-
碳酸盐岩地层中的油气成藏常被认为是多期成岩流体、多期烃类流体共同作用的结果[1⁃5],其过程由于储渗空间的强烈非均质性往往具有复杂性,给规模性勘探开发带来风险与挑战[6⁃8]。震旦系灯影组是四川盆地海相碳酸盐岩天然气勘探的重要层系[9],已相继发现了威远气田、安岳气田,累计三级储量近万亿立方米[10⁃12]。近年来,蓬莱地区多口钻井在震旦系灯影组二段、四段测试均获得高产工业气流[13⁃15],展示出该地区灯影组天然气勘探的巨大潜力。尽管该地区灯影组储层发育良好,并且紧邻寒武系生烃中心,烃源岩条件被认为比安岳地区更优越[15]。但实际勘探结果表明,受加里东期、印支期、燕山期、喜马拉雅期等构造运动影响,该区灯影组油气成藏经历复杂演化过程,天然气以原油裂解气成因为主,古油藏分布范围尚未落实,关键成藏阶段无法确定且争议较大。主力烃源岩不在下方,“倒灌”和“侧接”式的油气运聚过程不清楚。气藏内部气水共存,且气水界面不统一,这些都给勘探工作带来极大风险[16⁃18]。
储层孔隙度反映了储层储存和运移油气的能力,其现今孔隙度可以通过岩心物性测试、测井等资料得到,但碳酸盐岩储层的现今孔隙度与成藏时期的古孔隙度往往差异较大[4,14]。获得地质历史时期,特别是成藏期时的储层古孔隙度对于研究油气成藏过程有着重要的意义。川中地区灯影组古岩溶储层在形成后,经历了长期的成岩作用改造,成岩作用复杂且对孔隙度演化的影响强烈,并且多套储层垂向上叠置发育,形成了主要的油气运聚通道。油气成藏时期的储层古孔隙度直接影响了古油藏的分布范围,但目前对于该地区成藏时期古孔隙度特征的研究较少[17⁃20]。本文依据成岩矿物占位关系,结合激光原位微区定年和元素测试结果,建立研究区灯二段、灯四段成岩演化序列,应用孔隙反演回剥的方法,恢复储层的古孔隙度演化曲线,结合油气成藏关键阶段,揭示灯影组古岩溶储层成岩演化的成储—成藏效应。
-
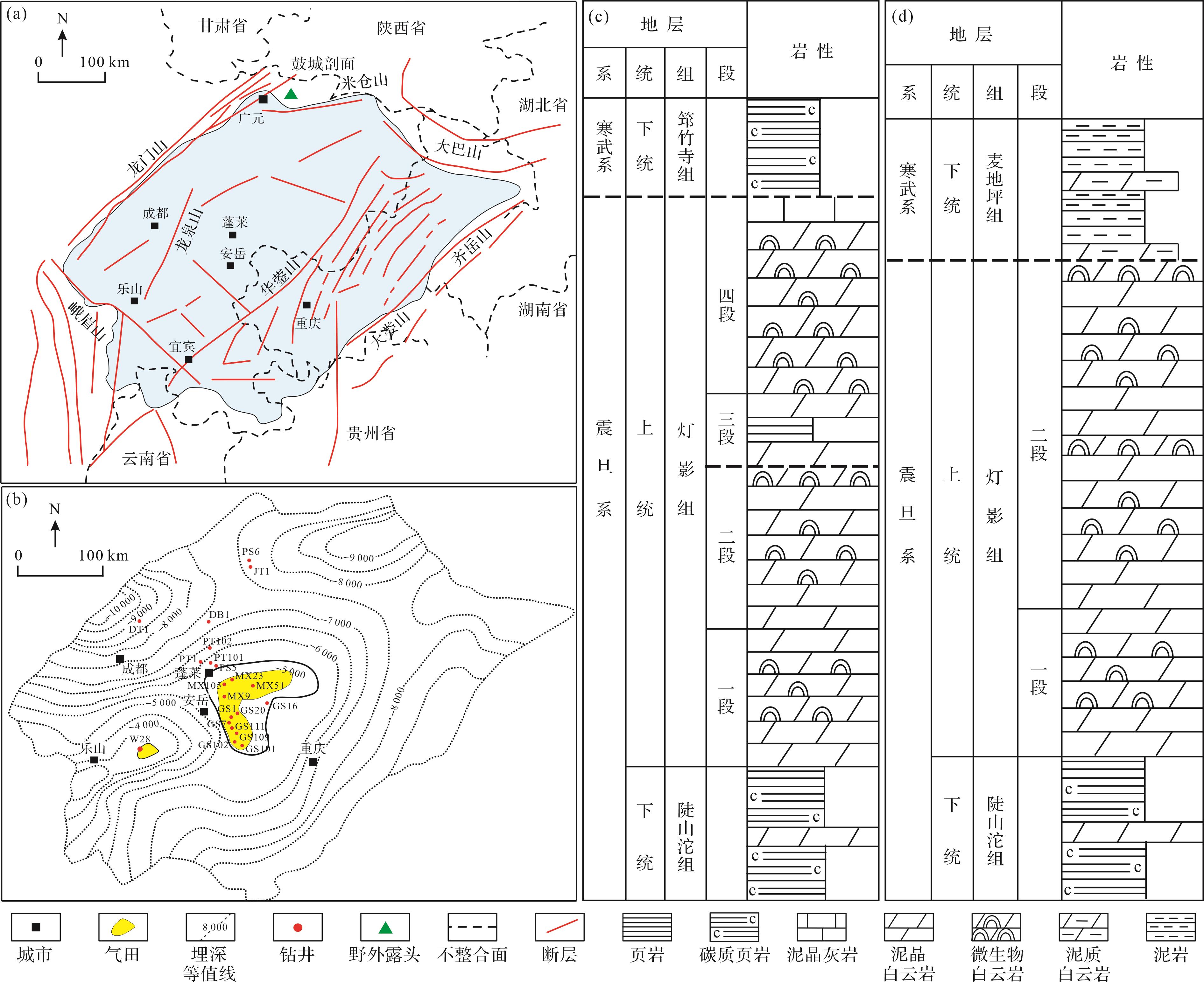
研究区位于四川盆地中部,包括安岳、蓬莱两个地区(图1a)[13]。本区发育加里东期形成的古隆起构造[21⁃22]。在多期构造改造过程中,古隆起整体继承发育(图1b),最终在喜山期后定型[1]。基于藻类含量和沉积构造类型,区内震旦系灯影组可被划分为四段,其中,灯二段和灯四段以叠层石、凝块石等微生物白云岩为主,灯一段以泥晶白云岩为主,灯三段以黑色泥页岩为主[2]。晚震旦世的桐湾期抬升运动,导致灯二段和灯四段顶部经历了剥蚀和广泛的岩溶作用,形成了大规模不整合面[23⁃24]。不同于安岳地区(图1c),蓬莱地区大部分缺失灯三段、灯四段,灯二段直接与上覆寒武系不整合接触(图1d)。在此背景下,灯二段、灯四段顶部形成了分布广泛的古岩溶改造成因藻类丘滩储层。近年来针对储层内沥青的定量研究表明,寒武系麦地坪组、筇竹寺组泥页岩均可以作为灯影组成藏的主力烃源岩[7]。
-
本次研究的14个灯二段岩心样品取自蓬莱地区的5口取心井(PS5井、PS1井、PT1井、PS2井、DB1井),16个灯四段岩心样品来自安岳地区4口取心井(MX105井、GS18井、MX51井、GS109井)和蓬莱地区的2口取心井(PS2井、DB1井)。在储层中成岩矿物类型的鉴定基础上,选取了7个白云石样品进行激光原位U-Pb同位素测年,包括1个基质白云石(MD)样品,3个纤状白云石(FD)样品和3个鞍状白云石(SD)样品。该实验是由成都创源微谱公司的Thermo Scientific quatraple iCap TQ电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(Q-ICP-MS)完成的,每个年龄数据大约需要对白云石矿物打80~115个激光点。具体参数包括直径为150 μm的激光光斑尺寸、3 J/cm2的激光能量和10 Hz的重复频率。白云石样品与NIST-614玻璃标准品和几种基质匹配的实验室工作方解石标准品一起测量,包括PTKD-2和WC-1[3⁃4]。对NIST-614玻璃标准物(包括未知样品)和方解石标准物进行重复测量,以校正207Pb/206Pb分馏和206Pb/238U比值中与仪器相关的漂移[3]。基于激光剥蚀脱气和不同质量分数的U、Pb同位素分析,以238U/206Pb、207Pb/206Pb值分别为横纵坐标、构建Tera-Wasserburg谐和曲线图计算碳酸盐矿物形成年龄,拟合出的不谐和曲线和Tera-Wasserburg反协和曲线下交点位置即为样品形成年龄。独立测年为268.5±2.7 Ma的WC-1方解石标准品和独立测年为153.5±1.9 Ma的PTKD-2方解石标准品也与白云石样品一起测年,作为对照标准品以确保再现性[25], 不同阶段得出的结果在参考值的2%以内。
根据U-Pb绝对年龄,选择了8个白云石晶体进行激光原位主量—微量元素和稀土元素分析。实验仪器为Q-ICP-MS。共测试了51个激光点位,其中基质白云石(MD)6个点位,纤状白云石(FD)15个点位,细晶白云石(FCD)12个点位,鞍状白云石(SD)18个点位。
-
根据碳酸盐岩气藏开发地质行业标准(SY/T 6110—2002)[26],研究区灯二段、灯四段储层均以Ⅲ类储层为主,这种划分方案体现不出灯影组储层的强烈非均质性,不能满足勘探开发需求。本次研究基于储渗空间类型的搭配关系,结合常规—成像测井等资料,将区内灯二段、灯四段储层均划分为两种类型:缝洞型和孔洞型。
-
灯二段缝洞型储层在岩心上呈浅灰、褐灰色,原岩岩性主要为凝块石白云岩或叠层石白云岩,充填物多为各类矿物和沥青(图2a,b)。该类储层的全直径岩心孔隙度介于2.12%~9.73%,平均为4.24%,全直径岩心渗透率介于0.56×10-3~5.88×10-3 μm2,平均为1.15×10-3 μm2。常规测井响应特征为:扩径明显,声波时差明显增大,高中子,电阻率明显降低且侵入特征明显。孔洞型储层岩心为浅灰、褐灰色,原岩为砂屑白云岩或凝块石白云岩(图2c,d),全直径岩心孔隙度介于1.39%~4.57%,平均为2.18%,全直径岩心渗透率介于0.17×10-3~2.17×10-3 μm2,平均为0.20×10-3 μm2。常规测井响应特征为:扩径不明显,电阻率明显降低,侵入特征不明显,密度降低。
-
灯四段缝洞型储层在岩心上呈浅灰、褐灰色,原岩为凝块石白云岩和叠层石白云岩(图2e,f),全直径岩心孔隙度介于2.22%~5.27%,平均为3.58%,全直径岩心渗透率介于0.33×10-3~8.96×10-3 μm2,平均为0.63×10-3 μm2。测井响应特征为:扩径明显,声波时差明显增大,高中子,电阻率明显降低且侵入特征明显。孔洞型储层为浅灰、褐灰色,原岩为砂屑白云岩、凝块石白云岩(图2g,h),全直径岩心孔隙度介于1.42%~4.51%,平均为2.92%,全直径岩心渗透率介于0.17×10-3~4.87×10-3 μm2,平均为0.32×10-3 μm2。常规测井响应特征为:扩径不明显,电阻率明显降低,侵入特征不明显,密度降低。
-
灯二段储层中最多可识别出9期成岩矿物(图3,4),灯四段储层中最多可识别出8期成岩矿物(表1)。第1期矿物为纤状白云石(FD)(图3a,b),俗称葡萄花边构造或葡萄状环边胶结(图3c,d),这一类白云石形成于同生海底阶段。前人研究提出纤状白云石(FD)的出现印证了灯影组沉积期海水Mg/Ca比演化规律,属于灯二段中—上部溶洞、溶缝内“白云石海”事件的结晶产物,能直接反映埃迪卡拉末期的海水化学性质,这一类白云石胶结物形成时间早,多具有单向延长的特征,被认为是文石类矿物被早期白云石化改造的结果[27]。同时,由于海平面频繁震荡,可出现同生期暴露前后的多期纤状白云石。相比灯四段(图4a),该类矿物在灯二段中发育时间长、发育期次多,在海底胶结阶段、准同生期大气淡水成岩阶段以及表生成岩阶段均有发育。第2期矿物为细晶白云石(FCD),这类白云石的自形程度高,镜下观察中晶体更为透亮,阴极射线下呈光亮发光特征,与纤状白云石、粒状白云石等较为暗淡、不发光的特征对比明显[1]。第1期沥青(B1,又称沥青膜或沥青线),志留纪末期伴随地层持续埋深,裂陷槽内烃源岩在志留纪末期达到生烃门限,开始第一期原油充注。储渗空间边缘的细晶白云石表面出现第一期油气充注形成的沥青膜(第1期沥青),这一现象在蓬莱和安岳地区均可观察到[28⁃29]。矿物占位关系表明,多期纤状白云石(FD)与细晶白云石(FCD)形成时间早于早期古油藏(B1)形成时期,第1期鞍状白云石(SD1)(图4b,c)、中晶白云石(MCD)(图3e,f)、第2期鞍状白云石(SD2)形成晚于第1期沥青(图4d~g)[13],但早于第2期沥青(B2)(图3g)。在第3期鞍状白云石(SD3)与方铅矿、闪锌矿共生后(图3h,i、图4h),形成了最晚一期成岩矿物为石英(Qtz)(图3i、图4i)。

图 3 研究区灯二段古岩溶储层成岩矿物特征
Figure 3. Diagenetic minerals in paleoreservoir of 2nd member, Dengying Formation in the study area

图 4 研究区灯四段古岩溶储层成岩矿物特征
Figure 4. Diagenetic minerals in paleoreservoir of 4th member, Dengying Formation in the study area
表 1 研究区灯影组古岩溶储层成岩矿物类型及充填序列
Table 1. Mineral types and diagenetic sequences of paleokarst reservoirs in the Dengying Formation in the study area
发育位置 储层类型 原岩类型 成岩矿物类型及充填序列 灯二段 缝洞型 叠层石白云岩或凝块石白云岩 (1)第1期+第2期+第3期纤状白云石(FD1、FD2、FD3)、(2)细晶白云石(FCD)、(3)第1期沥青(B1)、(4)第1期鞍状白石(SD1)、(5)中晶白云石(MCD)、(6)第2期鞍状白云石(SD2)、(7)第2期沥青(B2)、(8)方铅矿(Gn)+闪锌矿(Sp)+第3期鞍状白云石(SD3)、(9)石英(Qtz) 灯二段 孔洞型 凝块石白云岩 (1)第1期+第2期+第3期纤状白云石(FD1、FD2、FD3)、(2)细晶白云石(FCD)、(3)第2期鞍状白云石(SD2)、(4)第3期鞍状白云石(SD3)、(5)石英(Qtz) 灯四段 缝洞型 叠层石白云岩或凝块石白云岩 (1)第3期纤状白云石(FD3)、(2)细晶白云石(FCD)、(3)第1期沥青(B1)、(4)中晶白云石(MCD)、(5)第2期鞍状白云石(SD2)、(6)第2期沥青(B2)、(7)方铅矿(Gn)+闪锌矿(Sp)+第3期鞍状白云石(SD3)、(8)石英(Qtz) 灯四段 孔洞型 凝块石白云岩 (1)第3期纤状白云石(FD3)、(2)细晶白云石(FCD)、(3)中晶白云石(MCD)、(4)第2期鞍状白云石(SD2)、(5)第2期沥青(B2)、(6)方铅矿(Gn)+闪锌矿(Sp)+第3期鞍状白云石(SD3)、(7)石英(Qtz) -
激光原位元素含量测试结果表明(图5),灯二段与灯四段基质白云石样品中主量元素Ca含量的分布范围相近,介于226 860×10-6~251 387×10-6(平均值为236 538×10-6),略高于白云石的标准测量值(约217 071×10-6)[29]。灯二段与灯四段细晶白云石样品中主量元素Ca含量、微量元素Sr、Fe、Mn含量也呈现出相近的富集特征。第1期、第2期、第3期纤状白云石样品中主量元素Ca含量的分布范围分别为234 457×10-6~248 879×10-6、239 275×10-6~247 999×10-6和238 526×10-6~259 396×10-6,平均值分别为240 216×10-6、244 486×10-6和250 064×10-6,均略高于基质白云石。作为热液流体的直接产物,两期鞍状白云石的Ca含量差异明显,第1期鞍状白云石的Ca含量介于11 819×10-6~29 935×10-6,平均值仅为17 907×10-6。而第3期鞍状白云石的主量元素Ca含量介于248 323×10-6~261 980×10-6,平均值高达255 835×10-6。

图 5 研究区灯影组古岩溶储层成岩矿物主量—微量元素交会图
Figure 5. Cross⁃plot of major elements vs. trace elements in diagenetic minerals of Dengying Formation paleokarst reservoir in the study area
灯二段与灯四段不同期次的纤状白云石样品具有相似的微量元素Sr、Fe、Mn含量(图5c~e),Ba、Ni含量在不同期次中差异明显(图5a,f)。与第1期鞍状白云石的各类元素含量相比,第3期鞍状白云石的每种元素含量均明显更高,并且灯四段中第3期鞍状白云石的各项元素富集程度略高于灯二段的同类样品(图5c),并且在微量元素Sr、Ni和Fe含量方面更接近纤状白云石(图5d)。元素丰度的显著差异还表明,第1期鞍状白云石和第3期鞍状白云石具有不同的流体化学性质,明显属于不同阶段的热液流体,推测流体来源、类型明显不同(图5e),后者似乎与海水关系更密切(图5f)。
-
在所有白云石样品中,稀土元素总量普遍偏低,其中基质白云石的稀土元素总量明显较高,介于5.11×10-6~35.49×10-6,平均值高达12.93×10-6。纤状白云石的稀土元素总量变化很大,第1期到第3期纤状白云石的稀土元素总量分别介于0.91×10-6~2.15×10-6、1.43×10-6~2.94×10-6和5.40×10-6~8.55×10-6,稀土元素总量有逐渐升高的趋势。细晶白云石的稀土元素总量介于0.42×10-6~3.27×10-6,平均值为0.86×10-6。第1期鞍状白云石稀土元素总量介于0.48×10-6~4.31×10-6,平均值为1.85×10-6。第3期鞍状白云石稀土元素总量远高于第1期,介于7.86×10-6~11.07×10-6,平均值高达9.22×10-6。
经过PAAS标准化后可得到稀土元素配分曲线[30],结果表明基质白云石呈明显的Ce负异常(图6a),其他稀土元素相对平坦。第1期纤状白云石(图6b)到第3期纤状白云石的稀土元素配分曲线呈微弱“左”倾(图6c),重稀土元素微弱富集(图6d)。值得注意的是,第2期纤状白云石的稀土元素分配模式似乎已脱离海水特征,呈现出Ce正异常,说明第2期纤状白云石的结晶过程是在一个相对还原的环境中进行的(图6c),推测为非热液成因地层流体。第1期鞍状白云石呈明显的Ce负异常和Eu正异常,其他元素的曲线部分较为平坦。第3期鞍状白云石仅具有Eu正异常的特点,其他元素未见异常。细晶白云石稀土元素配分曲线具有明显的Ce负异常和微弱的Gd正异常。相比基质白云石,3期纤状白云石代表了海水流体,第1期鞍状白云石代表的第1期热液流体和细晶白云石代表的成岩流体具有海源流体特征,推测为被改造的海水。第3期鞍状白云石代表的第3期热液流体则未见海水亲缘性,从绝对年龄和元素特征推测与峨眉山大火成岩省活动有关[13,31]。
-
矿物占位关系和储层岩石学特征表明,灯二段、灯四段储层经历的成岩事件大体相似,但第一阶段成岩事件则具有不同的成储效应。以灯二段基质白云石的绝对年龄(607±26 Ma)为参考标准,结合成岩矿物定年结果(图7a),与前人研究获得的实验数据,可以清楚地区分灯二段、灯四段储层形成后的各个成岩事件。第一阶段成岩事件为多期纤状白云石胶结作用,作为储集空间中最早的胶结物,识别出的3期纤状白云石绝对年龄分别为606±21 Ma、604±42 Ma、590±15 Ma(图8),其形成时期略晚于灯二段或灯四段的表生成岩阶段。在阴极射线下(图3d),纤状白云石的暗淡发光特征表明流体类型偏氧化型,这一点也得到了中等—低Fe、Mn含量和稀土元素Ce负异常的印证(图5,6)。这些特征表明,纤状白云石极有可能形成于非埋藏成岩环境,流体来源为灯影组同期海水。岩心、薄片观察结果表明,3期纤状白云石在灯二段储层中均可观察到(图3),对先期形成的孔洞空间进行了明显的胶结破坏(图7b);但在灯四段储层,仅可以观察到第3期纤状白云石(FD3),对孔洞空间的破坏作用明显较弱(图4)。宏观、微观岩石学特征均表明灯二段储层这一阶段成岩事件对于储层物性的破坏性明显强于灯四段储层(图7b)。第二阶段成岩事件对应细晶白云石对于灯二段、灯四段储层的充填作用,其形成时间为498±12 Ma。在阴极射线下,细晶白云石的发光程度明显高于纤状白云石(图3d),同样具有Ce元素负异常,并且Fe、Mn富集程度与纤状白云石相近(图5,6),对应的流体类型可能是在地层条件下被微弱改造的海水[13]。

图 7 研究区灯影组古岩溶储层成岩矿物激光原位U⁃Pb同位素年龄岩心样品
Figure 7. Petrographic photographs of core specimen for in situ U⁃Pb dating in paleokarst reservoir, Dengying Formation in the study area

图 8 研究区灯影组古岩溶储层成岩矿物激光原位U⁃Pb同位素年龄
Figure 8. Plotted results of situ U⁃Pb dating in paleokarst reservoir, Dengying Formation in the study area
第三阶段为第1期古油藏充注事件,但这一期古油藏规模极为有限[8,32⁃33],后期裂解后形成第1期沥青,仅在少数井区可以观察到。第四阶段成岩事件为第1期热液流体沉淀出的鞍状白云石(SD1)(图7c),形成时间为403±30 Ma。稀土元素配分曲线表明,虽然两期白云石均具有热液流体典型的Eu元素正异常(图6),但第1期鞍状白云石具有明显的Ce元素负异常,与第3期鞍状白云石的曲线特征有明显差异,表明确实存在两期流体性质不同的热液流体,这一观点也可以表现为两期鞍状白云石在微量元素富集程度上的显著差异(图5)。第五阶段为中晶白云石(MCD)的充填作用,进一步破坏了储渗空间的保存。第六阶段成岩事件为第2期热液流体沉淀出的鞍状白云石(图7d),形成时间为259.4±3 Ma[13]。第七阶段成岩事件为第2期古油藏充注事件,是灯影组大规模古油藏的形成阶段[1],后期裂解后形成第2期沥青。第八阶段为方铅矿、闪锌矿和第3期鞍状白云石等代表的第3期热液活动,形成时间为199±12 Ma。最后一个阶段的成岩事件以石英胶结物为特征,黎凌川[31]使用Ar-Ar同位素测年法确定该阶段石英年龄为125.8±8.2 Ma,王国芝等[34]认为伴生萤石的Sm-Nd同位素年龄为130 Ma。
对储层的地质历史时期的古孔隙度演化研究是借助铸体薄片进行的,但铸体薄片反映的是面孔率特征,要得到真实的古孔隙度,需计算真实古孔隙度与面孔率的换算关系。根据前人的研究成果以及大量的油田实例[35],利用研究区的全直径岩心物性测试资料得到现今孔隙度;通过磨制大铸体薄片(6 cm×5 cm)的镜下照片及计算机图像分析技术得到样品的面孔率,将二者相匹配后通过实验数据拟合,得到现今孔隙度与面孔率的关系,并且要求相关系数R2要大于0.5。
选取研究区不同储层的典型视域薄片,人工圈绘出各期矿物充填物对孔隙度造成的影响,利用Image-Pro Plus 6.0软件计算各期矿物充填物及残留孔隙所占照片总体的百分含量,确定各期矿物充填物对面孔率的影响(图9)。根据成岩演化过程依次计算各期成岩矿物充填物对面孔率的影响,由此可获得成岩矿物充填开始时的反演回剥的古孔隙度。

图 9 回剥法恢复研究区灯影组古岩溶储层古孔隙度
Figure 9. Restoration of Dengying Formation paleokarst reservoir in study area using the stripping method
研究区灯影组在志留纪末期曾形成早期古油藏,由于海西早期发生抬升剥蚀而破坏[1],而后随着寒武系烃源岩的快速埋藏升温,大规模油气充注导致灯影组储层又经历了三个关键成藏阶段[13]。第一阶段为三叠纪末—侏罗纪初期的大规模古油藏形成阶段,第二阶段为白垩纪中期的大规模古油藏裂解成气阶段,第三阶段为古近纪—新近纪的气藏调整阶段[36⁃37]。原油的运移和聚集所对应的孔隙度下限比天然气更高,前人提出碳酸盐岩油藏古油藏形成的孔隙度下限为2.6%[22,38],若碳酸盐岩储层古孔隙度低于2.6%,则不利于古油藏运聚。古孔隙度恢复结果表明(图10)[1,3],灯二段缝洞型储层在大规模古油藏运聚时期的古孔隙度为4.84%,有利于古油藏运移聚集,原油裂解成气阶段的古孔隙度为4.24%,有利于气藏运移聚集,而后古孔隙度维持在4.24%,在气藏调整阶段仍有利于天然气聚集。灯二段孔洞型储层在大规模古油藏运聚时期的古孔隙度为2.18%,不利于大规模古油藏运移聚集,而后两个成藏阶段,古孔隙度维持在2.18%,有利于天然气的运移聚集。灯四段缝洞型储层在大规模古油藏运聚时期的古孔隙度为4.93%,有利于古油藏运移聚集,古油藏裂解成气阶段和气藏调整阶段时的古孔隙度分别为4.68%和3.58%,均有利于天然气运移聚集。灯四段孔洞型储层在大规模古油藏运聚时期的古孔隙度为3.05%,高于原油运移聚集的孔隙度下限,古油藏裂解成气阶段和气藏调整阶段时的古孔隙度维持在2.92%,有利于天然气运移聚集。
-
(1) 川中地区震旦系灯影组灯二段、灯四段储层根据储渗空间搭配关系,均可划分为缝洞型和孔洞型两种储层类型。灯二段储层中可识别出包括3期纤状白云石、3期鞍状白云石在内的9期成岩矿物。灯四段储层中识别出的成岩矿物与灯二段略有不同,仅可识别包括1期纤状白云石在内的8期成岩矿物。
(2) 研究区灯影组储层中识别出的成岩流体类型包括海水、被改造的海水、热液流体、非热液成因地层流体。包括3期海水胶结、3期热液活动等在内的多阶段成岩事件对储层物性具有破坏性。
(3) 灯二段缝洞型储层在古油藏形成阶段、原油裂解成气阶段、气藏调整阶段始终具有运聚能力,孔洞型储层则仅在原油裂解成气阶段、气藏调整阶段具备运聚能力。灯四段的缝洞型储层和孔洞型储层在三个关键成藏阶段均具有运聚能力。
Diagenetic Sequence, Reservoir-forming and Hydrocarbon Accumulation Effect of Paleokarst Reservoirs in the Dengying Formation, Central Sichuan Basin
-
摘要: 目的 川中地区震旦系灯影组古岩溶储层是我国海相天然气勘探的重点目标,具有成岩历史长、改造期次多、非均质性强等特点,导致油气成藏结果复杂化,制约了下步大规模勘探开发。 方法 对灯影组古岩溶储层开展了成岩矿物序列识别、激光原位U-Pb同位素定年、激光原位元素含量测试,结合岩心物性测试和图像软件识别,厘清了该区灯影组储层类型、成岩序列及成储—成藏效应。 结果 灯二段储层和灯四段储层均可被划分为缝洞型和孔洞型两种类型。识别出9个阶段的成岩—成藏事件,成岩流体可划分为3种类型:海水、被改造海水和热液流体。3期海水胶结(分别对应606±21 Ma、604±42 Ma和590±15 Ma)、3期热液活动(分别对应403±30 Ma、259.4±3 Ma和199±12 Ma)等成岩事件对储层物性具有破坏性。 结论 成岩演化过程中的古孔隙度恢复结果表明,灯二段缝洞型储层在古油藏形成阶段、原油裂解成气阶段、气藏调整阶段始终具有运聚能力,孔洞型储层则在后两个阶段具备运聚能力。灯四段的缝洞型储层和孔洞型储层在三个关键成藏阶段均具有运聚能力。Abstract: Objective The paleokarst reservoirs of the Sinian Dengying Formation in the central Sichuan Basin are key targets for marine natural gas exploration in China, characterized by long diagenetic history, multiple diagenetic events, and strong heterogeneity. These characteristics lead to the complexity of oil and gas accumulation results, which restricts the next large-scale exploration and development. Methods By diagenetic mineral sequences, U-Pb isotope dating and laser in-situ element measurement in the Dengying Formation paleokarst reservoirs, combined with physical property testing of cores and image software identification, reservoir type, diagenetic sequence, reservoir-forming and hydrocarbon accumulation effect are determined. Results Two-types reservoir are identified in the 2nd and 4th members of the Dengying Formation: a fracture-vug type and a pore-vug type. Nine-stages diagenesis-hydrocarbon accumulation events were identified. The diagenetic fluids were of three types: seawater, modified seawater and hydrothermal. Multi-stage diagenetic events including three-stages seawater cementation (606±21 Ma, 604±42 Ma and 590±15 Ma) and three-stages hydrothermal activity (403±30 Ma, 259.4±3 Ma and 199±12 Ma) had destructive effects on reservoir physical properties. Conclusions Reconstructed paleoporosity for the period of diagenetic evolution indicate that the fracture-vug type of reservoirs in the 2nd member of the Dengying Formation always enabled hydrocarbon migration and accumulation during the formation stage of paleo-oil reservoirs, also during the stage of crude oil cracking into gas and during the stage of gas reservoir adjustment. Pore-vug type reservoirs allowed migration and accumulation only in the latter two stages. In the 4th member, fracture-vug reservoirs enabled migration and accumulation in all three stages of hydrocarbon accumulation.
-
表 1 研究区灯影组古岩溶储层成岩矿物类型及充填序列
Table 1. Mineral types and diagenetic sequences of paleokarst reservoirs in the Dengying Formation in the study area
发育位置 储层类型 原岩类型 成岩矿物类型及充填序列 灯二段 缝洞型 叠层石白云岩或凝块石白云岩 (1)第1期+第2期+第3期纤状白云石(FD1、FD2、FD3)、(2)细晶白云石(FCD)、(3)第1期沥青(B1)、(4)第1期鞍状白石(SD1)、(5)中晶白云石(MCD)、(6)第2期鞍状白云石(SD2)、(7)第2期沥青(B2)、(8)方铅矿(Gn)+闪锌矿(Sp)+第3期鞍状白云石(SD3)、(9)石英(Qtz) 灯二段 孔洞型 凝块石白云岩 (1)第1期+第2期+第3期纤状白云石(FD1、FD2、FD3)、(2)细晶白云石(FCD)、(3)第2期鞍状白云石(SD2)、(4)第3期鞍状白云石(SD3)、(5)石英(Qtz) 灯四段 缝洞型 叠层石白云岩或凝块石白云岩 (1)第3期纤状白云石(FD3)、(2)细晶白云石(FCD)、(3)第1期沥青(B1)、(4)中晶白云石(MCD)、(5)第2期鞍状白云石(SD2)、(6)第2期沥青(B2)、(7)方铅矿(Gn)+闪锌矿(Sp)+第3期鞍状白云石(SD3)、(8)石英(Qtz) 灯四段 孔洞型 凝块石白云岩 (1)第3期纤状白云石(FD3)、(2)细晶白云石(FCD)、(3)中晶白云石(MCD)、(4)第2期鞍状白云石(SD2)、(5)第2期沥青(B2)、(6)方铅矿(Gn)+闪锌矿(Sp)+第3期鞍状白云石(SD3)、(7)石英(Qtz) -
[1] 范俊佳,姜华,鲁雪松,等. 四川盆地蓬莱地区震旦系灯影组气藏压力演化与成藏过程[J]. 天然气工业,2022,42(12):32-43. Fan Junjia, Jiang Hua, Lu Xuesong, et al. Pressure evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation process of Sinian Dengying Formation gas reservoirs in the Penglai area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(12): 32-43. [2] 赵虎,孙勇,吴勇,等. 四川盆地中江一蓬莱地区灯二段丘滩体储层地震识别及有利区预测[J]. 天然气地球科学,2023,34(6):980-991. Zhao Hu, Sun Yong, Wu Yong, et al. Seismic identification and favorable area prediction of hilly-shoal reservoir in the Second member of Dengying Formation in Zhongjiang-Penglai area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(6): 980-991. [3] 沈安江,赵文智,胡安平,等. 碳酸盐矿物定年和定温技术及其在川中古隆起油气成藏研究中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(3):476-487. Shen Anjiang, Zhao Wenzhi, Hu Anping, et al. The dating and temperature measurement technologies for carbonate mineralsand their application in hydrocarbon accumulation research in the paleo-uplift in central Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(3): 476-487. [4] 沈安江,胡安平,程婷,等. 激光原位U-Pb同位素定年技术及其在碳酸盐岩成岩—孔隙演化中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2019,46(6):1062-1074. Shen Anjiang, Hu Anping, Cheng Ting, et al. Laser ablation in situ U-Pb dating and its application to diagenesis-porosity evolution of carbonate reservoirs[J]. Pe-troleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6): 1062-1074. [5] 蒋裕强,陶艳忠,谷一凡,等. 四川盆地高石梯—磨溪地区灯影组热液白云石化作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2016,43(1):51-60. Jiang Yuqiang, Tao Yanzhong, Gu Yifan, et al. Hydrothermal dolomitization in Sinian Dengying Formation, Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(1): 51-60. [6] 蒋裕强,谷一凡,朱讯,等. 四川盆地川中地区震旦系灯影组热液白云岩储集相[J]. 天然气工业,2017,37(3):17-24. Jiang Yuqiang, Gu Yifan, Zhu Xun, et al. Hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies in the Sinian Dengying Fm, central Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(3): 17-24. [7] 郭旭升,胡东风,黄仁春,等. 川东北地区胡家坝震旦系灯影组古油藏特征及其油气勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2020,41(4):673-683. Guo Xusheng, Hu Dongfeng, Huang Renchun, et al. Feature of paleo-oil pools in the Sinian Dengying Formation, northeastern Sichuan Basin, and its significance to exploration[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 673-683. [8] 杨程宇,文龙,王铁冠,等. 川中隆起安岳气田古油藏成藏时间厘定[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2020,41(3):492-502. Yang Chengyu, Wen Long, Wang Tieguan, et al. Timing of hydrocarbon accumulation for paleo-oil reservoirs in Anyue gas field in Chuanzhong uplift[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(3): 492-502. [9] 邱楠生,刘一锋,刘雯,等. 沉积盆地地层古压力定量重建方法与研究实例[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2020,50(6):793-806. Qiu Nansheng, Liu Yifeng, Liu Wen, et al. Quantitative reconstruction of formation paleo-pressure in sedimentary basins and case studies[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2020, 50(6): 793-806. [10] 杨威,魏国齐,谢武仁,等. 四川盆地绵竹—长宁克拉通内裂陷东侧震旦系灯影组四段台缘丘滩体成藏特征与勘探前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(6):1174-1184. Yang Wei, Wei Guoqi, Xie Wuren, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration prospect of mound-shoal complexes on the platform margin of the Fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in the east of Mianzhu-Changning intracratonic rift, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6): 1174-1184. [11] 孙玮,刘树根,李泽奇,等. 四川盆地灯影组天然气晚期调整成藏的主控因素[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,48(6):641-652. Sun Wei, Liu Shugen, Li Zeqi, et al. Main controlling factors of late adjustment and accumulation of natural gas in Dengying Formation, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2021, 48(6): 641-652. [12] 谢武仁,杨威,汪泽成,等. 台缘带特征、形成主控因素及其对油气成藏的控制:以四川盆地灯影组为例[J]. 地质科学,2021,56(3):867-883. Xie Wuren, Yang Wei, Wang Zecheng, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors on the development of a platform margin belt and its effect on hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2021, 56(3): 867-883. [13] Su A, Chen H H, Feng Y X, et al. In situ U-Pb dating and geochemical characterization of multi-stage dolomite cementation in the Ediacaran Dengying Formation, central Sichuan Basin, China: Constraints on diagenetic, hydrothermal and paleo-oil filling events[J]. Precambrian Research, 2022, 368: 106481. [14] 杨跃明,王文之,文龙,等. 四川盆地大型古隆起斜坡区微生物碳酸盐岩储层沉积演化特征与天然气规模成藏模式[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(3):38-47. Yang Yueming, Wang Wenzhi, Wen Long, et al. Sedimentary evolution characteristics and large-scale natural gas accumulation pattern of microbial carbonate in the slope area of major paleouplift, the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(3): 38-47. [15] 刘树根,李泽奇,邓宾,等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组深层碳酸盐岩储层沥青赋存形态及其油气藏示踪作用[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(8):102-112. Liu Shugen, Li Zeqi, Deng Bin, et al. Occurrence morphology of bitumen in Dengying Formation deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs of the Sichuan Basin and its indicating significance to oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(8): 102-112. [16] 李建忠,陶小晚,白斌,等. 中国海相超深层油气地质条件、成藏演化及有利勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(1):52-67. Li Jianzhong, Tao Xiaowan, Bai Bin, et al. Geological conditions, reservoir evolution and favorable exploration directions of marine ultra-deep oil and gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(1): 52-67. [17] 姜华,李文正,黄士鹏,等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组跨重大构造期油气成藏过程与成藏模式[J]. 天然气工业,2022,42(5):11-23. Jiang Hua, Li Wenzheng, Huang Shipeng, et al. Process and model of hydrocarbon accumulation spanning major tectonic phases of Sinian Dengying Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(5): 11-23. [18] 李纯泉,陈红汉,肖雪薇,等. 四川盆地中部高石梯—磨溪地区震旦系灯影组储层沥青拉曼光谱分析[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2022,43(2):456-466. Li Chunquan, Chen Honghan, Xiao Xuewei, et al. Raman spectroscopy of bitumen from the Sinian Dengying Formation reservoirs, Gaoshiti-Moxi area, central Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(2): 456-466. [19] Roberts N M W, Rasbury E T, Parrish R R, et al. A calcite reference material for LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(7): 2807-2814. [20] 沈安江,李杰,龙晓平,等. 四川盆地北缘亢家洞灯影组四段焦沥青Re-Os定年与烃源岩示踪[J]. 岩石学报,2022,38(6):1702-1712. Shen Anjiang, Li Jie, Long Xiaoping, et al. Re-Os dating and oil-source correlation of the pyrobitumen in the member 4, Dengying Formation of the Kangjiadong paleo-reservoir, northern margin of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(6): 1702-1712. [21] 杨雨,汪泽成,文龙,等. 扬子克拉通西北缘震旦系油气成藏条件及勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2022,49(2):238-248. Yang Yu, Wang Zecheng, Wen Long, et al. Sinian hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration potential at the northwest margin of the Yangtze region, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(2): 238-248. [22] 宋泽章,葛冰飞,王文之,等. 超深层古油藏的定量表征及其对气藏形成的指示意义:以川中古隆起北斜坡灯影组为例[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(2):517-532. Song Zezhang, Ge Bingfei, Wang Wenzhi, et al. Quantitative characterization of ultra-deep paleo-oil reservoirs and its indication for deep gas accumulation: A case study on the Dengying Formation, the North slope of central Sichuan paleo-uplift[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(2): 517-532. [23] 黄士鹏,姜华,王铜山,等. 四川盆地8000m海相超深层天然气成藏条件及有利勘探区带[J]. 地质学报,2023,97(5):1544-1560. Huang Shipeng, Jiang Hua, Wang Tongshan, et al. Accumulation conditions and favorable exploration zones for natural gas in 8000 meters marine ultra-deep strata in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(5): 1544-1560. [24] 李剑,杨春龙,谢武仁,等. 四川盆地安岳气田震旦系台缘带和台内地区天然气成藏差异性及勘探领域[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2023,44(1):34-45. Li Jian, Yang Chunlong, Xie Wuren, et al. Differences of natural gas accumulation and play fairways in the marginal zone and interior of Sinian platform in Anyue gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(1): 34-45. [25] 杨威,魏国齐,武赛军,等. 四川盆地区域不整合特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2023,50(3):504-515. Yang Wei, Wei Guoqi, Wu Saijun, et al. Regional unconformities and their controls on hydrocarbon accumulation in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(3): 504-515. [26] Gu Y F, Zhou L, Jiang Y Q, et al. A model of hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies in Precambrian dolomite, central Sichuan Basin, SW China and its geochemical characteristics[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(1): 130-145. [27] Gu Y F, Wang Z L, Yang C C, et al. Effects of diagenesis on quality of Dengying Formation deep dolomite reservoir, central Sichuan Basin, China: Insights from petrology, geochemistry and in situ U-Pb dating[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2023, 10: 1041164. [28] Ding Y, Chen D Z, Zhou X Q, et al. Cavity-filling dolomite speleothems and submarine cements in the Ediacaran Dengying microbialites, South China: Responses to high-frequency sea-level fluctuations in an ‘aragonite-dolomite sea’[J]. Sedimentology, 2019, 66(6): 2511-2537. [29] 李红,王良军,柳益群,等. 四川盆地东部中二叠统茅口组热液活动特征[J]. 古地理学报,2021,23(1):153-174. Li Hong, Wang Liangjun, Liu Yiqun, et al. Hydrothermal activities in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation in eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2021, 23(1): 153-174. [30] Waheed S, Siddique N, Faiz Y. Rare earth and high field-strength elements in the Multani Mitti clay: A study using INAA[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2013, 37(2): 197-205. [31] 黎凌川.川中高石梯—磨溪构造寒武系龙王庙组成藏地球化学研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2017:1-51. Li Lingchuan. Geochemical study on hydrocarbon accumulation of the Cambrian formation in the middle Cambrian of the middle Sichuan[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2017: 1-51. [32] Fang X Y, Deng B, Geng A S, et al. Geochemical properties, mechanism of formation, and source of solid bitumen in the Ediacaran Dengying Formation from the central to northern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2024, 159: 106573. [33] 刘可禹,刘建良. 盆地沉积充填演化与含油气系统耦合模拟方法在超深层油气成藏模拟中的应用:以四川盆地中部震旦系灯影组为例[J]. 石油学报,2023,44(9):1445-1458. Liu Keyu, Liu Jianliang. Application of basin modeling method coupling sedimentary filling evolution with petroleum system in simulating ultra-deep oil-gas accumulations: A case study of Sinian Dengying Formation in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(9): 1445-1458. [34] 王国芝,刘树根,陈翠华,等. 四川盆地东南缘河坝MVT铅锌矿与古油气藏的成生关系[J]. 地学前缘,2013,20(1):107-116. Wang Guozhi, Liu Shugen, Chen Cuihua, et al. The genetic relationship between MVT Pb-Zn deposits and paleo-oil/gas reservoirs at Heba, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(1): 107-116. [35] 路允乾,蒋有录,王尉,等. 松辽盆地长岭断陷东岭地区营城组输导层孔隙演化与油气充注关系[J]. 石油实验地质,2018,40(4):485-492. Lu Yunqian, Jiang Youlu, Wang Wei, et al. Relationship between porosity of Yingcheng sand-body migration channel and hydrocarbon injection of Dongling area, Changling Fault Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(4): 485-492. [36] 沈安江,罗宪婴,胡安平,等. 从准同生到埋藏环境的白云石化路径及其成储效应[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2022,49(4):637-647. Shen Anjiang, Luo Xianying, Hu Anping, et al. Dolomitization evolution and its effects on hydrocarbon reservoir formationfrom penecontemporaneous to deep burial environment[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(4): 637-647. [37] 邓宾,吴娟,李文正,等. 烃类包裹体赋存碳酸盐矿物U-Pb定年及其在油气成藏期次研究中的应用:以川中震旦系灯影组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学,2023,34(11):1887-1898. Deng Bin, Wu Juan, Li Wenzheng, et al. U-Pb dating and trapped hydrocarbon inclusions in carbonate for petroleum accumulation: Case study from the Sinian Dengying Formation in the central Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(11): 1887-1898. [38] 李平平,郭旭升,郝芳,等. 四川盆地元坝气田长兴组古油藏的定量恢复及油源分析[J]. 地球科学,2016,41(3):452-462. Li Pingping, Guo Xusheng, Hao Fang, et al. Paleo-oil-reservoirs reconstruction and oil correlation of Changxing Formation in the Yuanba gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(3): 452-462. -





 下载:
下载: