-
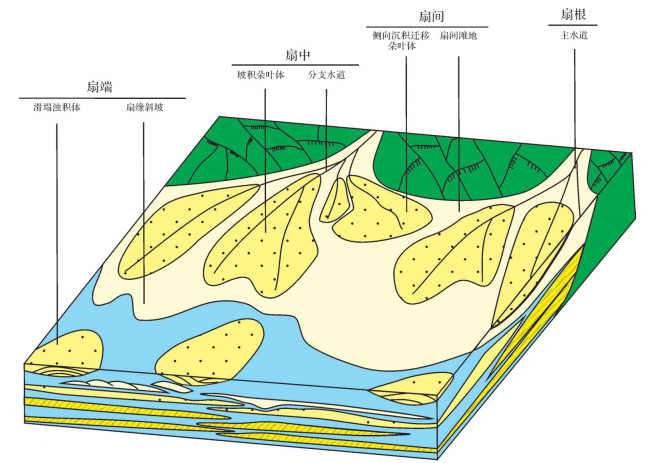
近岸水下扇是陆相断陷盆地陡坡带常见的一种沉积类型[1-5],可划分为扇根、扇中、扇端等3类亚相,一般认为扇中亚相是其主要的有利储集相带。但在油气勘探中发现,同一深度背景下的同一期扇体、同一亚相内部的含油性差异非常大,扇体表现为非常强的非均质性;另外还存在着扇体低部位出油、高部位出水的情况,油水关系矛盾。为进一步落实近岸水下扇的内部结构,厘清油水关系,笔者及团队在系统的地质、测井、地震资料分析的基础上,通过开展水槽沉积模拟实验,剖析近岸水下扇内部结构,建立扇体沉积模式,落实可能的圈闭类型,并在实验中发现了坡积朵叶体这种新的沉积类型。通过详细解剖坡积朵叶体的结构特征,分析其形成的机制和条件,以及与其相对应的圈闭类型及成藏模式,解决了近岸水下扇存在的油水关系矛盾等问题。
-
水槽沉积模拟实验是沉积学研究的重要手段[6-9]。实验在长江大学CNPC油气储层沉积模拟重点实验室的模拟湖盆内完成,整个实验室为16 m×6 m的大型水槽,本实验的实验区为5 m×5 m的可模拟基底沉降的活动底板区域,实验室条件符合陡坡带边界断裂持续沉降的活动特征。
-
在断陷湖盆陡坡带边界断裂幕式活动与水下砂砾岩沉积作用分析的基础上,以东营凹陷北部陡坡带东段盐家及西段利津地区沉积背景和水下砂砾岩沉积特征为依据,根据沉积模拟实验相似性理论,开展了双物源水下砂砾岩沉积模拟实验。整个实验分四4个期次进行,分别模拟沙四下(第一沉积期)、沙四上纯下早期(第二沉积期)、沙四上纯下晚期(第三沉积期)、沙四上纯上(第四沉积期)四个沉积阶段的沉积情况。每一期次均按洪水期—枯水期—间歇期的过程开展沉积模拟,实验方案及实验参数如下所示(表 1)。
表 1 水槽模拟实验实施方案及实验参数
Table 1. Implementation scheme and parameters of flume experiment

(1)构造活动强度:依据东营凹陷北部陡坡带不同阶段沉积地层厚度,结合边界断裂幕式沉降的特征,确定四个沉积期的基底沉降幅度。第一沉积期活动底板平均下降10 cm,分两次完成;第二沉积期平均下降12 cm,分三次完成;第三沉积期活动底板平均下降12 cm,分三次完成;第四沉积期活动底板平均下降10 cm,分两次完成。整个模拟过程活动底板共下降48 cm。
(2)地形坡度:沿陈家庄凸起南侧古基岩面发育的陈南断裂带控制了整个盆地的发育演化,该断裂带东西延伸约200 km,整体呈EW向延伸。其中东段基底坡度较陡,倾角可达30°~40°。断裂的西段坡度相对较缓,倾角约为10°~20°。根据实验装置条件,陡坡带东段沉积基底按30°设计,西段沉积基底按10°设计,设置两个物源。
(3)物源组成:考虑到粒度分析取样时可能仅仅取到了砂岩样品,并没有取砾岩样品,而砂砾岩体含有较多砾岩的实际情况,重新设计物源组成。砾石含量占30%,粒径平均1~4 mm,平均粒径2 mm;粗砂20%,中细砂占50%。两个物源分别采用两种颜色的砂交替进行。
(4)古水深设计:根据古水深资料,沙四段早期基本上是盐湖,水体面积小,水体深度小,因此设计初始水深最大40 cm,最小25 cm,实验过程保持水深不变;随着沉积作用进行,水深逐渐增加,第二期水深平均60 cm,第三期70 cm,第四期80 cm,使沉积物始终处于水下。
(5)砂砾石注入过程:分洪水期和枯水期交替进行,四个模拟期中每一个模拟期注入两次洪水、两次枯水,洪水期与枯水期注入时间比例按照1:3设计,洪水期砂砾石浓度按25%~30%设计,枯水期中细砂浓度按10%设计;每一个模拟期砂砾石使用量按8~10 t设计。
-
实验结果表明:陡坡带近岸水下扇是在断层幕式活动和气候控制下的阵发性洪水、洪水间歇期正常河流等多种沉积作用有序发育而形成的粗碎屑沉积体系。近岸水下扇扇主体为向岸一侧由快速堆积的砂砾岩体组成,在空间上呈朵体形态展布,可划分为扇根、扇中、扇端以及扇间4个亚相类型。由于水流频繁改道,形成纵向上多期叠置,平面上叠合连片的特征。扇外缘以深湖泥及滑塌浊积体组成,砂体分布较为局限。
扇主体的发育形态受控于物源供给量、地形坡度、构造活动强度及水体深度等因素的影响,坡度越大,构造活动越强,水体越深,近岸水下扇搬运距离越近。反之,向湖方向推进距离越远。通常情况下,陡坡带边界断层活动剧烈,近岸水带处于饥饿欠补偿的状态下,各期扇体始终以向岸退积序列为主[10-12]。实验第一及第二沉积期的模拟结果反映了上述特点。而在实验后两个沉积期的模拟过程中,随着边界断层活动的减弱及基底沉降量减小,枯水期沉积的扇体在早期洪水期沉积扇体的向湖盆中心一侧的斜坡上形成了一期新的沉积体。通过剖面切片解剖发现,该期沉积物在粒序上呈现明显的反韵律的旋回特征,在结构特征、形成机制以及油气成藏条件上与常规的近岸水下扇都具有较大的差异。该类沉积体超覆发育于前期形成的扇体的扇中—扇端亚相区域的斜坡上;区别于山坡高阶地风化堆积物形成的“坡积体”[13],将该类型的沉积体命名为“坡积朵叶体”。
-
坡积朵叶体作为陡坡带近岸水下扇体系内新发现的一种沉积类型,整体呈现出与其他扇体脱离的朵体扇的外形特征(图 1),其沿水流方向向上收缩,并向下散开。实验中可见坡积朵叶体沿不同的水流方向呈长舌状分布于洪水期形成扇体斜坡中下部,规模上大小不一,规模较大的沿水流方向可延伸1.5~2 m,宽度约0.6~1 m,厚度约10~20 cm,规模较小者长度仅0.5 m,宽0.2 m;按照1:500的实验比值计算,自然界中坡积朵叶体的规模长度可达750~1 000 m,宽度为300~500 m,厚度为50~100 m左右。

图 1 近岸水下扇坡积朵叶体沉积模式
Figure 1. Depositional pattern of slope accumulation lobes in the offshore underwater fan slope
实验纵剖面上坡积朵叶体一般紧邻上一期扇体,向上超覆在扇体水下部分的斜坡上,向下深入湖相泥岩中,延伸较远。横剖面上坡积朵叶体一般位于洪水期扇体的侧上方或扇间的位置,具有显著的填平补齐的特征。另外坡积朵叶体与早期扇体之间存在稳定的泥岩隔层,总体来看,坡积朵叶体为向四周尖灭的独立扇体;在扇体的远端地形转平的区域还会出现滑塌浊积体,滑塌浊积一般呈透镜体状,是包裹在泥岩中的独立砂体(图 2)。
-
坡积朵叶体岩石组分与注入的物源组成有关,单层沉积物在物源注入位置颗粒较粗,以砾石为主,杂乱分布,砾石、细砂岩、粉砂岩及泥岩共存,结构混杂。向前随着水流的推进逐步转变为细砂岩—粉砂岩,分选变好,颗粒支撑,泥质杂基。末端为湖相泥岩或页岩,夹滑脱入湖的砂质条带。
在沉积构造上,大部分坡积朵叶体上部含砾石带可见平行层理、交错层理发育。下部砂岩带以斜层理及平行层理为主,偶见羽状交错层理,反映水流改道的现象。顶部以及底部泥岩带以水平层理为主;少量坡积朵叶体砂质发育区可见变形构造、包卷层理等(图 3),反映出较强的水动力条件下滚动搬运的特征。
坡积朵叶体在相序上具有下细上粗的反韵律特征,分析原因主要是随物源注入量的持续增大,后期的沉积物漫过早期的沉积物,逐层向前推进,进而形成了前积的沉积序列。其沉积过程与扇三角洲的沉积特点相似,但没有明显的三角洲底积—前积—顶积的三层结构。实验切片中仅见到上部的含砾石层及下部的砂质前积层构成了坡积朵叶体的主体,其顶部及底部泥岩段为沉积间歇期自然沉降的泥质悬浮物,并非与坡积朵叶体同时形成(图 4)。
-
钻井证实,坡积朵叶体是济阳坳陷陡坡带近岸水下扇体系内普遍存在的沉积类型,在测井、录井、地震等多方面的信息中都有明显的响应。同时结合试验过程中沉积变化趋势分析,基本明确了现实沉积环境中坡积朵叶体的成因机制。
-
通过多年的勘探,在东营、车镇、渤南等多个凹陷均证实有坡积朵叶体发育,如L853、L94以及C302等井。区别于正常近岸水下扇扇主体退积正韵律的相序特征,钻井证实坡积朵叶体为具有反韵律特征的岩性体。与之相对应的在测井相上,坡积朵叶体自然电位曲线呈现出漏斗状的反旋回曲线特征(图 5)。
坡积朵叶体地震相特征上也与近岸水下扇主体有较大差别。近岸水下扇主体部分纵向上整体以快速退积为主,地震上表现为楔状叠置退积的反射;坡积朵叶体为向扇根及扇端上下两侧均尖灭的独立砂体,地震反射上呈现为与扇主体脱离的近平行于扇主体包络面的前积底超的中强反射(图 6)。
-
从实验过程、沉积构造的特征及实际钻探情况分析,坡积朵叶体的成因机制主要有直接沉积和后期垮塌滑动两种成因。其中以直接沉积为主,通常来说,沉积作用形成的坡积朵叶体发育反映沉积充填速度超过边界断层活动导致的可容空间扩大的速度,形成过程与实验模拟过程中第3沉积阶段与第4沉积阶段后半段的形成过程一致,对应图 2中的第3~2期与第4~2期。该类型的坡积朵叶体沉积厚度与平面分布范围较大,是坡积朵叶体的主要形成模式。利津洼陷的L853井区形成的坡积朵叶体就属于该类型。
同时陡坡带还存在少量的后期垮塌滑动形成的坡积体,主要是已沉积扇体受断裂沉降活动或者水流的影响而活化,形成部分垮塌或整体块体滑移至前期的近岸水下扇体的斜坡上。该类型的坡积朵叶体实质上为滑塌浊积体的过渡相。因搬运距离相对较近,未演化为浊流沉积。随着搬运距离的增大,以及内部结构组分分异性的增强,后期可转变为正粒序的滑塌浊积体。车镇洼陷的C302井区坡积朵叶体是该类型的典型代表,垮塌滑动形成的坡积朵叶体一般规模相对较小,且夹于较厚的泥岩层之中。
-
坡积朵叶体的发育与近岸水下扇主体部分类似,同样受物源供给量、边界断层活动性、水动力条件以及沉积坡度等多方面沉积因素的影响。
物源供给量是影响和控制坡积朵叶体规模的重要因素,物源供给量越大,早期形成的湖盆边缘的可容空间越容易被填满,进而后期的扇体可以越过前期扇体形成进积序列,坡积朵叶体就越容易发育,直接沉积形成的坡积朵叶体的规模就越大。
边界活动性也会影响坡积体形成。边界断层活动性越强,地层沉降越快,导致水下可容空间持续增大,砂砾岩体快速堆积,以退积序列为主,沉积作用难以形成大规模的坡积朵叶体;当边界断层活动性减弱后,水体相应变浅,扇体迅速填满湖盆边缘的水下可容空间。扇体斜坡的上部出露水面,在后期的沉积过程中为沉积物通道,沉积物过路不留。此时扇体的前方或侧缘可容空间大,沉积物在这些区域卸载堆积,易形成前积特征的坡积朵叶体。
水动力条件是垮塌滑动型的坡积朵叶体形成的重要控制因素。水动力条件强,水体携带泥砂能力越强,对前期形成的扇体的冲刷改造作用就越强。早期形成的扇体易遭受破坏,在水流搬运和重力作用下形成整体的垮塌滑动,形成与扇主体脱离的坡积朵叶体。另外,断层沉降引起的地震等活动,也可以导致扇体的垮塌滑移。
沉积坡度也会影响坡积朵叶体的形成。扇体在水下能够稳定存在,沉积卸载的斜坡一般要小于一定的角度,即休止角。沉积坡度陡,扇体的稳定性相应变差。当沉积坡度超过休止角,沉积物才具有向前搬运的能力。不论是沉积型还是垮塌型的坡积朵叶体,实验中证实均在休止角大于5°的情况下才可以形成。
总体来说,沉积作用形成的坡积体在水体相对较浅,物源供应充足,断层活动性减弱的时期容易形成;垮塌滑动型的坡积朵叶体多见于水动力较强,沉积坡度较陡的地区。
-
坡积朵叶体作为近岸水下扇体系内的一种沉积类型,发育区紧邻各个洼陷的深湖区,具有优越的油源条件[14-15];长时间推进的前积层序有利于颗粒的分选,可以有效提高储层的物性条件;前积特征表征了沉积上存在的某一个独立的沉积旋回,可形成独立的圈闭。湖相悬浮沉积伴随近岸水下扇发育的各个阶段,在砂砾岩体发育时期,表现为砂砾岩体楔形插入湖相泥岩中,而在间歇期表现为湖相泥岩披覆于整个扇体之上,可以作为坡积朵叶体良好的分隔封盖条件。坡积朵叶体形成期的枯水期—间歇期山区河流沉积作用时间长,但水动力相对较弱、碎屑物质含量降低,泥质成分比重升高,更有利于泥岩盖层的形成。
坡积朵叶体优越的油源、储层条件以及储盖组合,决定其可以形成独立于扇主体的岩性油气藏,与扇主体具有各自独立的油水系统[16-18],这也解决了近岸水下扇低部位出油,高部位出水的矛盾。
从坡积朵叶体形成机制和形成条件可知,寻找断层活动强度相对较弱的层系和地区是勘探的重要方向,从利津洼陷陈南断层的活动速率统计发现(图 7),沙四上纯上时期是沙四段断层活动的衰减期,有利于坡积朵叶体的形成。利津地区L853井区钻井情况也证实了该地区纯上时期发育了大范围的与扇主体脱离的坡积朵叶体,形成了独立的岩性圈闭并成藏(图 8)。通过沿物源推进方向的南北向油藏对比,清晰地展示出L853井区油藏由沙四上纯下亚段的连片成藏体系转变为到沙四上纯上亚段的独立的坡积朵叶体岩性圈闭成藏系统。
-
(1)坡积朵叶体是近岸水下扇体系内的一种新的沉积相类型,它是一种发育于陡坡带砂砾岩体与滑塌浊积岩之间位置,向扇根方向尖灭的独立砂体,具有独特的前积反韵律的旋回特征。
(2)坡积朵叶体主要有直接沉积及垮塌滑动两种成因机制。发育分布受控于物源量、边界断层活动强度、水动力条件、地形坡度等多方面因素的影响,水体较浅、物源充足、边界断层活动减弱、沉积坡度大于5°是坡积朵叶体形成的有利条件。
(3)坡积朵叶体的储盖结构决定其易于形成岩性圈闭,结合区域沉积背景,东营凹陷沙四上纯上以及沙三上时期是坡积朵叶体发育最集中的两个时期,对东营凹陷以及其他地区陡坡带的砂砾岩体油气勘探具有一定的指示意义。
Sedimentary Model and Genetic Mechanism for the Alluvial Lobes of the Offshore Underwater Fan Slope
-
摘要: 通过水槽沉积模拟实验,发现近岸水下扇体系内存在一种特定沉积背景下与扇主体伴生的新沉积类型——坡积朵叶体。这种朵叶体发育于陡坡带砂砾岩体与滑塌浊积岩之间,是向扇根方向尖灭且缺失其所对应的扇根连接的独立砂体。区别于常规的近岸水下扇退积式正韵律的粒序,坡积朵叶体具有独特的前积反韵律的旋回特征,自然电位曲线多为漏斗状的反旋回,地震表现为向上下两侧尖灭的中强反射。研究结果认为坡积朵叶体主要有直接沉积和后期垮塌滑动两种成因机制,所需沉积背景条件为水体较浅,物源供应充足,休止角大于5°。该类型的沉积体与早期扇体与晚期扇体中间均发育泥岩隔层,自成圈闭,具有重要的油气勘探价值。Abstract: Based on the flume deposition simulation, there exists a new sedimentary type in the near-shore underwater fan system, which is associated with the fan body under a specific sedimentary background-slope accumulation lobes. It is an independent sand body developed between the sandy gravel rock body and the fluxoturbidite in the steep slope belt, which is pointed out by the fan root direction and lacks the corresponding fan root connection. Different from the normal grain sequence of the normal positive rhythm for the offshore subsurface fan recession, the porphyritic lobes have a unique characteristic of a reverse cycle of proplanar reverse rhythm, the spontaneous potential curve is mostly a funnel-shaped reverse cycle, and the earthquake is a medium strong reflection to the top and bottom of both sides. According to the study, there are mainly two genetic mechanisms of direct deposition and late-stage collapse and sliding, and the required sedimentary background conditions are shallow water and an abundant material supply, with a resting Angle of greater than 50. The mudstone interlayer is developed in the middle of the early and late fan body and the sedimentary body.
-
表 1 水槽模拟实验实施方案及实验参数
Table 1. Implementation scheme and parameters of flume experiment
-
[1] 孙龙德.东营凹陷北部斜坡带沙三-四段砂砾岩体与油气聚集[J].沉积学报, 2003, 21(2):278-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.02.014 Sun Longde. Sandstone-conglomerate bodies in Sha 3~4 members and hydrocarbon accumulation in northern slope of Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2003, 21(2):278-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.02.014 [2] 鄢继华, 陈世悦, 姜在兴.东营凹陷北部陡坡带近岸水下扇沉积特征[J].石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 29(1):12-16, 21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sydxxb200501003 Yan Jihua, Chen Shiyue, Jiang Zaixing. Sedimentary characteristics of nearshore subaqueous fans in steep slope of Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China(Edition of Natural Science), 2005, 29(1):12-16, 21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sydxxb200501003 [3] 孔凡仙.东营凹陷北带砂砾岩扇体勘探技术与实践[J].石油学报, 2000, 21(5):27-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.05.006 Kong Fanxian. Exploration technique and practice of sandy-conglomeratic fans in the northern part of Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2000, 21(5):27-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2000.05.006 [4] 张善文, 隋风贵, 王永诗.济阳坳陷下第三系陡岸沉积模式[J].沉积学报, 2001, 19(2):219-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.02.010 Zhang Shanwen, Sui Fenggui, Wang Yongshi. Depositional models on the steep slope of Paleogene, Jiyang sub-basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(2):219-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.02.010 [5] 赵红兵, 严科.近岸水下扇砂砾岩沉积特征及扇体分布规律[J].断块油气田, 2011, 18(4):438-441. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkyqt201104007 Zhao Hongbing, Yan Ke. Depositional characteristics of glutenite and distribution pattern of fan on nearshore subaqueous fan[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2011, 18(4):438-441. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dkyqt201104007 [6] 刘忠保, 张春生, 龚文平, 等.牵引流砂质载荷沿陡坡滑动形成砂质碎屑流沉积模拟研究[J].石油天然气学报(江汉石油学院学报), 2008, 30(6):30-38. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jhsyxyxb200806006 Liu Zhongbao, Zhang Chunsheng, Gong Wenping, et al. A study on sedimentary simulation of sandy clastic current formed by sliding of traction current with sandy load along steep slope[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology (Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute), 2008, 30(6):30-38. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jhsyxyxb200806006 [7] 程立华, 陈世悦, 吴胜和, 等.断陷盆地陡坡带扇三角洲模拟及沉积动力学分析[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(4):29-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200504005 Cheng Lihua, Chen Shiyue, Wu Shenghe, et al. The simulation and sedimentary dynamic analysis of fan delta in the steep slope of fault basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(4):29-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200504005 [8] 王颖, 王晓州, 王英民, 等.沉积物理模拟实验在确定重力流临界坡度中的应用[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 37(4):463-468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2010.04.016 Wang Ying, Wang Xiaozhou, Wang Yingmin, et al. Determination of the gravity flow critical gradient using sedimentary simulation experiment[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 2010, 37(4):463-468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2010.04.016 [9] 刘晖, 操应长, 姜在兴, 等.断陷湖盆可容空间变化特征的模拟实验研究[J].油气地质与采收率, 2008, 15(6):22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2008.06.006 Liu Hui, Cao Yingchang, Jiang Zaixing, et al. Simulation experiment on the changed characteristics of the accommodation in faulted lacustrine basins[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2008, 15(6):22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2008.06.006 [10] 宋明水, 李存磊, 张金亮.东营凹陷盐家地区砂砾岩体沉积期次精细划分与对比[J].石油学报, 2012, 33(5):781-789. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201205006 Song Mingshui, Li Cunlei, Zhang Jinliang. Fine division and correlation of conglomerate sedimentary cycles in Yanjia area of Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(5):781-789. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201205006 [11] 宋国奇, 刘鑫金, 刘惠民.东营凹陷北部陡坡带砂砾岩体成岩圈闭成因及主控因素[J].油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(6):37-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.009 Song Guoqi, Liu Xinjin, Liu Huimin. Study on genetic mechanism and controlling factors of conglomerate diagenesis trap in northern Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2012, 19(6):37-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.009 [12] 操应长, 金杰华, 王艳忠, 等.东营凹陷北带古近系沙四段砂砾岩体沉积特征及沉积模式[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2014, 34(4):13-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2014.04.002 Cao Yingchang, Jin Jiehua, Wang Yanzhong, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and model for the sandstones and conglomerates in the 4th member of the Palaeogene Shahejie Formation, northern Dongying Depression, Shandong[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2014, 34(4):13-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2014.04.002 [13] 武刚.埕东凸起西南坡沙三段砂砾岩体坡积相沉积模式[J].特种油气藏, 2012, 19(3):22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2012.03.005 Wu Gang. Depositional model of slope wash facies of Es3 glutenite in the southwest slope of Chengdong uplift[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2012, 19(3):22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2012.03.005 [14] 王惠勇, 韩宏伟, 张云银, 等.东营北带东段胜坨-盐家地区砂砾岩扇体地层产状研究[J].石油物探, 2015, 54(2):203-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2015.02.012 Wang Huiyong, Han Hongwei, Zhang Yunyin, et al. Study on the occurrence of glutenite fans in Shengtuo-Yanjia area, the east section of northern Dongying Sag[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2015, 54(2):203-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2015.02.012 [15] 印森林, 唐勇, 胡张明, 等.构造活动对冲积扇及其油气成藏的控制作用:以准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠系-三叠系冲积扇为例[J].新疆石油地质, 2016, 37(4):391-400. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjsydz201604003 Yin Senlin, Tang Yong, Hu Zhangming, et al. Controls of tectonic activity on alluvial fan deposits and hydrocarbon accumulation:A case study of Permian and Triassic alluvial fans in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2016, 37(4):391-400. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjsydz201604003 [16] 冯有良, 徐秀生.同沉积构造坡折带对岩性油气藏富集带的控制作用:以渤海湾盆地古近系为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(1):22-25, 31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.01.005 Feng Youliang, Xu Xiusheng. Syndepositional structural slope-break zone controls on lithologic reservoirs-a case from Paleogene Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(1):22-25, 31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.01.005 [17] 姜在兴, 杨伟利, 于雯泉, 等.湖缘峡谷及其含油性[J].地学前缘, 2005, 12(3):186-194. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.020 Jiang Zaixing, Yang Weili, Yu Wenquan, et al. The lake-margin canyon and its hydrocarbon potential[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(3):186-194. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.020 [18] 朱筱敏, 张守鹏, 韩雪芳, 等.济阳坳陷陡坡带沙河街组砂砾岩体储层质量差异性研究[J].沉积学报, 2013, 31(6):1094-1104. http://www.cjxb.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1016.shtml Zhu Xiaomin, Zhang Shoupeng, Han Xuefang, et al. On the differences of reservoir quality of Shahejie Fm. in steep slope zones of Jiyang Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(6):1094-1104. http://www.cjxb.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract1016.shtml -




 下载:
下载: