR) and compared it with the data spectrum analysis results of the standard eccentricity, slope, and precession (ETP) composite curve, identifying the astronomical cycle signals in mixed fine-grained rocks in wells Lei 15, Lei 14, and Lei 61. Then, we used the 405-kyr long eccentricity cycle for astronomical tuning. We set the age 43.4±1.7 Ma at 2 766.61 m in well Lei 14 as the anchor point to establish an absolute astronomical time scale. (3) 6 long eccentricity cycles of 405 kyr and ~17 short eccentricity cycles of ~129 kyr were identified in the Fourth member of the Shahejie Formation. Combining the connection between the Earth's orbital period and high-frequency sequences, a fine stratigraphic division and correlation at the eccentricity scale was established. Conclusions By conducting cyclostratigraphic research on the Fourth member of the Shahejie Formation in the Leijia area, its astronomical cycle signals can be effectively identified. This method quantitatively establishes a fine stratigraphic division and comparison framework with time attributes, which plays an important role in guiding further oil and gas exploration in the area and broadens the applicability of cyclostratigraphy in the Bohai Bay Basin.
Objective Selective dissolution is common in marine carbonates, and its origin is typically related to meteoric fluids, although other possible origins lack investigation. Methods In this study, the origin of the marine selective dissolution of the Buqu Formation of the well GK-1 in the South Qiangtang Basin of China is investigated based on petrography, stable carbon and oxygen isotopes, and elemental geochemistry. Results Eight sedimentary cycles (C1 to C8 from bottom to top) were recognized from the studied Buqu Formation. Each cycle has limestone in the lower part and dolostone in the upper part. These eight cycles were divided into two types (A and B) according to different carbonate components. The limestone in the type A cycle (C1-C4) is dominated by bioclastic packstone and grainstone, while that in the type B cycle (C5-C8) is dominated by bioclastic wackestone and packstone. Upwards from the type A cycle to the type B cycle, the content of aragonite fossils (gastropods and bivalves) in the limestone decreases and the content of peloids increases. The dolomite in both type A and type B cycles is crystalline dolomite, with ooid ghosts showing selective dissolution pores. Importantly, the overall percentage of selective dissolution pores in type A cycles is significantly higher than that in type B cycles. In terms of geochemistry, the carbon and oxygen isotopes of dolostone are higher than those of the limestone in each cycle. Rare earth elements and yttrium concentrations (0.44×10-6-7.25×10-6) of dolostone and limestone are extremely low, and the Y/Ho ratios (35.63-75.55) are basically within the range of modern seawater. Dolostone exhibits a seawater-like PAAS-normalized REY pattern, showing a left-leaning style with relatively depleted LREE and enriched HREE, while the PAAS-normalized REY pattern of the limestone is relatively flat. Furthermore, Ce/Ce* values of the dolostone range from 0.55 to 0.78 (average 0.63), and the Ce/Ce* value of the limestone ranges from 0.80 to 0.88 (average 0.84). The concentrations of redox-sensitive elements (U, Mo, V) are very low, and the V/(V+Ni) ratios range from 0.01-0.39. In each cycle, Cu and Zn in the dolostone are higher in content than in the limestone, and type A cycles have higher Cu and Zn content overall than type B cycles. Conclusions Based on lithology and sedimentary components, the Buqu Formation of well GK-1 was likely deposited in shallow marine grain-shoal settings, with seawater restricted from type A cycles to type B cycles. Based on comprehensive petrological and geochemical analysis, the selective dissolution herein is interpreted to be produced by early marine diagenesis, rather than meteoric diagenesis or deep burial. During early marine diagenesis, aragonite may be selectively dissolved by undersaturated pore fluids via organic matter decomposition. In the sedimentary cycles, the differential development of selective dissolution is probably controlled by aragonite content, paleoproductivity, and the early marine diagenetic redox boundary. In a single cycle, the dolostone interval is characterized by higher paleoproductivity and more oxic pore water than the limestone interval during early diagenesis, favoring the production of undersaturated fluids and the formation of selective dissolution pores. Compared to type B cycles, type A cycles have higher aragonite content, higher paleoproductivity, and a lower early marine diagenetic redox boundary, thus resulting in the better development of selective dissolution.
Objective In this study, to redetermine the stratigraphic boundary of the Carboniferous-Permian Taiyuan Formation and Shanxi Formation in the Yichuan area of the Ordos Basin and to solve the problem of sedimentary age attribution of coal-bearing natural gas mudstone section near the boundary of the Taiyuan Formation-Shanxi Formation. Methods We selected the sandstone and mudstone samples of the transition layer between the Taiyuan Formation and Shanxi Formation in the typical coring well Yi 120 to conduct the U-Pb dating of detrital zircon and we used the maximum depositional age ( MDA ) estimation method, combined with previous research results on the zircon age of the Taiyuan Formation-Shanxi Formation in the North China Plate, to constrain the depositional age of the study interval. Results Experiments show that the maximum likelihood age (MLA) of the sandstone and mudstone at the top of the Taiyuan Formation is 298±2 Ma, which represents the age of the latest deposition of the strata. This interval was deposited in the Early Asselian period, which is consistent with the Asselian sedimentary age determined by conodont. The MLAs of the sandstone samples at the bottom of the Shanxi Formation is 295±1 Ma, representing the age of the earliest deposition, which was deposited in the Middle-Late Arthurian period. Conclusions Based on the above research and analysis, we conclude that the boundary between the Taiyuan Formation and Shanxi Formation in the study area should be above the sand-mudstone section at the top of the Taiyuan Formation; that is, the marine sand-mudstone layer at the top of the Taiyuan Formation in the study area should belong to the Taiyuan Formation, which provides a certain basis for the stratigraphic division of the Taiyuan Formation-Shanxi Formation in the study area.
Objective The study of the beach-bar sand bodies of the Quaternary Qigequan Formation in the Tainan area of the eastern Qaidam Basin deeply can provide a basis for the exploration prospects of natural gas in the study area and the prediction of favorable exploration zones and exploration targets. Methods Based on the analyses of core observations and drill-log data combined with analyses of thin-sections,grain-size standard deviation,grain-size cumulative proba-bility curves,environmental sensitive grain-size composition and other parameters.These grain-size variations and the hydrodynamic influence of the shore-shallow-lake beach-bar sand bodies of the Qigequan Formation in this area were studied in detail. Results (1) the sedimentary environment during the Qigequan period in the Tainan area was a shore and shallow lake. Beach-bar sand bodies are well developed, with fine grains, and loose, poorly cemented rock which is readily broken. The lithology is mainly fine lithic feldspar sandstone/siltstone of medium-to-poor maturity and medium-to-poor roundness sorting. (2) During the overall deposition period of the Qigequan Formation, the cumulative probability curves of the grain size of the beach-bar sand bodies in the study area occurred in six patterns, mainly a one-hop one-suspension type (64.4%), a multi-segment type (11.9%), and a two-hop one-suspension type (7.5%). (3) During the deposition period, the grain-size standard deviation in the study area revealed four patterns, mainly multimodal (50.0%), followed by bimodal (33.4%), unimodal (8.3%) and trimodal (also 8.3%). Combined with the cumulative curves of grain-size probability and paleogeomorphological analysis, four environmentally sensitive grain-size components were found. The grain sizes from fine to coarse correspond to suspension transport, wave action, coastal current action and storm wave action. Of these, the most important hydrodynamic force was wave action, and the average proportion of the environmentally sensitive grain-size component accounts for 27.9% of the total size range. The suspension effect on grain size averages 15.3%; the coastal current effect averages 11.4%; and the storm wave effect is the weakest (average 2.3%). (4) The study of the plane distributions of the percentage of environmentally sensitive grain size components indicates that the influence of suspension on the development of beach-bar sand bodies is enhanced from the core to the wing of the Tainan anticline, while the influence of wave action is exactly the converse. The influence of coastal flow on the beach-bar sand bodies is concentrated on the eastern and western wings of the anticline. Conclusions The study reveals the plane distribution range of high-quality beach-bar sand bodies in the Tainan area, and provides technical support for natural gas exploration and development in this area.
Objective The coal-bearing strata of the Carboniferous Taiyuan Formation (C3t) are widely distributed in the Dawangzhuang area of the Jiyang Depression. The high-quality reservoir control factors in the coal-bearing strata have an important impact on oil and gas exploration, but its reservoir characteristics and genetic model are still unclear. Methods Based on thin section identification, cathodoluminescence, scanning electron microscopy, fluid inclusion, C-O isotopes, in⁃situ laser ablation, and other technical methods, combined with burial history and tectonic evolution history, the characteristics and genetic model of high-quality clastic reservoirs in coal measures of the Carboniferous Taiyuan Formation in the Dawangzhuang area of Jiyang Depression were studied. Results The clastic reservoir of the Taiyuan Formation coal measure strata in the Dawangzhuang area of Jiyang Depression is dominated by lithic quartz sandstone, and the reservoir space of high-quality reservoir is dominated by secondary pores, which are primarily interstitial and feldspar dissolution pores formed by atmospheric fresh water and organic acid dissolution. The cements are two phases of quartz overgrowth and two phases of carbonate cements, though they are mainly carbonate cements. The two phases of quartz overgrowth are derived from the pressure solution of quartz particles and the source of feldspar dissolution, respectively. The siderite is a diagenetic carbonate rock formed by precipitation of pore water in the synsedimentary-early diagenetic stage, and the ankerite is related to CO2 formed by decarboxylation of organic acid. Conclusions The sedimentary facies controls the distribution of lithofacies in high-quality reservoirs. The high-quality reservoirs are controlled by the late uplift of atmospheric fresh water leaching and buried organic acid dissolution, as well as tectonic activity. The distance between the high-quality reservoirs and the docking faults should be large to avoid the further precipitation of CO2 produced by decarboxylation, which can form ankerite and destroy the reservoir properties.
Objective As hydrocarbon organic matter, oil or natural gas remains in source rocks or reservoirs, and the formation and evolution of bitumen interstitials are closely related to the evolution history of oil reservoirs. It is an important symbol of oil and gas accumulation and transformation processes. Previous studies have conducted many analyses on the types, genesis, and thermal evolution of bitumen components in reservoirs, but the restriction mechanism of bitumen on reservoirs is still unclear. Methods This study takes the Cretaceous Baxigai Formation reservoir in the Yingmai 467 well block in the west of Tabei as an example. With the help of casting thin sections, fluorescent thin sections, and laser Raman experiments, combined with logging parameter identification, the relationship between bitumen and oil and gas reservoir stages was discussed, and the influence of different bitumen types on reservoir quality was identified. Results (1) Based on the main components and formation stages, the bitumen interstitial materials in the study section are divided into two categories; type I is mainly intergranular filling, and most are yellow-brown and brown-black under the fluorescence microscope. The main components are oily and bituminous bitumen, and the bitumen reflectivity is more than 1 %. Type II is distributed on the edge of the pore in the form of bitumen lining. Under the fluorescence microscope, it is mostly orange and blue (white) in color, with colloidal bitumen as the main component. The bitumen reflectivity is low, ranging from 0.42%-0.79%. (2) The bitumen interstitial material in Yingmai 467 well block is mainly type I bitumen. Because the oil and gas in the source rock of the Huangshanjie Formation migrated through the unconformity at the bottom of the Shushanhe Formation, the fault was filled into Brazilian reorganized massive sand layer 2 and the Brazilian reorganized thin sand layer, and gas washing occurred. Type II bitumen was precipitated by retrograde condensation from the source rock oil and gas of the second phase of the Qiakemake Formation along the Cretaceous bottom and the Yingmai 7 fault zone into the Baxigai Formation. It was affected by the thickness of the sand body and mainly distributed in the first layer of massive sand. (3) Type I bitumen has a strong effect on reservoir reconstruction and occupies part of the pore space; type II bitumen has little effect on reservoir porosity. Conclusions It is of practical significance to find out the types of bitumen interstitials in the Cretaceous Baxigai Formation in Yingmai 467 well block in the west of Tabei, and to clarify the influence of different bitumen types on reservoir quality, which is of practical significance to deepen the geological understanding of the study area.
Objective China possesses abundant terrestrial shale oil resources with significant potential for exploration. Now, substantial breakthroughs have been made in the exploration and development of shale oil in the Shahejie Formation (Es1) in Jiyang Depression, but there are still some problems to be solved in the differences of reservoir properties among black mudstones of different lithofacies. Methods This study focused on the black mudstone of the Shahejie Formation in the Jiyang Depression, southern Bohai Bay Basin. The laminated strata types and combinations, pore types and structures were examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), rock pyrolysis, fluorescence analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and low-temperature gas adsorption. Results Five distinctive categories of mineral types were identified: feldspar-quartz lamina, clay mineral-rich lamina, aragonite lamina, micritic calcite-dominated lamina, and organic-rich lamina. Their vertical stacking occurs in three binary layer combinations: organic-rich + micritic calcite, organic-rich + aragonite, and organic-rich + feldspar-quartz. The porosities of the organic-rich + aragonite and organic-rich + feldspar-quartz binary lamina combination mudstones are higher than the other combinations, and possess better pore structure and connectivity. In the organic-rich + aragonite combination, shale oil is present in a free state within interlayer spaces, and is the most mobile. The mobility of the free oil and adsorbed oil in the organic-rich + aragonite mudstone is poorer. The lowest-mobility oil occurs mainly as adsorbed material in the organic-rich + feldspar-quartz combination mudstone. Conclusions The different strata combinations in the mudstone structure influence the porosity, pore structure and hydrocarbon storage capacity of these black mudstones. Based on the findings of this study, shale oil reservoir storage models were developed for each combination to provide a rational foundation for the future extraction of shale oil and gas in the region.
Objective In the Tainan region of Qinghai oil field, within the middle to upper strata of the Sebei Group, notable beach-bar sedimentary sand bodies form key high-quality reservoirs. The genesis and spatial distribution of these beach-bar sands have long been debated, creating a bottleneck in further exploration and exploitation of the gas field. This scenario underscores an imperative need for in-depth characterization within the Tainan area's beach-bar structures. It's essential to precisely identify the various sedimentary microfacies and to construct an appropriate beach-bar depositional model, which will significantly enhance our understanding and utilization of these vital geological resources. Methods Informed by the principles of sedimentology, this methodology takes into account the varying hydrodynamic conditions prevalent during the formation of beach-bar systems, which consequentially result in differing grain sizes and permeability of the sand bodies. By centering on the median grain size as a pivotal metric, we synthesize a log response template for lithofacies, thereby establishing refined standards and dynamic responses for well-log interpretations of sedimentary microfacies. This advanced approach facilitates a more nuanced and scientifically grounded delineation of beach-bar sedimentary microfacies. Leveraging insights from modern sedimentary analogues and through a meticulous analysis of sand bodies within regions of dense well networks, the study employs horizontal well and production data to validate the rationality of microfacies classifications. Acknowledging the multifaceted genesis of beach-bars, influenced by a spectrum of environmental and geological factors, this research culminates in the proposition of a sophisticated beach-bar depositional model tailored for inland rift lake basins. This model reflects a deep integration of complex formation processes and characteristics unique to such environments. Results In the Tainan region, nestled within the middle and upper stratifications of the Sebei Group, a remarkable differentiation of beach and bar subfacies emerges. These can be intricately divided into distinct microfacies, including the bar core, bar margin, beach core, and beach margin. The bar sands, strategically overlaid on the beach sands, distinctly orient perpendicular to the prevailing northwest winds. Their morphology is characterized by either lens-like or crescent shapes, stretching an impressive length of approximately 1 250 meters and spanning a width of around 250 meters. This results in a linear length-to-width correlation, approximately 5, a ratio that harmoniously aligns with modern sedimentary environments. The beach sands exhibit a seamless, contiguous spread, predominantly extending in a perpendicular fashion relative to the source direction. This pattern becomes particularly pronounced during periods of low water levels. In drawing parallels with the beach-bar deposits found in Tengiz Lake, there is a notable correspondence in the extension direction, distribution patterns, and the critical length-width ratios of the bar sands. This comparative analysis underscores the similarity in sedimentary processes across diverse geographical locales. Furthermore, the abundant supply of source materials lays a robust foundation for the genesis and evolution of these beach-bar structures. A confluence of multifaceted factors, including the nuances of ancient tectonics, the intricacies of paleogeography, the dynamics of ancient monsoons, and the variances in past water depths, collectively weave a complex tapestry that dictates the developmental scale, the morphological characteristics, and the precise geographic localization of these beach-bar formations. Conclusions A "shallow lake, wave modification, oblique-arrangement" depositional model for beach-bar systems is proposed, offering theoretical guidance for identifying beach-bar systems in inland rift lake basins. This model encapsulates the dynamic interplay of wind-driven waves and shallow lake environments in shaping the beach-bar structures, emphasizing the importance of understanding both the physical processes and the sedimentological context in these unique settings. This approach provides a comprehensive framework for analyzing and interpreting beach-bar systems within inland rift basins, enriching the understanding of their formation and distribution.
Objective Systematic study of sedimentary systems and models is the foundation for clarifying the development mechanism of high-quality reservoirs in clastic rocks. Methods A systematic study was conducted using drill cores, thin section and paleontological fossil identification, grain size analysis, well-logging and seismic interpretation of the sedimentary system and evolution of the Oligocene in the study area to restore the sedimentary environment of the Paleogene. Results The lithology of the lower part of the Oligocene (Yacheng Formation) is mainly composed of medium coarse sandstone and conglomerate sandstone. The sandstone is poorly sorted, with mineral composition gradually stabilizing and maturity gradually increasing upwards from bottom to top. The cumulative curve of particle size probability shows suspended and jumping characteristics, with extremely low fossil abundance. The sedimentary facies types are mainly fan delta, shore shallow lake and lakeshore plain. The lithology of the upper part of the Oligocene (Lingshui Formation) is mainly composed of fine sandstone and mudstone, with a significant increase in fossil abundance. The sedimentary facies are mainly coastal shallow marine, shallow-water continental shelves and deep-water continental shelves. The study area underwent a transition from marine terrestrial transitional sedi-mentation to shallow marine sedimentation during the Oligocene. During the depositional period of the Yacheng Formation, the basin was experiencing strong faulting and rapid compensation. The main features of the seismic phases are accumulative and chaotic reflection structures. Fault activity in the area led to the formation of a structural pattern with alternating concave and convex features, resulting in shallow water bodies. Shallow lake facies were developed at the center of the depression and fan delta facies are developed on steep slopes and deeper water bodies. Braided river delta facies are present on gentle slopes and shallower water bodies. During the sedimentation period of the Lingshui Formation, the basin was undergoing rapid faulting and under-compensation. The seismic phase is mainly characterized by parallel sub-parallel reflection structures. Fracture activity caused the deepening of sedimentary water bodies. The overall development resulted in both shallow- and deep-water shelf facies in the center of the depression, with sporadic fan delta facies around the periphery. Conclusions The Oligocene in the YA area is a strongly faulted sedimentary system in which the sedimentary facies types and distribution were significantly influenced by tectonic movement. The filling style and sedimentary evolution of the basin reflect its sedimentary pattern during that period of time.
Objective Member 1 of the Neogene Shawan Formation is the main target interval in the Chepaizi area of Junggar Basin. There have been different studies on its depositional types and distribution. Methods Based on the previous studies, using mud logging, core logging, and seismic data, and adopting the methods and techniques of sequence stratigraphy, seismic geomorphology, and sedimentology, the sequence stratigraphic framework of the section was established. The depositional faces were investigated, and the geomorphology was restored. Results The First member of the Shawan Formation was divided into one third-order sequence and four fourth-order sequences. The first sand group, the lower part of the second sand group, the upper part of the second sand group, and the third sand group correspond to lowstand system, transgressive system, lower highstand system, and upper highstand system tracts, respectively. In addition, they correspond to the fourth-order sequences: PSS1, PSS2, PSS3, and PSS4, respectively. There were likely two provenances of member 1 of the Neogene Shawan Formation in the Chepaizi area: Zaire Mountain to the northwest and Tianshan Mountain to the south. The sedimentary environment from the northwest provenance belonged to the shallow fan delta, and the sedimentary environment from the south provenance belonged to the braided river delta. There were two different scale shallow fan delta complex sedimentary bodies, with two complex fan deltas in northern Chepaizi uplift. The slope of the northeast Chepaizhi was steeper, the gully scale was smaller, a series of complex sedimentary bodies of steep slope type shallow water fan delta were formed, and the complex fan delta is smaller and has depositional characteristics from gravity current. The sediments are poorly sorted, bearing muddy gravel, with no clear stratigrafication except for fining upward. The slope of the southwest Chepaizi was more moderate, the valley scale was larger, and a series of complex sedimentary bodies of gentle slope type shallow water fan delta were formed. The scale of the composite fan delta is larger and has depositional characteristics from traction current. The sediments are subangular-subround, well sorted, cross-bedded, with the orientation along the long axis of the gravel. In the lowstand and transgressive system tracts, the onlap pinch-out boundaries of the fan delta sedimentary wedge were consistent with the paleogeomorphology. The complex fan delta of the lowstand system tracts was distributed below the structural slope-break zone, reaching in the south and the east of Chepaizi area where the braided river delta reached, and they interacted with each other. The lacustrine range was the smallest during this stage. In transgressive system tracts and lower highstand system tracts, the fan deltas were distributed above the slope-break zone, and the lacustrine range was the largest. In the upper highstand system tracts, the fan deltas were distributed near the structural slope-break zone. Conclusions The paleogeomorphology and the relative lacustrine level change controlled the sedimentary characteristics of the the complex fan delta of the Sha-1 member in the Chepaizi area.
Objective The Santanghu Basin is an important oil and gas exploration area in northern Xinjiang. A thorough understanding of sedimentary facies, sandbody distribution, and associated provenance system within the basin is crucial for guiding the oil and gas exploration and development in the study area. Methods Using core and well logging data, the distribution characteristics and depositional evolution were studied for the Lower to Middle Jurassic Tiaohu-Malang Sags in the Santanghu Basin. Additionally, heavy minerals and detrital U-Pb dating were combined to analyze the provenance for key stratigraphic intervals. Results During the Lower to Middle Jurassic, the Tiaohu-Malang Sags were in braided-river deltaic depositional environments. During the depositional period of the Badaowan Formation, the braided-river deltaic system in the north was more developed and extended far to the south, whereas the southern system had a limited distribution. The Sangonghe Formation was dominated by braided-river delta front and prodelta-shallow lake deposits as the lacustrine basin expanded. As the depocenter migrated southward during the early Xishanyao, a large number of braided-river distributary channels and delta-front sandbodies developed in the north, intersecting with the lower braided-river delta plain and delta front of the southern system. Sediments originated from a mix of short-distance and long-distance source areas. The short-distance sources were the thrust-nappe belts in the northern and southern margins of the basin, whereas the long-distance source likely came from the Edelunjin Mountains, transported into the northeastern part of the Tiaohu Sag and the northern part of the Malang Sag through low paleotopographic areas. Conclusions Analysis of the sedimentary system and the ‘source-to-sink’ system reveals the distribution of sedimentary facies and sandbodies in the Middle Jurassic Tiaohu-Malang Sags. This provides a geological basis for oil and gas exploration in the Santanghu Basin.
Objective The Shaximiao Formation of Middle Jurassic in the central Sichuan Basin represents a key tight gas reservoir target. Currently, exploration and development of the First member of the Shaximiao Formation remain in early stages, with comprehensive research still limited, especially in systematic provenance studies controlling the distribution of high-quality sand bodies. Methods Integrating petrological analysis and elemental geo-chemistry, this study investigates the provenance of the First member of the Shaximiao Formation in central Sichuan Basin. Results (1) The sandstone of the First member of the Shaximiao Formation is mainly composed of feldspathic litharenite and lithic arkose. The igneous rock fragments are predominantly andesite, which is rarely found in the underlying strata but is common in northeastern and southeastern Sichuan Basin. (2) The dominant heavy minerals are garnet and epidote. The latter is scarce in the lower strata but is well-developed in northeastern and southeastern Sichuan Basin. (3) Discrimination diagrams of F1-F2, SiO2-TiO2, La/Th-Hf and Co/Th-La/Sc indicate that the provenance of the First member of the Shaximiao Formation is mainly felsic volcanic rocks, with minor sedimentary rocks. Conclusions The sandstone of the First member of the Shaximiao Formation in central Sichuan Basin is primarily sourced from the Dabashan Orogenic Belt in the northeastern part of the basin, with limited contribution from surrounding areas in other directions. This understanding provides strong support for delineating favorable tight gas zones and guiding exploration and development activities in the Sichuan Basin.
Objective The pre-salt carbonate reservoir formation process in the Ordos Basin is controversial. Calcite containing hydrocarbon and asphalt inclusions developed in the pre-salt reservoir of the Ordovician Majiagou Formation in the Wusenqi area is an important indicator of the fluid source and hydrocarbon accumulation process. Methods Through core observation, rock thin section identification, cathodoluminescence, rare earth elements, C, O, Sr isotopes, microfluorescence, and laser Raman experiments, calcite development stages were divided, the sources of vein forming fluids were analyzed, and fluid inclusions were studied to reveal the significance of fluid activities associated with hydrocarbons for hydrocarbon accumulation. Results The results show that four stages of calcite veins (C1, C2, C3, and C4) are developed in the carbonate reservoir in the Wusenqi area, and the characteristics and sources of secondary calcite veins are different in different periods. The C1 and C4 vein forming fluids are derived from the dissolved surrounding rocks, and the strontium carbon and oxygen isotopes are consistent with those of Ordovician seawater, and the rare earth partition pattern is characteristic of seawater. C2 calcite veins have extremely negative carbon isotope values, high 87Sr/86Sr values and total rare earth content, positive Eu anomaly, and fluid source from external strata. C3 calcite has a negative carbon isotope value, higher 87Sr/86Sr values, and total rare earth content, and the fluid is also derived from the external formation. In addition, asphaltic inclusions developed on calcite veins of C2 and C3 stages, indicating that oil and gas cracked after entering the reservoir. Conclusions The study area may have experienced two periods of oil and gas charging from external formation sources, and the study of calcite veins is helpful for constraining the process of oil and gas accumulation in the Ordos Basin and other basins.
Objective The Dianqianbei Depression is not only an important exploration and producing area of marine shale gas in southern China, but also an important large-super large Mississippi Valley (MVT) type lead-zinc metallogenic area associated with key metals in China. Asphalt or ancient reservoirs with high Pb and Zn contents are constantly found in lead-zinc deposits. It is of great significance to explore the distribution characteristics of trace elements in black shale kerogen in the study area for lead-zinc prospecting. Methods Taking the black shale outcrops in Dashiban, Liangfengao and Maoba areas in the eastern part of the Dianqianbei Depression as the research object, the kerogen in black shale was pretreated by microwave digestion method, and the trace elements in black shale and kerogen were analyzed and tested in combination with petrographic and mineralographic observation. The material contribution of mineralization and the sedimentary environment of black shale were studied by the geochemical characteristics of elements in black shale kerogen. Results The whole rock Pb, Zn, Cd, Bi, Sb, V, Cr, and Ni contents are higher than those in kerogen, and the contents of Ag, Ge, U and Th in kerogen are higher than those in whole rock. The light rare earth is relatively enriched and the heavy rare earth is relatively depleted in the whole rock and kerogen. Eu and part of Ce in the whole rock show weak negative anomalies. The kerogen shows strong Ce and Eu weak negative anomalies, and the total rare earth content is higher than that of the whole rock.Three redox indicators (U/Th, Ni/Co, and V/Cr ) in the kerogen of the Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation showed that the Wufeng Formation was oxygen-poor-anoxic, and the Longmaxi Formation was oxygen-rich-oxygen-poor; the ancient water depth calculated by Co element in the study area is 6.85-54.37 m. The paleoclimate reflected by Sr/Cu is warm and humid, and the Sr/Ba value is less than 0.5, representing the sedimentary environment of brackish water. Furthermore, the Wufeng Formation has greater paleoproductivity than the Longmaxi Formation. Conclusions Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in the study area are an oxygen-rich-oxygen-poor turbulent sedimentary environment, with a warm and humid climate of brackish water shallow shelf facies sedimentary characteristics. The trace elements in the black shale kerogen can provide a basis for the evaluation of regional prospecting areas.
Since 1983 Bimonthly
Sponsor: Committee of Sedimentology, Chinese Society for Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry
Commission on Sedimentary Geology, Geological Society of China
Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, CAS
Editor-in-chief: Wang Chengshan
Research Trends
Sedimentologica Research Teammore
Sedimentologica Voicemore
- Asymmetry of extreme Cenozoic climate–carbon cycle events
- Towards understanding the origin of massive dolostones
- Zn isotopic evidence for paleoenvironmental evolution during the Cretaceous ocean anoxic event OAE2
- Coupling relationship between deep time long period climate change and chemical weathering of silicate rocks
- Microbially mediated organomineralization in the formation of ooids
Sedimentology Classmore
-
Sedimentology Class: Active Marine Carbon During Sturtian “Snowball Earth” Glaciation
-
Sedimentology Class: Source-to-Sink System Budget Analysis of Continental Fluvial-Lacustrine Sedimentary Association: A case study from the Middle Jurassic in the northern Qaidam Basin
-
Sedimentology Class: Research Processes on Deep-water Interaction Between Contour Current and Gravity Flow Deposits, 2000 to 2022
-
Sedimentology Class: Wildfire Records Across the Triassic-Jurassic Boundary in the Southern Margin of the Junggar Basin, and Global Correlations