HTML
-
源—汇系统最早起源于美国1988年开始酝酿的“洋陆边缘计划”(Margins Office,2003),1998年美国国家自然科学基金会(NSF)和联合海洋学协会(JOI)提出了《洋陆边缘科学计划2004》(Margins Program Science Plans 2004)(Margins Office, 2003),其中沉积学和地层学项目组制定了S2S——从源到汇复合体系科学计划,开始在沉积学研究中引入源—汇分析的概念和思想[1⁃4]。近二十年来,源—汇概念开始在大陆边缘沉积作用研究中兴起,被认为是沉积体系半定量分析的基础[1]。2010年及以后的多次AAPG年会上,源—汇分析一直是研究热点之一[1],目前逐渐成为陆相湖盆沉积学研究的前沿领域。
陆相盆地源—汇系统研究作为沉积学领域中的重大革新,不同类型盆地、不同时空尺度的源—汇系统研究均取得一定进展。李忠等[5⁃6]研究塔里木盆地记录“泛非”事件的碎屑锆石揭示了构造活动区古地貌、古地理及“源—汇”系统特征;徐长贵等[7⁃9]在渤海湾盆地的“源—汇”系统研究中,建立了不同的源—汇模式,初步形成“源—汇”系统量化表征和工业化应用流程。有关珠江口盆地深水区陆架坡折深水扇“源—汇”系统的研究成果众多[10⁃14],浅水区珠一坳陷“源—汇”系统的研究仅有少量文献涉及,且侧重于区带级的源—汇系统分类[15⁃16],而针对单构造的源—汇耦合关系研究相对较少。
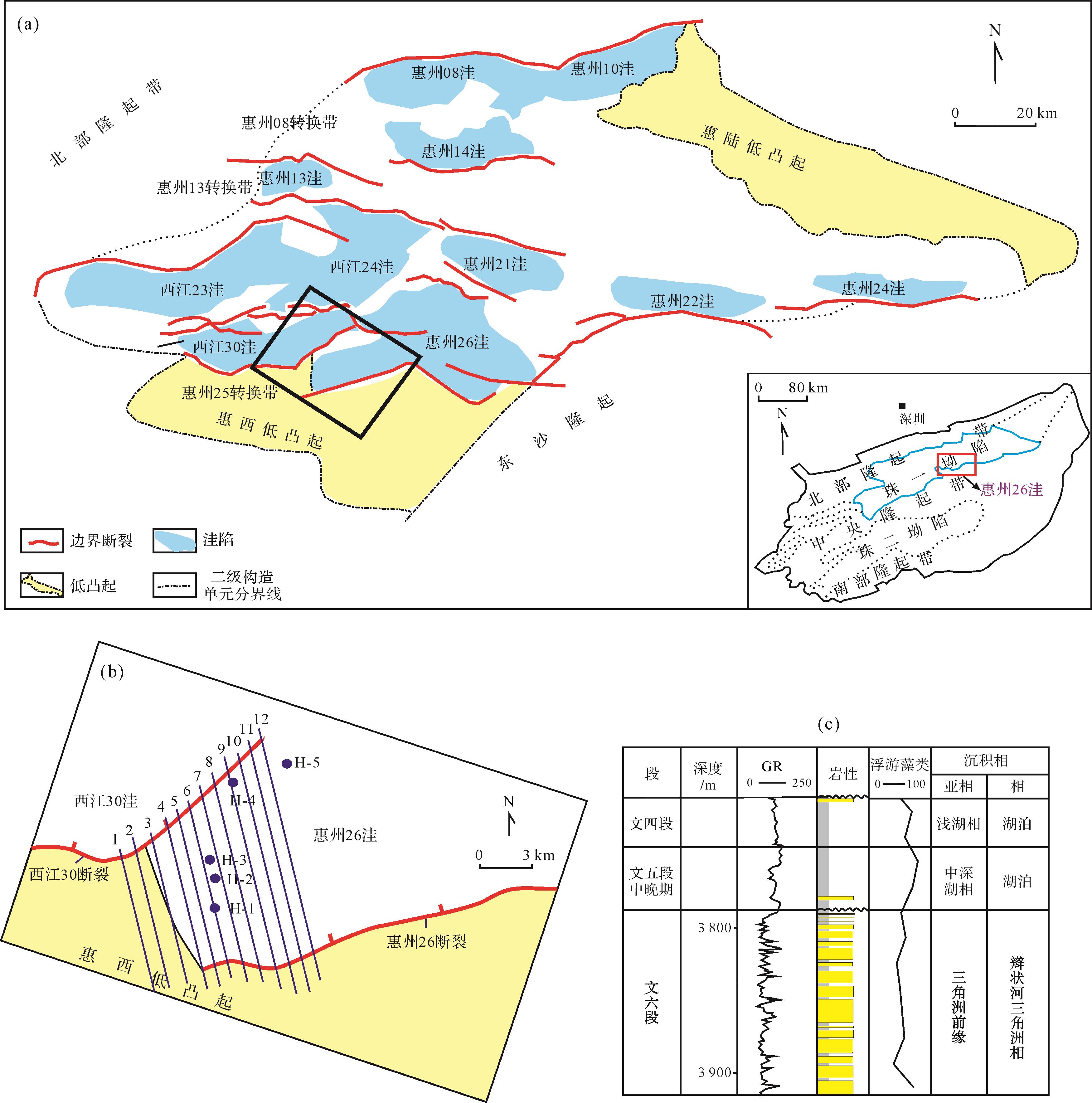
惠州26洼是珠江口盆地古近系油气勘探重要区域[17⁃19],长期以来,惠州26洼中深层古近系的勘探发现主要集中在古近系文昌组受不同类型转换带控制的湖相辫状河三角洲砂岩储层[20⁃21],勘探模式相对单一。随着大型转换型构造圈闭先后钻探完毕,利用源—汇理论寻找隐蔽砂体是该区中深层新一轮勘探的重点方向。本文以惠州26洼惠州25转换带为例,结合钻井和地震资料,综合层序地层学、古地貌重建、地震相精细刻画等分析方法重建文昌组五段沉积早期低位体系域源—渠—汇耦合关系并建立沉积模式,以期为该区油气勘探提供部署建议。
-
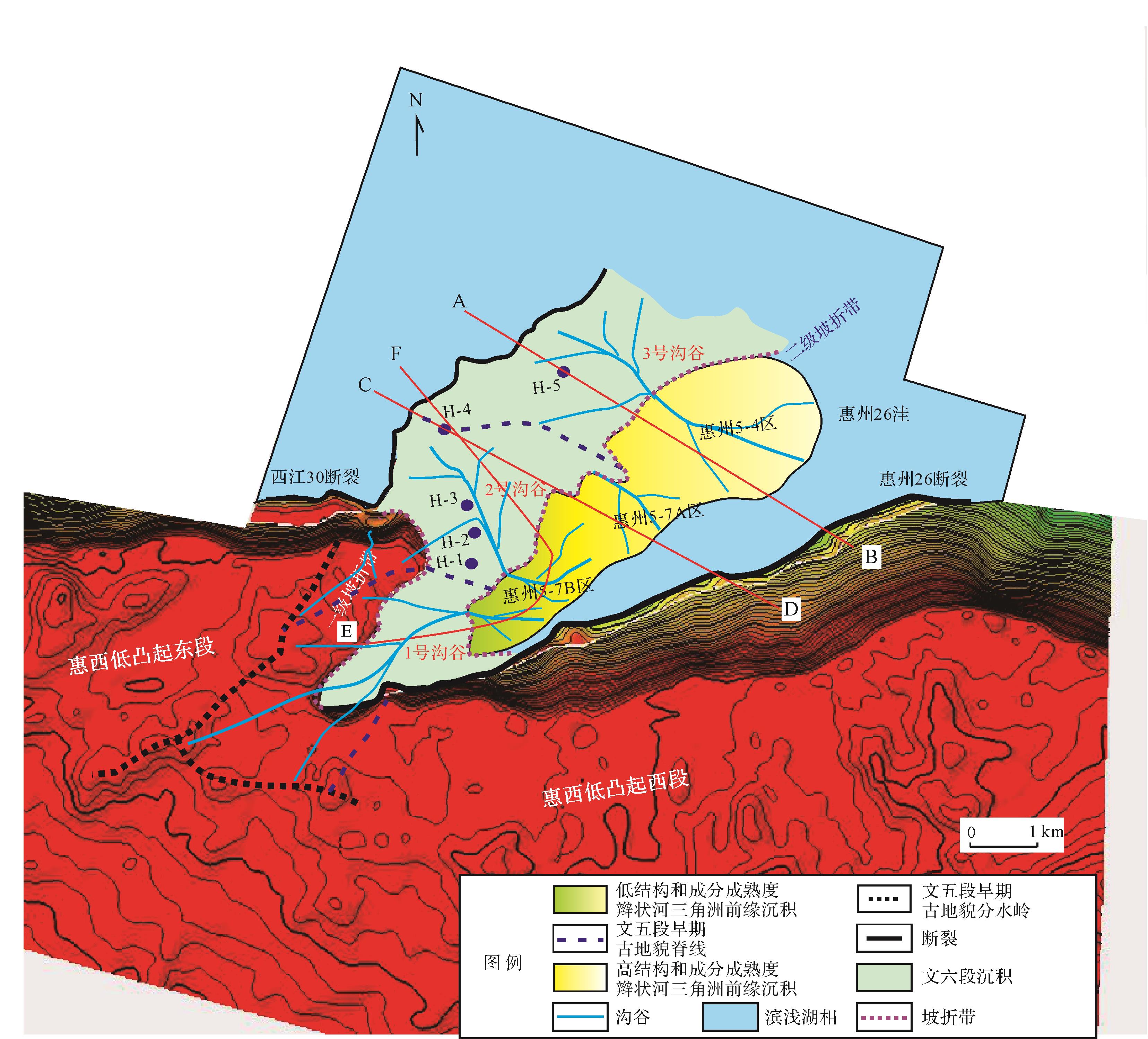
惠州26洼属于珠江口盆地次级构造单元,位于珠一坳陷的中部,是珠江口盆地最富烃的洼陷之一[17⁃18](图1)。惠州25转换带位于珠江口盆地惠州26洼西南部,主体由两条NE向北倾同向铲式断裂,即西江30断裂和惠州26断裂联合控制形成同向叠覆型转换带[20],南部毗邻东沙隆起,西侧与西江30洼相接,研究面积近400 km2(图1a,b)。
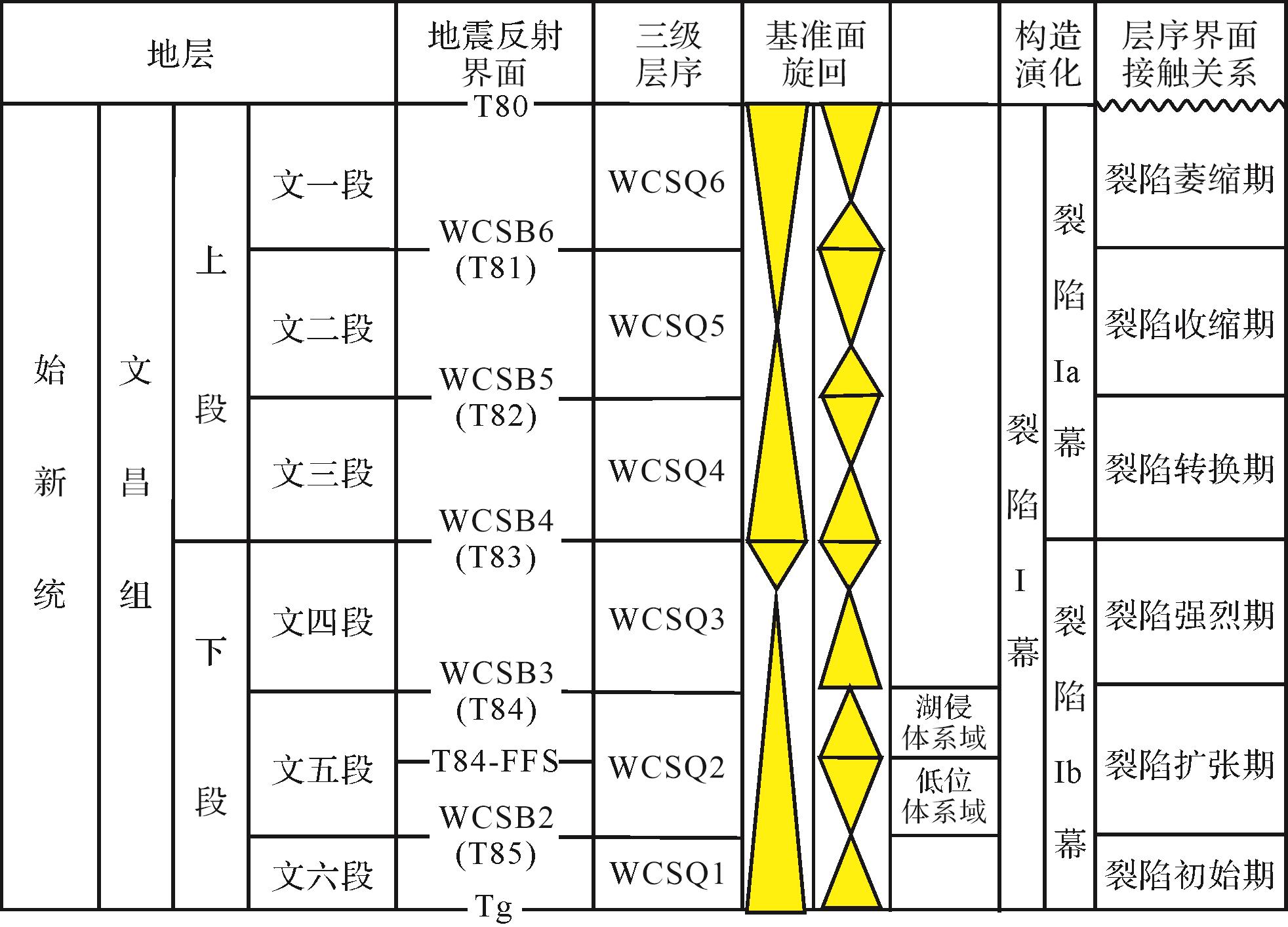
受惠州运动[22]影响,惠州凹陷文昌组沉积发生了由南向北的“异迁移”,即凹陷两侧同沉积控洼断裂的差异活动,导致凹陷内惠州26洼与其北部洼陷即西江24洼的三级层序发生侧向迁移、斜列叠置[23],因此,惠州26洼仅发育下文昌组文六—文四段地层(图2)。研究区惠州25转换带共有5口钻探井,其分布位置如图1b所示,5口井均揭示文六—文四段地层,而钻遇储层和油层主要分布在文六段(图1c)。随着勘探的深入,寻求文昌组其他层系隐蔽砂体是该区油气勘探和重点部署方向。
-
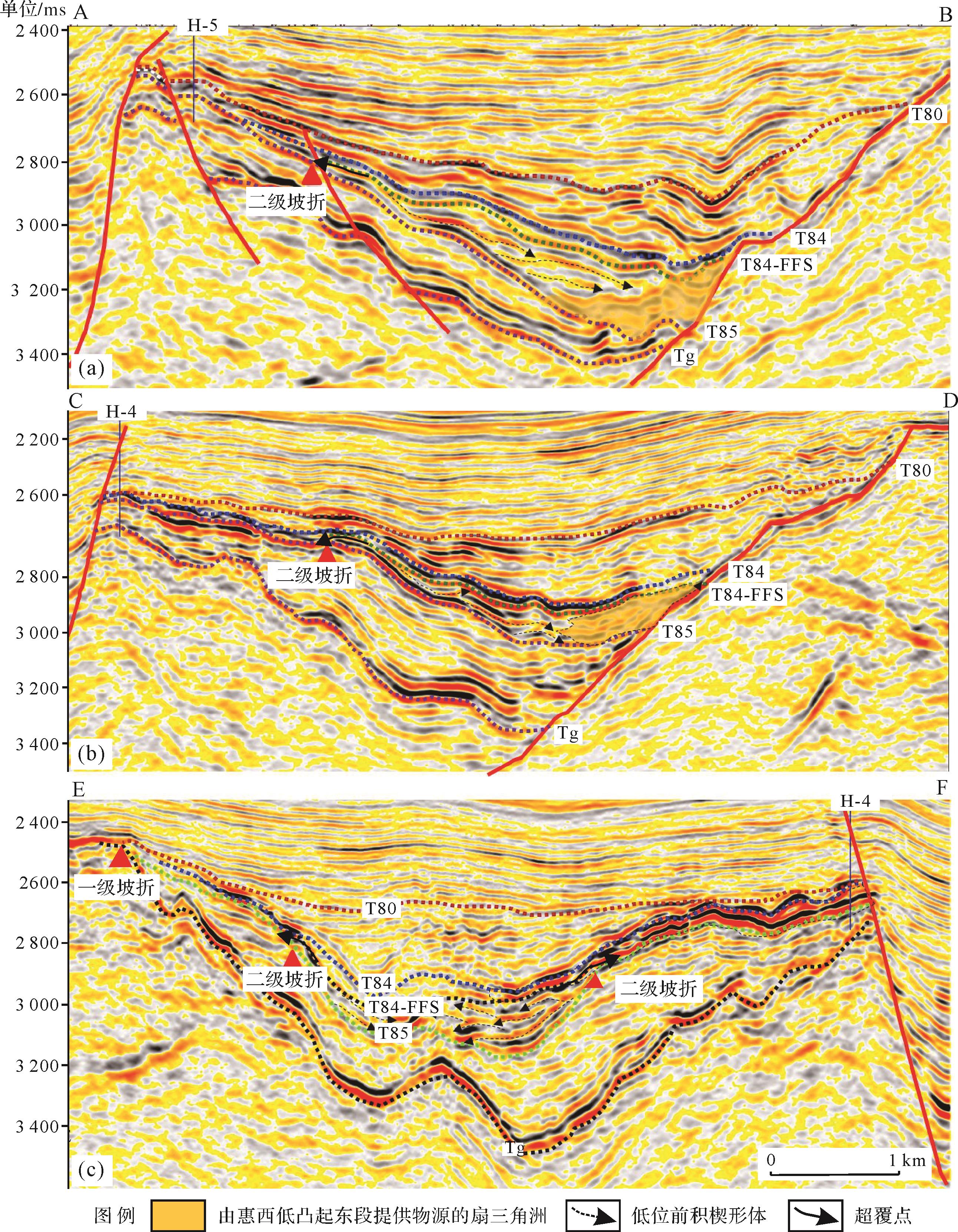
根据Vail的经典层序地层学理论[24],依据层序地层划分原则,利用地震、岩性、岩相、测井、古生物等识别标志,结合区域地质背景,对文五段进行层序界面识别,结果表明:文五段底界面T85具三级层序底界面属性(WCSB2),文五段顶界面T84具三级层序顶界面(WCSB3)和最大湖泛面(MFS)双重属性,其内部可进一步识别出一个初始湖泛面T84-FFS(图2)。
WCSB2识别标志:1)地震反射波终止面。WCSB2为一区域不整合面,对应于地震反射界面T85,侧向延伸稳定(图3b),与上覆地层呈明显的超覆不整合接触关系。2)钻井资料证实岩相突变,其下伏地层为辫状河三角洲砂岩沉积,上覆地层以泥岩沉积为主(图1c)。3)岩电突变面,钻测井曲线上表现为文六段高幅度箱状砂岩突变到文五段低幅微齿泥岩(图1c)。

Figure 3. Map of early paleogeomorphology and two⁃stage slope break characteristics of the 5th member of the Wenchang Formation in Huihzou 25 transfer zone
初始湖泛面识别标志:初始湖泛面与WCSB2之间地层暂无井钻遇,但从地震反射波阻抗差异可以进行识别。初始湖泛面对应于地震反射界面T84-FFS,与WCSB2界面呈现上超接触关系,反应T84-FFS界面为一沉积转换面,该界面与WCSB2之间地层可见明显楔形前积特征,且前积体向物源方向呈退积特征,表明文五段沉积早期湖水水位具有缓慢上升特征(图3b)。
WCSB3识别标志:1)地震反射波终止面。WCSB3为一区域不整合面,对应于地震反射界面T84,侧向延伸稳定(图3b),与上覆地层呈明显的超覆不整合接触关系。2)H-5井古生物资料(图1c)显示WCSB3界面上下浮游藻类含量具有由高到低的变化特征,反应WCSB3之下地层沉积环境为中深湖相,而WCSB3之上地层沉积环境为浅湖相,即WCSB3具最大湖泛面(MFS)双重属性。
根据上述层序界面特征,确定惠州25转换带文五段具三级层序属性特征,依据初始湖泛面和最大湖泛面特征,进一步划分出低位体系域和湖侵体系域,地震相、钻井相互标定,建立了研究区文五段等时地层格架(图2)。
-
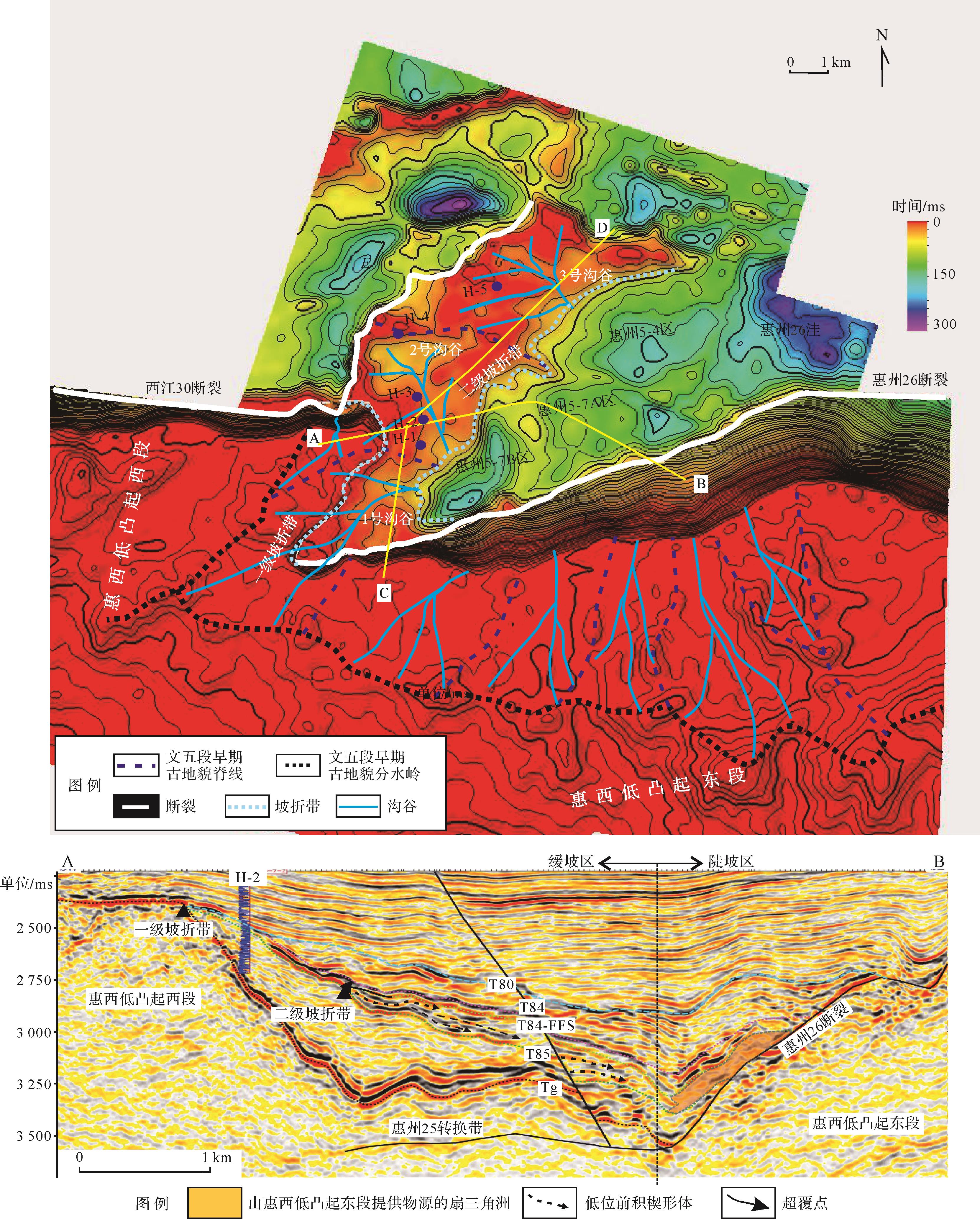
在建立等时地层格架基础上,综合考虑研究区文五段地层发育特征,利用残余地层厚度发育,恢复了研究区文五段沉积早期古地貌(图3a)。地层厚度由大到小反映了古地貌由低变高,即地层越厚,古地貌越低;地层越薄,古地貌越高[25]。
文五段早期,研究区具四周高、中间低地貌特征,根据沉积差异可分为缓坡区和陡坡区,缓坡区是本次研究重点,以低位体系域发育为主,陡坡区受惠州26主控断裂影响,以发育扇三角洲沉积为主(图3b)。平面上(图3a),缓坡区具两级坡折古地貌格局,两级坡折带均具沉积坡折属性,其中一级坡折带是惠西低凸起花岗岩基岩[24]与惠州25转换带洼内文六段碎屑岩[20]沉积分界线,二级坡折带为文六段碎屑岩沉积与文五段早期沉积分界线,二级坡折之下可识别出惠州5-4、惠州5-7A、惠州5-7B三个沉积中心;剖面上(图3b),二级坡折之下可见明显低位域前积楔形体,二级坡折之上缺失文五段早期沉积地层。综合地貌特征即沉积地层厚度由洼陷中心向二级坡折、一级坡折具明显减薄趋势,可以判断研究区文五段早期沉积中心分布在二级坡折之下,且具多物源多沉积中心发育特征。
-
西高东低及两级坡折地貌为低位体系域砂体的发育创造了条件。根据盆—山耦合关系,垂直二级坡折带延伸方向,沟谷规模越大相对应的物源供给规模也越大,其可将“源”—“渠”—“汇”3要素有机整合。在不同物源体系中,准平原化地貌(古隆起、古凸起)展布特征及沟槽间配置关系可指示物源方向[26⁃28]。
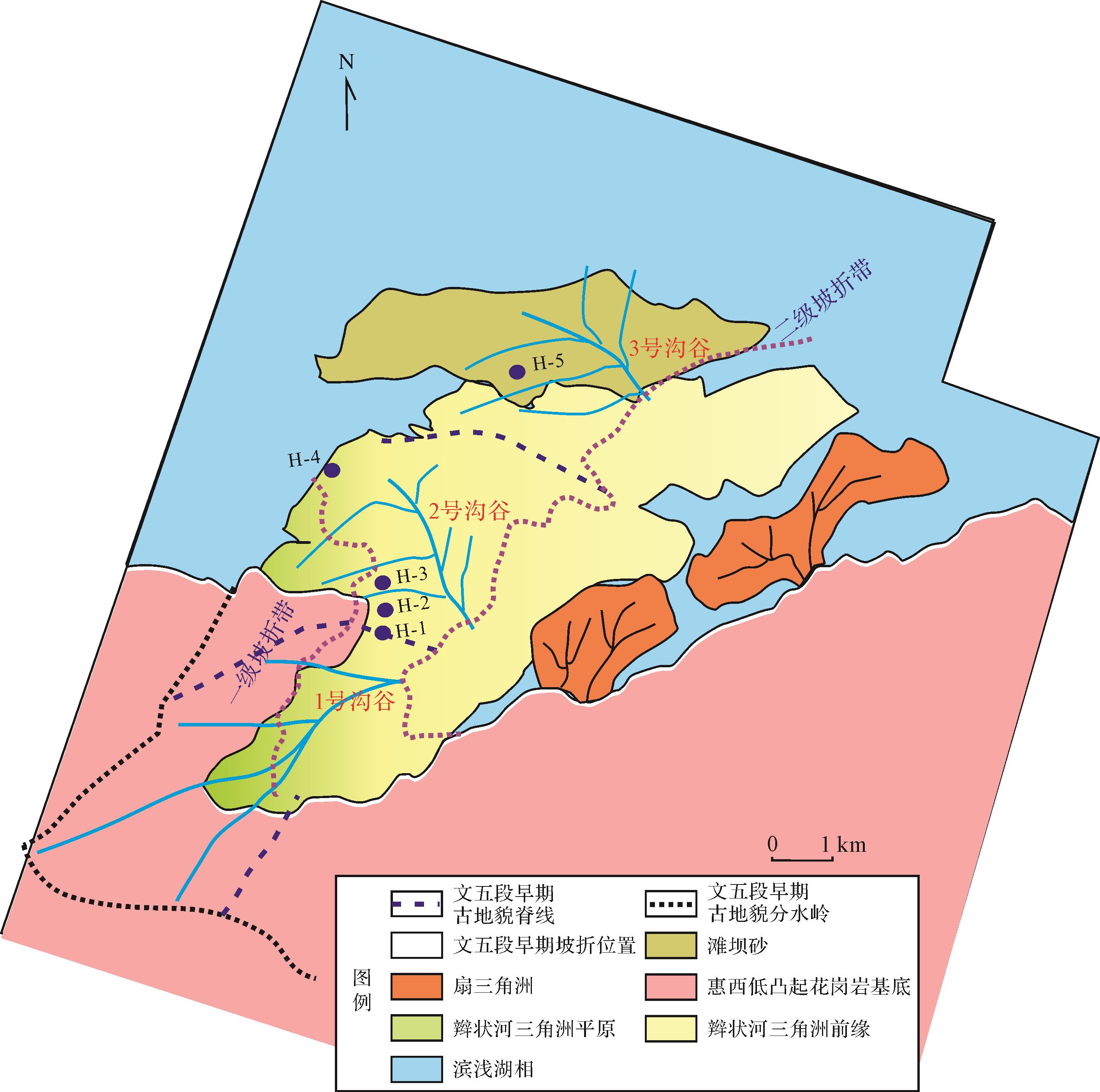
结合古地貌、文六段沉积相图(据葛家旺等[20]修改)叠加文五段早期两级坡折和沟谷位置图(图4)及过两级坡折带延伸方向典型地震剖面(图3b)分析,研究区文五段低位体系域沉积物源多样(图4),既有一级及二级坡折带间的文六段碎屑岩沉积,也有一级坡折之上惠西低凸起西段花岗岩母岩。

Figure 4. Sedimentary facies map of the 6th member of the Wenchang Formation in Huizhou 25 transfer zone (modified from Ge et al.[20]) superimposed on location map of two⁃stage slope break and cleuch in the 5th member of the Wenchang Formation
-
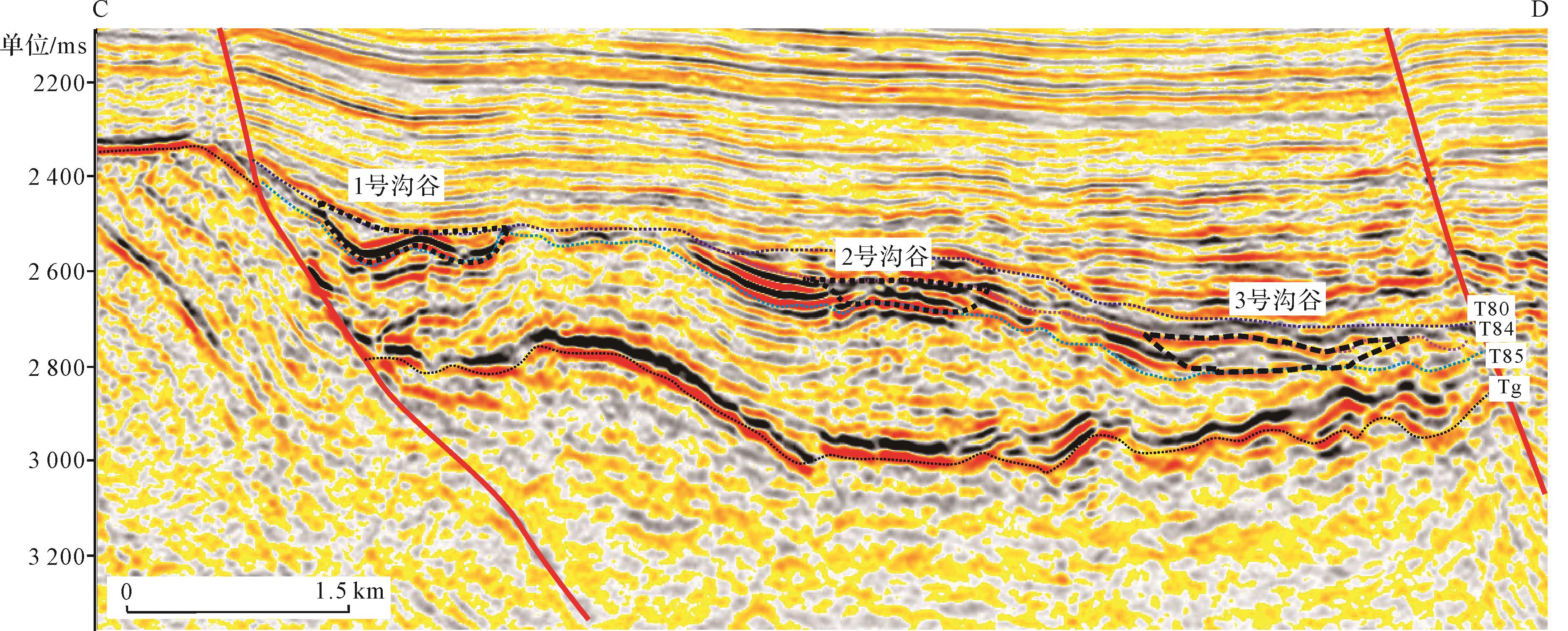
在确定物源区基础上,依据物源区等值线高低(图3a)可识别出负向构造单元的沟谷体系。根据一级坡折之上惠西低凸起地貌高点及坡向变化,点出最高点的连线作为分水岭(黑色虚线),降水在重力作用下沿着分水岭两侧冲刷搬运;确定好分水岭方案后,沿着垂直分水岭方向发育一系列脊线(蓝色虚线)与槽线(沟谷,蓝色实线),槽线是重要的一级汇水体系。根据一级与二级坡折带之间碎屑岩沉积区高点及坡向变化,点出最高点的连线作为分水岭(蓝色虚线),在分水岭之间识别出槽线(沟谷,蓝色实线)。根据统计,研究区可识别出1、2、3号沟谷(图3a、图5):2、3号沟谷均位于一级坡折与二级坡折之间,主要受控于古地貌。

Figure 5. Characteristics of early sedimentary gullies in the 5th member of Wenchang Formation of Huizhou 25 transfer zone
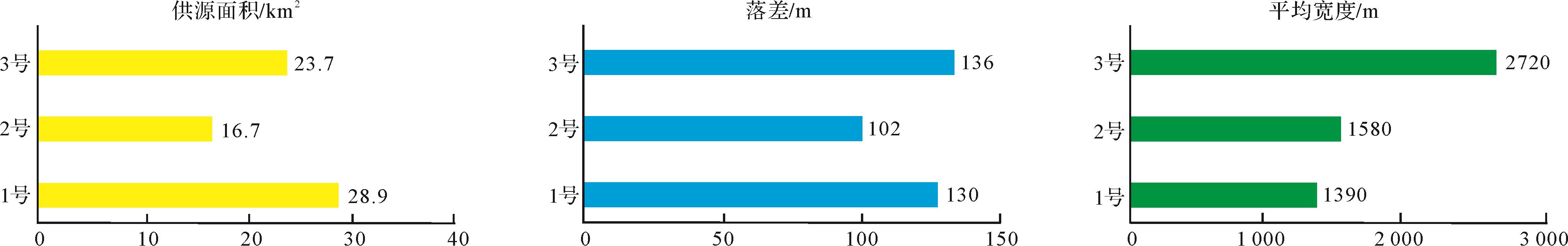
本次研究考虑盆—山耦合关系,分沟谷形态、供源面积、延伸距离、宽度、落差对二级坡折带残留的1~3号沟谷规模进行统计(图5,6);1号沟谷位于惠州25转换带最南端,地势最高,以“W”型沟谷为主,供源面积28.9 km2,长距离延伸,落差达130 m,平均宽度达1 390 m;2号沟谷剖面形态呈“U”型,供源面积16.7 km2,中长距离延伸,沟槽差异沉降量为102 m,平均宽度1 580 m;3号沟谷剖面形态呈“U”型,供源面积23.7 km2,延伸距离短于2号沟谷,但沟谷沉降量和平均宽度大于2号沟谷,分别为136 m、2 720 m。

Figure 6. Parameters of early sedimentary gullies in the 5th member of Wenchang Formation of Huizhou 25 transfer zone
综合对比供源面积、落差、沟谷平均宽度数据判断供源参数,1号、3号、2号有差异:1号沟谷具供源面积大、落差大、平均宽度小的特征,属于高能W型谷,输砂能力强;3号沟谷具供源面积较大、落差大、平均宽度大的特征,属于平底谷,沉积物供给强度大,输砂能力强;而2号沟谷具供源面积小、落差小、平均宽度适中的特征,属于平底谷,相对于1号和3号沟谷,具沉积物供给强度小和输砂能力弱的特征(图6)。
-
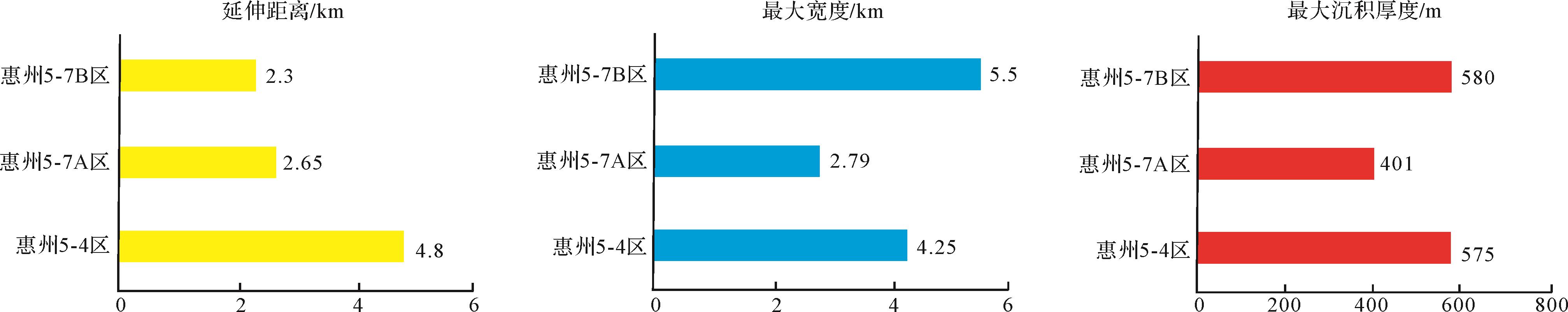
根据上述分析,综合影响低位体系域发育的地貌背景、地震相、空间分布特征,将研究区低位体系域划分为惠州5-4沉积区和惠州5-7A沉积区、惠州5-7B沉积区,并通过统计二级坡折带之上地貌特征、分水岭特征、沟谷特征、母岩性质及二级坡折带之下低位楔形前积体顺物源方向的延伸长度、垂直物源方向的展布宽度和最大沉积区低位体系域发育规模、源—渠—汇耦合关系和沉积模式进行预测:1)惠州5-4沉积区低位楔形前积地震反射特征典型(图7a),低位楔形前积体走向延伸距离4.8 km,最大宽度4.25 km,最大厚度575 m,规模最大(图8),推测其源—渠—汇耦合关系及沉积模式为:以二级坡折带下伏文六段高结构和成分成熟度的滩坝相砂体和辫状河三角洲前缘亚相砂体为物源通过3号沟谷搬运入湖卸载沉积,形成辫状河三角洲前缘沉积(图9);2)从沟谷溯源看,惠州5-7A区物源方向并没有见到明显沟谷,但该区依然见到明显低位楔形前积地震反射特征(图7b),低位楔形前积体走向延伸距离2.65 km,最大宽度2.79 km,最大厚度401 m,规模最小。结合古地貌、物源及地震相推测惠州5-7A区源—渠—汇耦合关系及沉积模式为:以二级坡折带下伏文六段高结构和成分成熟度的辫状河三角洲前缘亚相砂体为母岩,经重力作用入湖卸载形成辫状河三角洲前缘沉积(图9);3)惠州5-7B区低位体系域具双向下超低位楔形前积地震反射特征(图7c),低位楔形前积体走向延伸距离2.3 km,最大宽度5.5 km,最大厚度580 m,规模仅次于惠州5-4区(图8),推测其源—渠—汇耦合关系及沉积模式为:以二级坡折之上H-1/2/3/4井钻遇的文六段辫状河三角洲前缘亚相砂体、辫状河三角洲平原亚相砂体及一级坡折之上惠西低凸起西段花岗岩为母岩分别通过2号、1号沟谷搬运入湖沉积,形成辫状河三角洲前缘沉积,但相对于惠州5-7A区和惠州5-4区,其结构和成分成熟度较低。

Figure 7. Characteristics of seismic facies, early sedimentary stage of the 5th member of Wenchang Formation, Huihzou 25 transfer zone
-
研究区是珠江口盆地中深层古近系油气勘探最早获得商业突破区,截止目前,已发现的H5-4文昌组六段油藏和H5-7文昌组六段含油构造[18⁃20],其中探井H-5井钻遇H5-4油藏,探井H-1/2/3/4井钻遇H5-7含油构造,均见丰富油气显示,证实该区中深层古近系勘探潜力大。
惠州5-4沉积区低位体系域相对于惠州5-7A沉积区具有砂体规模最大,横向延伸较长特征,且具备较好结构和成分成熟度辫状河三角洲前缘规模优质储层发育的先决条件。惠州5-4沉积区低位体系域砂岩储层之下发育的文六段辫状河三角洲外前缘—前三角洲泥岩埋深大于4 000 m,抗压实能力弱,相对于惠州5-7区具有更好的底封能力;储层之上为文五段中晚期湖侵泥岩且已被H-4井和H-5井钻遇,厚度大于50 m,为一套区域性盖层。即垂向上,底封层、顶封层与惠州5-4沉积区低位体系域砂体构成良好的储盖组合。
从油气运聚成藏角度分析,惠州5-4区低位体系域砂体处于湖盆中心生成的油气向惠州5-7区侧向仓储式运移聚集成藏的必经之路[20],因此,惠州5-4区相对于惠州5-7区具有更好的油源条件。综上,惠州5-4区低位体系域砂体相对惠州5-7区具有储层优、封盖条件好、旁生侧储、近源成藏优势,为下一步隐蔽油藏有利勘探目标。
-
(1) 惠州25转换带文五段具有三级层序格架特征,依据初始湖泛面和最大湖泛面特征,将文五段进一步划分出低位体系域和湖侵体系域。
(2) 综合定量表征文五段早期低位体系域的源—渠—汇耦合关系,将低位体系域划分为惠州5-4沉积区、惠州5-7A沉积区和惠州5-7B沉积区:惠州5-4沉积区和惠州5-7A沉积区低位体系域具有盆内文六段滩坝相、辫状河三角洲前缘亚相砂体等高成分和结构成熟度母岩经沟谷搬运入湖规模沉积的源—渠—汇特征;惠州5-7B沉积区低位体系域具有盆内文六段辫状河三角洲平原、前缘亚相砂体和盆外惠西低凸起花岗岩混合母岩经沟谷搬运入湖规模沉积的源—渠—汇特征,其砂体成分和结构成熟度低于惠州5-4和惠州5-7A区。
(3) 惠州5-4区低位体系域砂体具有规模大、储层优、封盖条件优的特征,且相对于惠州5-7区低位体系域砂体具有旁生侧储、近源成藏优势,为下一步隐蔽油藏有利勘探目标。










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: